Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,710 View
- 43 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
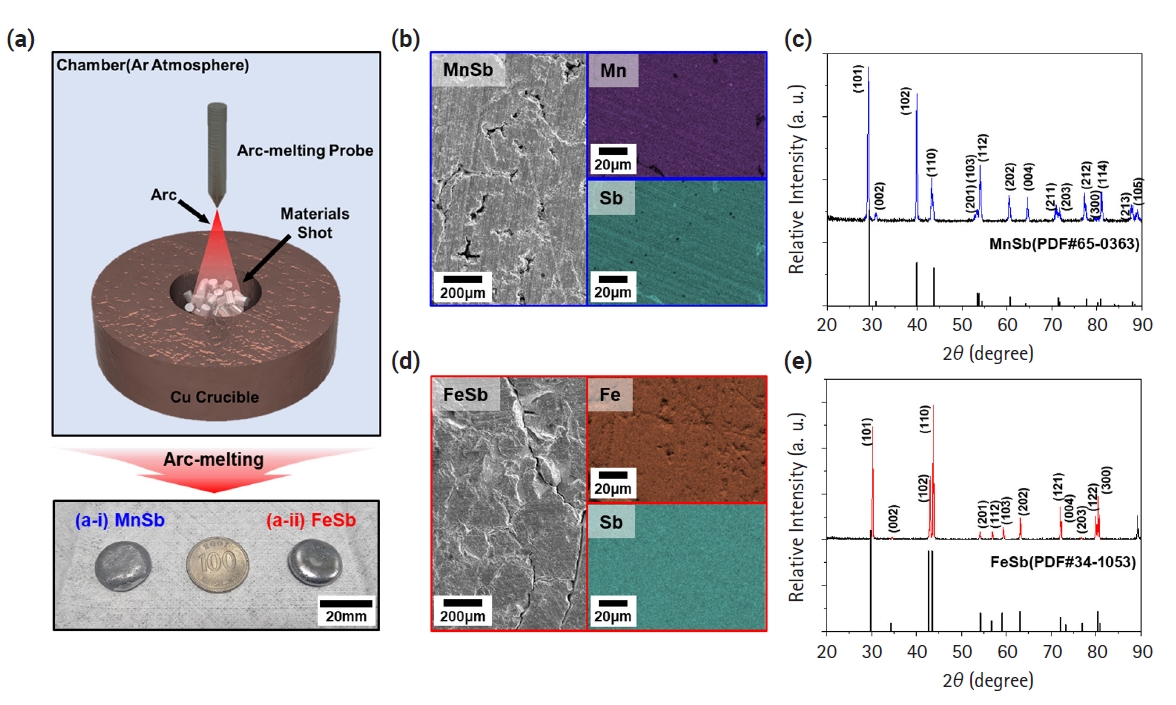
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Polymer Composite with Enhanced Insulation and Mechanical Properties using Aluminum Borate Nanowhiskers
- Junhyeok Choi, Sangin Lee, Kiho Song, Taekyung Kim, Changui Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):356-362. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.356
- 914 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
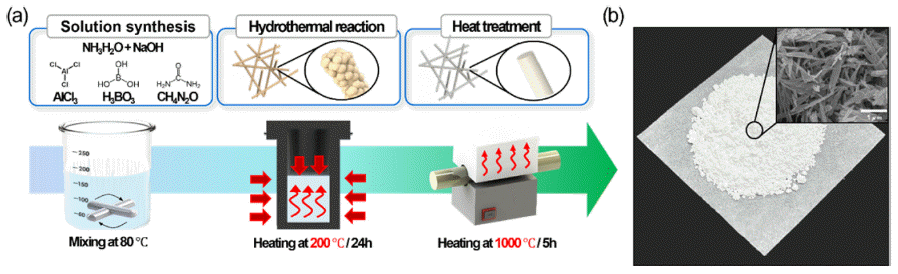
PDF Inorganic-organic composites find extensive application in various fields, including electronic devices and light-emitting diodes. Notably, encapsulation technologies are employed to shield electronic devices (such as printed circuit boards and batteries) from stress and moisture exposure while maintaining electrical insulation. Polymer composites can be used as encapsulation materials because of their controllable mechanical and electrical properties. In this study, we propose a polymer composite that provides good electrical insulation and enhanced mechanical properties. This is achieved by using aluminum borate nanowhiskers (ABOw), which are fabricated using a facile synthesis method. The ABOw fillers are created via a hydrothermal method using aluminum chloride and boric acid. We confirm that the synthesis occurs in various morphologies based on the molar ratio. Specifically, nanowhiskers are synthesized at a molar ratio of 1:3 and used as fillers in the composite. The fabricated ABOw/epoxy composites exhibit a 48.5% enhancement in mechanical properties, similar to those of pure epoxy, while maintaining good electrical insulation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
Kiho Song, Sang in Lee, Hyunseung Song, Changui Ahn
