Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Metallic Tantalum Powder by Magnesium-gas Reduction of Tantalum Oxide
- Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):390-394. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.390

- 776 View
- 14 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Metallic tantalum powder is manufactured by reducing tantalum oxide (Ta2O5) with magnesium gas at 1,073–1,223 K in a reactor under argon gas. The high thermodynamic stability of magnesium oxide makes the reduction reaction from tantalum oxide into tantalum powder possible. The microstructure after the reduction reaction has the form of a mixture of tantalum and magnesium oxide, and the latter could be entirely eliminated by dissolving in weak hydrochloric acid. The powder size in SEM microstructure for the tantalum powder increases after acid leaching in the range of 50–300 nm, and its internal crystallite sizes are observed to be 11.5 to 24.7 nm with increasing reduction temperatures. Moreover, the optimized reduction temperature is found to be 1,173 K as the minimum oxygen concentration is approximately 1.3 wt.%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A review of tantalum resources and its production
Xue WEI, Long-gong XIA, Zhi-hong LIU, Le-ru ZHANG, Qi-hou LI
Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China.2023; 33(10): 3132. CrossRef - Valuable metal recovery from waste tantalum capacitors via cryogenic crushing-alkaline calcination-leaching process
Longgong Xia, Xue Wei, Hongjun Wang, Fengchun Ye, Zhihong Liu
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2022; 16: 1637. CrossRef
- A review of tantalum resources and its production
- [English]
- A Study on the Recovery of Li2CO3 from Cathode Active Material NCM(LiNiCoMnO2) of Spent Lithium Ion Batteries
- Jei-Pil Wang, Jae-Jung Pyo, Se-Ho Ahn, Dong-Hyeon Choi, Byeong-Woo Lee, Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(4):296-301. Published online August 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.4.296
- 3,357 View
- 74 Download
- 11 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
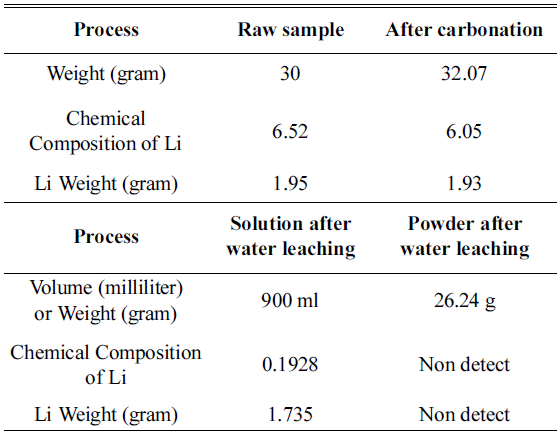
PDF In this study, an experiment is performed to recover the Li in Li2CO3 phase from the cathode active material NMC (LiNiCoMnO2) in waste lithium ion batteries. Firstly, carbonation is performed to convert the LiNiO, LiCoO, and Li2MnO3 phases within the powder to Li2CO3 and NiO, CoO, and MnO. The carbonation for phase separation proceeds at a temperature range of 600°C~800°C in a CO2 gas (300 cc/min) atmosphere. At 600~700°C, Li2CO3 and NiO, CoO, and MnO are not completely separated, while Li and other metallic compounds remain. At 800 °C, we can confirm that LiNiO, LiCoO, and Li2MnO3 phases are separated into Li2CO3 and NiO, CoO, and MnO phases. After completing the phase separation, by using the solubility difference of Li2CO3 and NiO, CoO, and MnO, we set the ratio of solution (distilled water) to powder after carbonation as 30:1. Subsequently, water leaching is carried out. Then, the Li2CO3 within the solution melts and concentrates, while NiO, MnO, and CoO phases remain after filtering. Thus, Li2CO3 can be recovered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Selective lithium Pre-Leaching from spent NMC black mass via pyrolysis (Carbothermal thermal Treatment) and controlled leaching
