Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
- Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):96-101. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.96
- 912 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
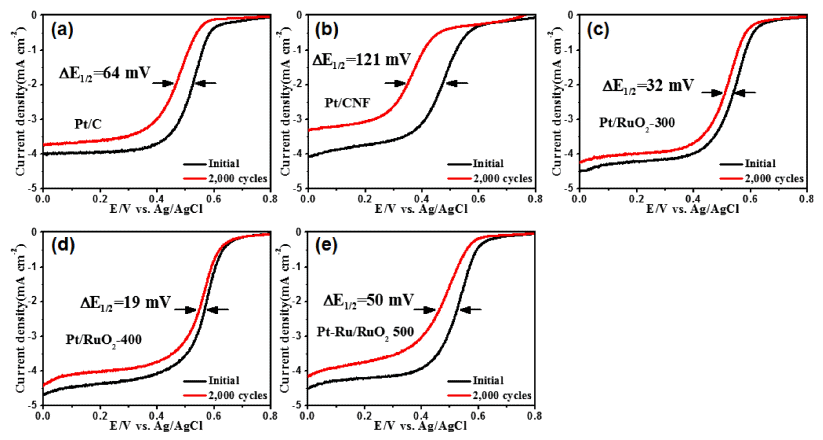
PDF Well-dispersed platinum catalysts on ruthenium oxide nanofiber supports are fabricated using electrospinning, post-calcination, and reduction methods. To obtain the well-dispersed platinum catalysts, the surface of the nanofiber supports is modified using post-calcination. The structures, morphologies, crystal structures, chemical bonding energies, and electrochemical performance of the catalysts are investigated. The optimized catalysts show well-dispersed platinum nanoparticles (1-2 nm) on the nanofiber supports as well as a uniform network structure. In particular, the well-dispersed platinum catalysts on the ruthenium oxide nanofiber supports display excellent catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reactions with a half-wave potential (E1/2) of 0.57 V and outstanding long-term stability after 2000 cycles, resulting in a lower E1/2 potential degradation of 19 mV. The enhanced electrochemical performance for oxygen reduction reactions results from the well-dispersed platinum catalysts and unique nanofiber supports.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Porous Electrodes for Zinc-Ion Supercapacitors with Improved Energy Storage Performance
Geon-Hyoung An
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(8): 505. CrossRef - Surface tailoring of zinc electrodes for energy storage devices with high-energy densities and long cycle life
Geon-Hyoung An, SeungNam Cha, Jung Inn Sohn
Applied Surface Science.2019; 467-468: 1157. CrossRef - Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Young-geun Lee, Geon-hyeong An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(3): 182. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Porous Electrodes for Zinc-Ion Supercapacitors with Improved Energy Storage Performance
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Nitrogen-doped Carbon Nanofibers for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- Geon-Hyoung An, Eun-Hwan Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):420-425. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.420

- 637 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF N-doped carbon nanofibers as catalysts for oxygen-reduction reactions are synthesized using electrospinning and carbonization. Their morphologies, structures, chemical bonding states, and electrochemical performance are characterized. The optimized N-doped carbon nanofibers exhibit graphitization of carbon nanofibers and an increased nitrogen doping as well as a uniform network structure. In particular, the optimized N-doped carbon nanofibers show outstanding catalytic activity for oxygen-reduction reactions, such as a half-wave potential (E1/2) of 0.43 V, kinetic limiting current density of 6.2 mA cm-2, electron reduction pathways (n = 3.1), and excellent long-term stability after 2000 cycles, resulting in a lower E1/2 potential degradation of 13 mV. The improvement in the electrochemical performance results from the synergistic effect of the graphitization of carbon nanofibers and the increased amount of nitrogen doping.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Perforated Polygonal Cobalt Oxides using a Carbon Nanofiber Template
- Dong-Yo Sin, Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):350-355. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.350
- 826 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
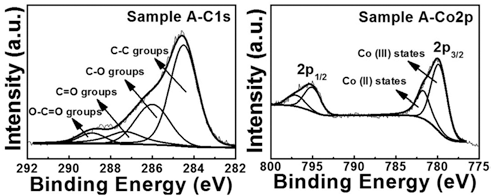
PDF Perforated polygonal cobalt oxide (CO3O4) is synthesized using electrospinning and a hydrothermal method followed by the removal of a carbon nanofiber (CNF) template. To investigate their formation mechanism, thermogravimetric analysis, field-emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Xray photoelectron spectroscopy are examined. To obtain the optimum condition of perforated polygonal CO3O4, we prepare three different weight ratios of the Co precursor and the CNF template: sample A (Co precursor:CNF template- 10:1), sample B (Co precursor:CNF template-3.2:1), and sample C (Co precursor:CNF template-2:1). Among them, sample A exhibits the perforated polygonal CO3O4 with a thin carbon layer (5.7-6.2 nm) owing to the removal of CNF template. However, sample B and sample C synthesized perforated round CO3O4 and destroyed CO3O4 powders, respectively, due to a decreased amount of Co precursor. The increased amount of the CNF template prevents the formation of polygonal CO3O4. For sample A, the optimized weight ratio of the Co precursor and CNF template may be related to the successful formation of perforated polygonal CO3O4. Thus, perforated polygonal CO3O4 can be applied to electrode materials of energy storage devices such as lithium ion batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Young-geun Lee, Geon-hyeong An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(3): 182. CrossRef - Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 96. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Flake-like LiCoO2 Nanopowders using Electrospinning
- Bon-Ryul Koo, Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):108-113. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.108
- 810 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
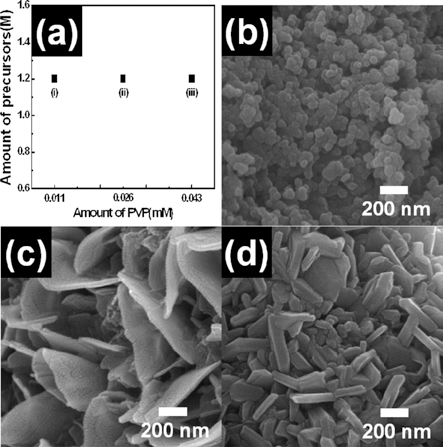
PDF Flake-like LiCoO2 nanopowders were fabricated using electrospinning. To investigate their formation mechanism, field-emssion scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were carried out. Among various parameters of electrospinning, we controlled the molar concentration of the precursor and the PVP polymer. When the molar concentration of lithium and cobalt was 0.45 M, the morphology of LiCoO2 nanopowders was irregular and round. For 1.27 M molar concentration, the LiCoO2 nanopowders formed with flake-like morphology. For the PVP polymer, the molar concentration was set to 0.011 mM, 0.026 mM, and 0.043 mM. Irregular LiCoO2 nanopowders were formed at low concentration (0.011 mM), while flake-like LiCoO2 were formed at high concentration (0.026 mM and 0.043 mM). Thus, optimized molar concentration of the precursor and the PVP polymer may be related to the successful formation of flake-like LiCoO2 nanopowders. As a results, the synthesized LiCoO2 nanopowder can be used as the electrode material of Li-ion batteries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(2): 96. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of SnO2-CoO/carbon-coated CoO Core/shell Nanowire Composites
Yu-Jin Lee, Bon-Ryul Koo, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(5): 360. CrossRef
- Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