Journal of Powder Materials.2024; 31(6): 513. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Al18B4O33 Spherical Powder with Increased Fluidity via Control of B2O3 Particle Size and Distribution
- [English]
- Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
- Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(4):318-323. Published online August 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.4.318
- 1,685 View
- 9 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
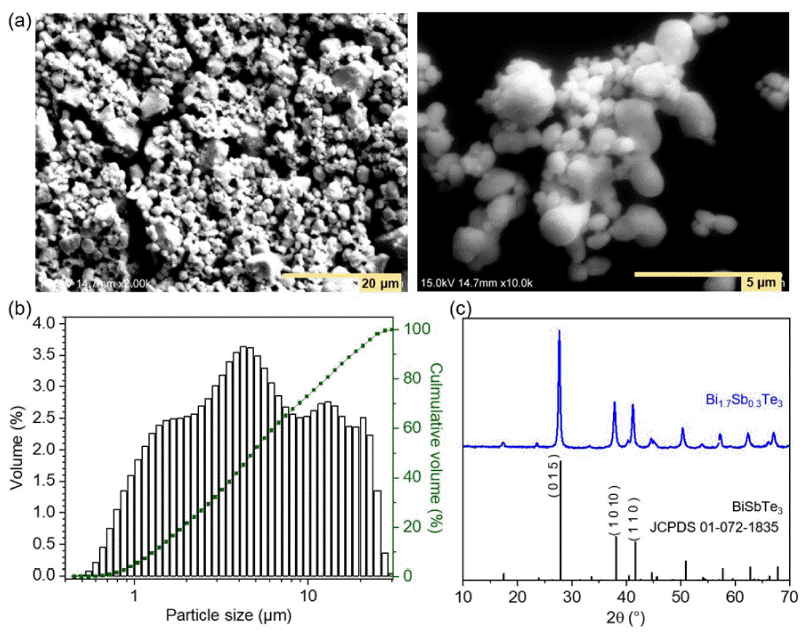
PDF The thermoelectric effect, which converts waste heat into electricity, holds promise as a renewable energy technology. Recently, bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3)-based alloys are being recognized as important materials for practical applications in the temperature range from room temperature to 500 K. However, conventional sintering processes impose limitations on shape-changeable and tailorable Bi2Te3 materials. To overcome these issues, three-dimensional (3D) printing (additive manufacturing) is being adopted. Although some research results have been reported, relatively few studies on 3D printed thermoelectric materials are being carried out. In this study, we utilize extrusion 3D printing to manufacture n-type Bi1.7Sb0.3Te3 (N-BST). The ink is produced without using organic binders, which could negatively influence its thermoelectric properties. Furthermore, we introduce graphene oxide (GO) at the crystal interface to enhance the electrical properties. The formed N-BST composites exhibit significantly improved electrical conductivity and a higher Seebeck coefficient as the GO content increases. Therefore, we propose that the combination of the extrusion 3D printing process (Direct Ink Writing, DIW) and the incorporation of GO into N-BST offers a convenient and effective approach for achieving higher thermoelectric efficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 119. CrossRef
- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