Amir Hossein Mohammad Zadeh, Spencer Cunnigham, Devon Gray, Sevan Bedrossian, Baian Almusned, Jeffrey Daniel Henderson, Gisele Azimi
Waste Management.2026; 212: 115339. CrossRef - Hydrogen Reduction of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries
Jae-Ho Hwang, Sang-Yeop Lee, So-Yeong Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
Resources Recycling.2025; 34(3): 34. CrossRef - Reduction Roasting of Cathode Materials of NCM Based Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4(g)
Jae-Ho Hwang, Sang-Yeop Lee, Ho-Sang Sohn
Resources Recycling.2025; 34(4): 48. CrossRef - High‐Rate Rechargeable Li/SOCl2 Batteries Enabled by Cobalt Phthalocyanine Cathodic Catalysts
Yingxuan Song, Haibo Ouyang, Zhanwei Xu, Zeyang Zhang, Kang Li, Jianfeng Huang, Zhi Li, Tian Wang, Jun Yang
Small.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Reduction Roasting of Black Mass Recovered from NCM-based Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Using CH4 Gas
Sang-Yeop Lee, Jae-Ho Hwang, Ho-Sang Sohn
Resources Recycling.2025; 34(5): 93. CrossRef - Metals Recovery from Spent Lithium-ion Batteries Cathode Via Hydrogen Reduction-water Leaching-carbothermic or Hydrogen Reduction Process
Tahereh Rostami, Behnam Khoshandam
Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration.2024; 41(3): 1485. CrossRef - Influence of Flow-Gas Composition on Reaction Products of Thermally Treated NMC Battery Black Mass
Christin Stallmeister, Bernd Friedrich
Metals.2023; 13(5): 923. CrossRef - Holistic Investigation of the Inert Thermal Treatment of Industrially Shredded NMC 622 Lithium-Ion Batteries and Its Influence on Selective Lithium Recovery by Water Leaching
Christin Stallmeister, Bernd Friedrich
Metals.2023; 13(12): 2000. CrossRef - Environmentally Friendly Recovery of Lithium from Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
Lilian Schwich, Bernd Friedrich
Metals.2022; 12(7): 1108. CrossRef - Early-Stage Recovery of Lithium from Tailored Thermal Conditioned Black Mass Part I: Mobilizing Lithium via Supercritical CO2-Carbonation
Lilian Schwich, Tom Schubert, Bernd Friedrich
Metals.2021; 11(2): 177. CrossRef - Exploring a green route for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: Revealing and solving deep screening problem
Jiadong Yu, Quanyin Tan, Jinhui Li
Journal of Cleaner Production.2020; 255: 120269. CrossRef
- Selective lithium Pre-Leaching from spent NMC black mass via pyrolysis (Carbothermal thermal Treatment) and controlled leaching
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of TiC powder by carburization of TiH2 powder
- Hun-Seok Lee, Hyang-Im Seo, Young-Seon Lee, Dong-Jun Lee, Jei-Pil Wang, Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):29-33. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.29

