Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Development of Aluminum Alloys for Additive Manufacturing Using Machine Learning
- Sungbin An, Juyeon Han, Seoyeon Jeon, Dowon Kim, Jae Bok Seol, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):202-211. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00150

- 784 View
- 51 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study introduces a machine learning approach for designing new aluminum alloys tailored for directed energy deposition additive manufacturing, achieving an optimal balance between hardness and conductivity. Utilizing a comprehensive database of powder compositions, process parameters, and material properties, predictive models—including an artificial neural network and a gradient boosting regression model, were developed. Additionally, a variational autoencoder was employed to model input data distributions and generate novel process data for aluminum-based powders. The similarity between the generated data and the experimental data was evaluated using K-nearest neighbor classification and t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding, with accuracy and the F1-score as metrics. The results demonstrated a close alignment, with nearly 90% accuracy, in numerical metrics and data distribution patterns. This work highlights the potential of machine learning to extend beyond multi-property prediction, enabling the generation of innovative process data for material design.
- [Korean]
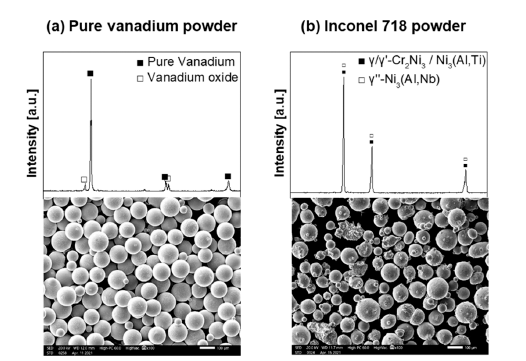
- Joint Properties of Inconel 718 Additive Manufactured on Ti-6Al-4V by FGM method
- Chan Woong Park, Jin Woong Park, Ki Chae Jung, Se-Hwan Lee, Sung-Hoon Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):417-422. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.417
- 583 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In the present work, Inconel 718 alloy is additively manufactured on the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, and a functionally graded material is built between Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V alloys. The vanadium interlayer is applied to prevent the formation of detrimental intermetallic compounds between Ti-6Al-4V and Inconel 718 by direct joining. The additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 alloy is performed by changing the laser power and scan speed. The microstructures of the joint interface are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and micro X-ray diffraction. Additive manufacturing is successfully performed by changing the energy input. The micro Vickers hardness of the additive manufactured Inconel 718 dramatically increased owing to the presence of the Cr-oxide phase, which is formed by the difference in energy input.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


