Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Hexagonal Boron Nitride Nanocrystals and Their Application to Thermally Conductive Composites
- Jae-Yong Jung, Yang-Do Kim, Pyung-Woo Shin, Young-Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):414-419. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.414

- 1,503 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Much attention has been paid to thermally conductive materials for efficient heat dissipation of electronic devices to maintain their functionality and to support lifetime span. Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), which has a high thermal conductivity, is one of the most suitable materials for thermally conductive composites. In this study, we synthesize h-BN nanocrystals by pyrolysis of cost-effective precursors, boric acid, and melamine. Through pyrolysis at 900°C and subsequent annealing at 1500°C, h-BN nanoparticles with diameters of ~80 nm are synthesized. We demonstrate that the addition of small amounts of Eu-containing salts during the preparation of melamine borate precursors significantly enhanced the crystallinity of h-BN. In particular, addition of Eu assists the growth of h-BN nanoplatelets with diameters up to ~200 nm. Polymer composites containing both spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) and Eu-doped h-BN nanoparticles (4 vol%) show an enhanced thermal conductivity (λ ~ 1.72W/mK), which is larger than the thermal conductivity of polymer composites containing spherical Al2O3 (70 vol%) as the sole fillers (λ ~ 1.48W/mK).
- [Korean]
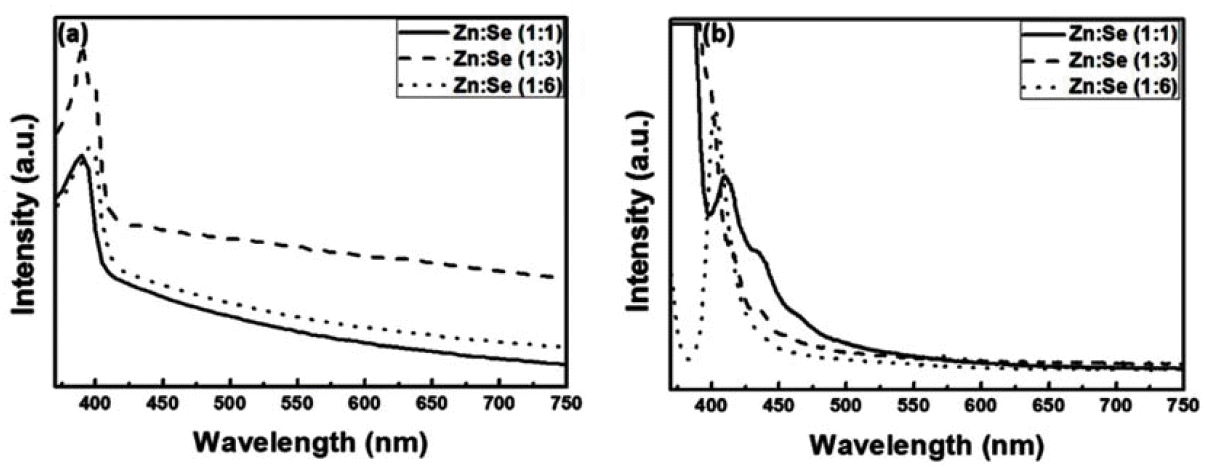
- The Effect of Surface Defects on the Optical Properties of ZnSe:Eu Quantum Dots
- Da-Woon Jeong, Ji Young Park, Han Wook Seo, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Tae-Yeon Seong, Bum Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):348-352. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.348
- 1,323 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Quantum dots (QDs) are capable of controlling the typical emission and absorption wavelengths because of the bandgap widening effect of nanometer-sized particles. These phosphor particles have been used in optical devices, photovoltaic devices, advanced display devices, and several biomedical complexes. In this study, we synthesize ZnSe QDs with controlled surface defects by a heating-up method. The optical properties of the synthesized particles are analyzed using UV-visible and photoluminescence (PL) measurements. Calculations indicate nearly monodisperse particles with a size of about 5.1 nm at 260°C (full width at half maximum = 27.7 nm). Furthermore, the study results confirm that successful doping is achieved by adding Eu3+ preparing the growth phase of the ZnSe:Eu QDs when heating-up method. Further, we investigate the correlation between the surface defects and the luminescent properties of the QDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An investigation into the effective surface passivation of quantum dots by a photo-assisted chemical method
So-Yeong Joo, Hyun-Su Park, Do-yeon Kim, Bum-Sung Kim, Chan Gi Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
AIP Advances.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Multimodal luminescence properties of surface-treated ZnSe quantum dots by Eu
Ji Young Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Kyoung-Mook Lim, Yong-Ho Choa, Woo-Byoung Kim, Bum Sung Kim
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 8. CrossRef
- An investigation into the effective surface passivation of quantum dots by a photo-assisted chemical method
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