- 645 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Titanium carbide (TiC) powders are successfully synthesized by carburization of titanium hydride (TiH2) powders. The TiH2 powders with size lower than 45 μm (-325 Mesh) are optimally produced by the hydrogenation process, and are mixed with graphite powder by ball milling. The mixtures are then heat-treated in an Ar atmosphere at 800-1200oC for carburization to occur. It has been experimentally and thermodynamically determined that the dehydrogenation, “TiH2 = Ti + H2”, and carburization, “Ti + C = TiC”, occur simultaneously over the reaction temperature range. The unreacted graphite content (free carbon) in each product is precisely measured by acid dissolution and by the filtering method, and it is possible to conclude that the maximal carbon stoichiometry of TiC0.94 is accomplished at 1200°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
Jae Jin Sim, Sang Hoon Choi, Ji Hwan Park, Il Kyu Park, Jae Hong Lim, Kyoung Tae Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 251. CrossRef
- Pre-treatments of initial materials for controlling synthesized TaC characteristics in the SHS process
- [Korean]
- Study on the Reduction of Forging Oxide Scale using Hydrogen
- Dong-Won Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun, Shun-Myung Shin, In-Soo Kim, Jei-Pil Wang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(3):174-179.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.3.174

- 805 View
- 18 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The study on the fabrication of iron powder from forging scales using hydrogen gas has been conducted on the effect of hydrogen partial pressure, temperature, and reactive time. The mechanism for the reduction of iron oxides was proposed with various steps, and it was found that reduction pattern might be different depending on temperature. The iron content in the scale and reduction ratio of oxygen were both increased with increasing reactive time at 0.1atm of hydrogen partial pressure. On the other hand, for over 30 minutes at 0.5 atm of hydrogen partial pressure, the values were found to be almost same. In the long run, iron metallic powder was obtained with over 90% of iron content and an average size of its powder was observed to be about 100µm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review on Polyaniline/Ferrite Nanocomposites for Gas Sensing Applications
Shreedhara Kondajji Murugendrappa, Ashwini Rayar, Naveen Chikkahanumajja Surendranatha, Thejas Ramakrishnaiah, Prasanna Gunderi Dhananjaya
physica status solidi (a).2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of expanded graphite content on the performance of MgO‐C refractories
Junseong Kim, Seunghwa Jeong, Minsuk Lee, Dong Jae Kang, Hong‐woo Park, Hwa‐In Lee, Dong‐Yeol Yang, Eun Hee Kim, Soonil Lee, Seung‐Cheol Yang, Sang‐Chae Jeon
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2023; 20(6): 3803. CrossRef - Smithing Processes Based on Hammer Scale Excavated from the Third- to Fourth-Century Ancient Iron-Making Sites of the Korean Peninsula
Dayeon Jung, Heehong Kwon, Namchul Cho
Materials.2022; 15(12): 4188. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review on Polyaniline/Ferrite Nanocomposites for Gas Sensing Applications
- [Korean]
- Trend in Research and Development of Recovery of Valuable Metallic Powder from Wasted Batteries
- Shun-Myung Shin, Sung-Ho Joo, Dong-Won Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jei-Pil Wang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(1):60-67.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.1.060

- 781 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A study on Zn recovery from other metals in the spent mixed batteries through a sequence of hydrometallurgical processes
Dong Ju Shin, Sung-Ho Joo, Chang-Hyun Oh, Jei-Pil Wang, Jin-Tae Park, Dong Joon Min, Shun Myung Shin
Environmental Technology.2019; 40(26): 3512. CrossRef - Development of Batch-Type Electric Furnace for Recovery of Valuable Materials from Spent Batteries
Shun Myung Shin, Dong Won Lee, Jung Yeul Yun, Byung Ho Jung, Jei Pil Wang
Applied Mechanics and Materials.2014; 607: 197. CrossRef
- A study on Zn recovery from other metals in the spent mixed batteries through a sequence of hydrometallurgical processes
- [English]
- Oxidation Study on the Fabrication of Fe-36Ni Oxide Powder from Its Scrap
- Jung Yeul Yun, Man Ho Park, Sangsun Yang, Dong-Won Lee, Jei-Pil Wang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(1):48-52.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.1.048

- 466 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A study of oxidation kinetic of Fe-36Ni alloy has been investigated using thermogravimetric apparatus (TGA) in an attempt to define the basic mechanism over a range of temperature of 400 to 1000°C and finally to fabricate its powder. The oxidation rate was increased with increasing temperature and oxidation behavior of the alloy followed a parabolic rate law at elevated temperature. Temperature dependence of the reaction rate was determined with Arrhenius-type equation and activation energy was calculated to be 106.49 kJ/mol. Based on the kinetic data and micro-structure examination, oxidation mechanism was revealed that iron ions and electrons might migrate outward along grain boundaries and oxygen anion diffused inward through a spinel structure, (Ni,Fe)_3O_4.
- [Korean]
- Extraction of Vanadium Powder by Metallothermic Reduction
- Dong-Won Lee, Sang-Hyun Heo, Jong-Taek Yeom, Jei-Pil Wang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(1):43-47.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.1.043

- 748 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The extraction of metallic pure vanadium powder from raw oxide has been tried by Mg-reduction. In first stage, V_2O_5 powders as initial raw material was reduced by hydrogen gas into V_2O_3 phase. V_2O_3 powder was reduced in next stage by magnesium gas at 1,073K for 24 hours. After reduction reaction, the MgO component mixed with reduced vanadium powder were dissolved and removed fully in 10% HCl solution for 5 hours at room temperature. The oxygen content and particle size of finally produced vanadium powders were 0.84 wt% and 1 µm, respectively
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of tantalum metal powder by magnesium gas reduction of tantalum pentoxide with different initial particle size
Seon-Min Hwang, Su-Jin Park, Jei-Pil Wang, Yong-Ho Park, Dong-Won Lee
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2021; 100: 105620. CrossRef - Metallic Niobium Powder Reduced by Atmospheric Magnesium Gas with Niobium Pentoxide Powder
Su-Jin Park, Seon-Min Hwang, Jei-pil Wang, Young-Guk Son, Dong-Won Lee
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2021; 62(1): 34. CrossRef - Fabrication of Metallic Tantalum Powder by Magnesium-gas Reduction of Tantalum Oxide
Dong-Won Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(5): 390. CrossRef - Effect of magnesium on the phase equilibria in magnesio-thermic reduction of Nb2O5
Kyunsuk Choi, Hanshin Choi, Hyunwoong Na, Il Sohn
Materials Letters.2016; 183: 151. CrossRef
- Preparation of tantalum metal powder by magnesium gas reduction of tantalum pentoxide with different initial particle size
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Ultrafine and Less Agglomerated TiCN Powders by Magnesiothermic Reduction
- Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(5):356-361.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.5.356

- 649 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The ultra-fine and less agglomerated titanium carbonitride particles were successfully synthesized by magnesiothermic reduction with low feeding rate of TiCl_4+1/4C_2Cl_4 solution. The sub-stoichiometric titanium carbide (TiC_0.5sim0.6) particles were produced by reduction of chlorine component by liquid magnesium at 800°C of gaseous TiCl_4+1/4C_2Cl_4 and the heat treatments in vacuum were performed for 5 hours to remove the residual magnesium and magnesium chloride mixed with produced TiC_sim0.5. The final TiC_sim0.5N_0sim0.5 particle with near 100 nm in mean size and high specific surface area of 65m2/g was obtained by nitrification under nitrogen gas at 1,150°C for 2 hrs.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Ultrafine Tungsten-based Composite Powders by Novel Reduction Process
- Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(5):338-342.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.5.338

- 532 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A novel chemical method was evaluated to fabricate the ultrafine tungsten heavy alloy powders with bater-base solution made from the ammonium metatungstate (AMT), iron(II) chloride tetrahydrate (FeCl_2cdot4H_2O), nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate (NiCl_2cdot6H_2O) as source materials and the sodium tungstate dihydrate (NaWO_4cdot2H_2O) as Cl-reductant. In the preparation of mixtures the amounts of the source components were chosen so as to obtain alloy of 93W-5Ni-2Fe composition(wt.%). The obtained powders were characterized by X-ray diffraction, XRF, field-emission scanning microscope (FESEM), and chemical composition was analyzed by EDX.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Zr-Ti Alloy Powder by Magnesium Reduction
- Dong-Won Lee, Geun-Tae Park, Tae-Soo Lim, Hye-Moon Lee, Ji-Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(4):359-364.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.4.359

- 890 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Zr-Ti alloy powders were successfully synthesized by magnesium thermal reduction of metal chlorides. The evaporated and mixed gasses of ZrCl_4+TiCl_4 were injected to liquid magnesium and the chloride components were reduced by magnesium leading to the formation of MgCl_2. The released Zr and Ti atoms were then condensed to particle forms inside the mixture of liquid magnesium and magnesium chloride, which could be dissolved fully in post process by 1~5% HCl solution at room temperature. By the fraction-control of individually injected ZrCl_4 and TiCl_4 gasses, the final compositions of produced alloy powders were changed in the ranges of Zr-0 wt.%~20 wt.%Ti and their purity and particle size were about 99.4% and the level of several micrometers, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Vanadium Powder by Magnesiothermic Reduction
Dong Won Lee, Hak Sung Lee, Jung Yeul Yun, Young Ho Kim, Jei Pil Wang
Advanced Materials Research.2014; 1025-1026: 509. CrossRef - Extraction of Vanadium Powder by Metallothermic Reduction
Dong-Won Lee, Sang-Hyun Heo, Jong-Taek Yeom, Jei-Pil Wang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(1): 43. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Vanadium Powder by Magnesiothermic Reduction
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of Stainless Steel Composites with Nano-sized TiCxNy
- Tae-Ho Ban, Sung-Bum Park, Soo-Jeong Jo, Dong-Won Lee, Farkhod R. Turaev, Yong-Il Park, Sung-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(3):290-296.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.3.290

- 379 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Titanium carbonitride is more perspective materials compared to titanium carbide. It can be used in tool industry and special products because of its higher strength, abrasive wear-resistance and especially its strong chemical stability at high temperatures. We produced STS+TiCxNy composite by the spark plasma sintering for higher strength and studied the characteristics. The planar and cross-sectional microstructures of the specimens were observed by scanning electron microscopy. Characterizations of the carbon and nitride phases on the surface of composite were carried out using an X-ray diffractometer. During annealing TiCxNy particles diffusion into STS 430 was observed. After annealing, sintering isolations between particles were formed. It causes decreasing of mechanical strength. In addition when annealing temperature was increased hardness increased. Heterogeneous distribution of alloying elements particles was observed. After annealing composites, highest value of hardness was 738.1 MHV.
- [English]
- Oxygen-Response Ability of Hydrogen-Reduced Nanocrystalline Cerium Oxide
- Dong-Won Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(3):250-255.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.3.250

- 600 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The potential application of ultrafine cerium oxide (ceria, CeO_2) as an oxygen gas sensor has been investigated. Ceria was synthesized by a thermochemical process: first, a precursor powder was prepared by spray drying cerium-nitrate solution. Heat treatment in air was then performed to evaporate the volatile components in the precursor, thereby forming nanostructured CeO_2 having a size of approximately 20 nm and specific surface area of 100 m2/g. After sintering with loosely compacted samples, hydrogen-reduction heat treatment was performed at 773K to increase the degree of non-stoichiometry, x, in CeO_2-x. In this manner, the electrical conductivity and oxygen-response ability could be enhanced by increasing the number of oxygen vacancies. After the hydrogen reduction at 773K, CeO_1.5 was obtained with nearly the same initial crystalline size and surface. The response time t_90 measured at room temperature was extremely short at 4 s as compared to 14 s for normally sintered CeO_2. We believe that this hydrogen-reduced ceria can perform capably as a high-performance oxygen sensor with good response abilities even at room temperature.
- [Korean]
- Hydrogenation Behavior of Sponge Titanium
- Ji-Hwan Park, Dong-Won Lee, Jong-Ryoul Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(5):385-389.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.5.385

- 843 View
- 3 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Titanium powders have been usually produced by de-hydrogenating treatment in vacuum with titanium hydride (TiH_2) powders prepared by milling of hydrogenated sponge titanium, TiH_x. The higher stoichiometry of x in TiH_x, whose maximum value is 2, is achieved, crushing behavior is easier. TiH_x powder can be, therefore, easy to manufactured leading to obtain higher recovery factor of it. In addition, contamination of the powder can also minimized by the decrease of milling time. In this study, the hydrogenation behavior of sponge titanium was studied to find the maximum stoichiometry. The maximum stoichiometry in hydride formation of sponge titanium could be obtained at 750°C for 2 hrs leading to the formation of TiH_sim1.99 and the treating temperatures lower or higher than 750°C caused the poor stoichiometries by the low hydrogen diffusivity and un-stability of TiH_x, respectively. Such experimental behavior was compared with thermodynamically calculated one. The hydrogenated TiH_1.99 sponge was fully ball-milled under -325 Mesh and the purity of pure titanium powders obtained by de-hydrogenation was about 99.6%.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Ball Milling Conditions on the Microstructure and Dehydrogenation Behavior of TiH2 Powder
Ji Young Kim, Eui Seon Lee, Ji Won Choi, Youngmin Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 132. CrossRef - Study on Manufacture of High Purity TiCl4 and Synthesis of High Purity Ti Powders
Jieun Lee, Jin-Ho Yoon, Chan Gi Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(4): 282. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment Temperature and Atmosphere on the Microstructure of TiH2-WO3 Powder Mixtures
Han-Eol Lee, Yeon Su Kim, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(1): 41. CrossRef - Titanizing on the surface of iron metal foam
Su-In Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun, Tae-Soo Lim, Byoung-Kee Kim, Young-Min Kong, Jei-Pil Wang, Dong-Won Lee
Thermochimica Acta.2014; 581: 87. CrossRef - Study on synthesis of Zr–Ti alloy powder using molten magnesium
D.-W. Lee, Y.-K. Baek, W.-J. Lee, J.-P. Wang
Materials Research Innovations.2013; 17(sup2): s113. CrossRef - Direct synthesis of zirconium powder by magnesium reduction
Dong-Won Lee, Jung-Yeul Yun, Sung-Won Yoon, Jei-Pil Wang
Metals and Materials International.2013; 19(3): 527. CrossRef - Synthesis of Zr-Ti Alloy Powder by Magnesium Reduction
Dong-Won Lee, Geun-Tae Park, Tae-Soo Lim, Hye-Moon Lee, Ji-Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(4): 359. CrossRef
- Effect of Ball Milling Conditions on the Microstructure and Dehydrogenation Behavior of TiH2 Powder
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Ultrafine C/N Controled TiCxNy Powders by Magnesium Reduction
- Dong-Won Lee, Byoung-Kee Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun, Ji-Hoon Yu, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(2):142-147.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.2.142

- 795 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The ultrafine titanium carbonitride (TiC_xN_y) particles below 100 nm in mean size, including various carbon and nitrogen contents (x=0.55~0.9, y=0.1~0.5), were successfully synthesized by new Mg-thermal reduction process. Nanostructured sub-stoichiometric titanium carbide (TiC_x) particles were initially produced by the magnesium reduction of gaseous TiCl_4+x/2C_2Cl_4 at 890°C and post heat treatments in vacuum were performed for 2 hrs to remove residual magnesium and magnesium chloride mixed with TiC_x. Finally, well C/N-controled TiC_xN_y phases were successfully produced by nitrification heat treatment under normal N_2 gas atmosphere at 1150°C for 2 hrs. The values of purity, mean particle size and oxygen content of produced particles were about 99.3%, 100 nm and 0.2 wt.%, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characteristics of Stainless Steel Composites with Nano-sized TiCxNy
Tae-Ho Ban, Sung-Bum Park, Soo-Jeong Jo, Dong-Won Lee, Farkhod R. Turaev, Yong-Il Park, Sung-Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(3): 290. CrossRef
- Characteristics of Stainless Steel Composites with Nano-sized TiCxNy
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Ultrafine TiCN Powders by Mg-reduction of Metallic Chlorides
- Dong-Won Lee, Jin-Chun Kim, Yong-Jin Kim, Byoung-Kee Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(2):98-103.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.2.098

- 766 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The ultrafine titanium carbonitride particles (TiC_0.7N_0.3) below 100nm in mean size were successfully synthesized by Mg-thermal reduction process. The nanostructured sub-stoichiometric titanium carbide (TiC_0.7) particles were produced by the magnesium reduction at 1123K of gaseous TiC_l4+xC_2Cl_4 and the heat treatments in vacuum were performed for five hours to remove residual magnesium and magnesium chloride mixed with TiC_0.7. And final TiC_0.7N_0.3 phase was obtained by nitrification under normal N_2 gas at 1373K for 2 hrs. The purity of produced TiC_0.7N_0.3 particles was above 99.3% and the oxygen contents below 0.2 wt%. We investigated in particular the effects of the temperatures in vacuum treatment on the particle refinement of final product.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Ultrafine and Less Agglomerated TiCN Powders by Magnesiothermic Reduction
Dong-Won Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(5): 356. CrossRef - Preparation of Ultrafine C/N Controled TiCxNyPowders by Magnesium Reduction
Dong-Won Lee, Byoung-Kee Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun, Ji-Hoon Yu, Yong-Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2010; 17(2): 142. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Ultrafine and Less Agglomerated TiCN Powders by Magnesiothermic Reduction
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Characterization of WS2 Nanoparticles by Chemical Vapor Condensation
- Dong-Won Lee, Ju-Hyeong Kim, O. Tolochko, Jung-Yeul Yun, Byung-Kee Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(4):314-319.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.4.314

- 612 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nano-sized tungsten disulfide (WS_2) powders were synthesized by chemical vapor condensation (CVC) process using tungsten carbonyl (W(CO)_6) as precursor and vaporized pure sulfur. Prior to the synthesis of tungsten disulfide nanoparticles, the pure tungsten nanoparticles were produced by same route to define the optimum synthesis parameters, which were then successfully applied to synthesize tungsten disulfide. The influence of experimental parameters on the phase and chemical composition as well as mean size of the particles for the produced pure tungsten and tungsten disulfide nanoparticles, were investigated.
- [Korean]
- Characteristics of L10 Ordered Fe50Pt50 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Chemical Vapor Condensation Process
- Gyeong-Mo Lee, Ji-Hun Yu, Dong-Won Lee, Byung-Kee Kim, Hyeok-Don Kim, Tae-Suk Jang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(5):281-286.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.5.281

- 525 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ordered L1_0 to FePt nanoparticles are strong candidates for high density magnetic data storage media because the L1_0 phase FePt has a very high magnetocrystalline anisotropy (K_usim6.6-10times107erg/cm3), high coercivity and chemical stability. In this study, the ordered L1_0 FePt nanoparticles were successfully fabricated by chemical vapor condensation process without a post-annealing process which causes severe particle growth and agglomeration. The Fe_50Pt_50 nanopowder was obtained when the mixing ratio of Fe(acac) and Pt(arac) was 2.5 : 1. And the synthesized FePt nanoparticles were very fine and spherical shape with a narrow size distribution. The average particle size of the powder tended to increase from 5 nm to 10 nm with increasing reaction temperature from 800°C to 1000°C. Characterisitcs of FePt nanopowder were investigated in terms of process parameters and microstructures.
- [Korean]
- Trend of Advanced Technology for the Synthesis of Nanopowders in Russia by Chemical Process
- Dong-Soo Kim, Dong-Won Lee, Byoung-Kee Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2006;13(4):233-242.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2006.13.4.233

- 494 View
- 0 Download
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Nanostructured Ceria Powders for an Oxygen-sensor by Thermochemical Process
- Dong-Won Lee, Joon-Hwan Choi, Tae-Soo Lim, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2006;13(3):192-198.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2006.13.3.192

- 391 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The nanostructured cerium oxide powders were synthesized by spray thermal decomposition process for the use as the raw materials of resistive oxygen sensor. The synthesis routes consisted of 1) spray drying of water based organic solution made from cerium nitrate hydrate (Ce(NO_3)_36H_2O) and 2) heat treatment of spray dried precursor powders at 400°C in air atmosphere to remove the volatile components and identically to oxidize the cerium component. The produced powders have shown the loose structure agglomerated with extremely fine cerium oxide particles with about 15 nm and very high specific surface area (110m2/g). The oxygen sensitivity, n (LogproptoLog (P_O2/Po)-n and the response time, t_90 measured at 600°C in the sample sintered at 1000°C, were about 0.25 and 3 seconds, respectively, which had much higher performances than those known in micron or 100sim200nm sized sensors.
- [Korean]
- A Study on Oxidation-Resistance of Iron Nanoparticles Synthesized by Chemical Vapor Condensation Process
- Dong-Won Lee, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeoung-Hyun Bae, Tae-Suk Jang, Byoung-Kee Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(3):225-230.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.3.225

- 614 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In order to prevent the oxide formation on the surface of nano-size iron particles and thereby to improve the oxidation resistance, iron nanoparticles synthesized by a chemical vapor condensation method were directly soaked in hexadecanethiol solution to coat them with a polymer layer. Oxygen content in the polymer-coated iron nanoparticles was significantly lower than that in air-passivated particles possessing iron-core/oxide-shell structure. Accordingly, oxidation resistance of the polymer-coated particles at an elevated temperature below 130°C in air was 10~40 times higher than that of the air- passivated particles.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


