Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
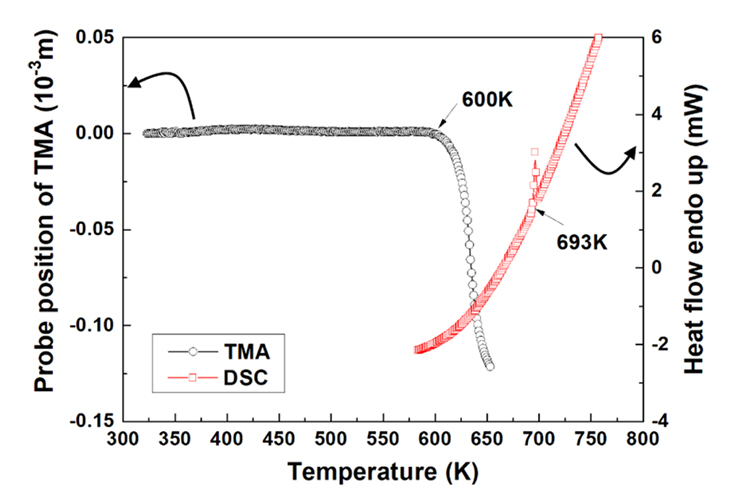
- Fabrication of Bi2Te2.5Se0.5 by Combining Oxide-reduction and Compressive-forming Process and Its Thermoelectric Properties
- Young Soo Lim, Gil-Geun Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):50-56. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.50
- 1,077 View
- 20 Download
- [Korean]
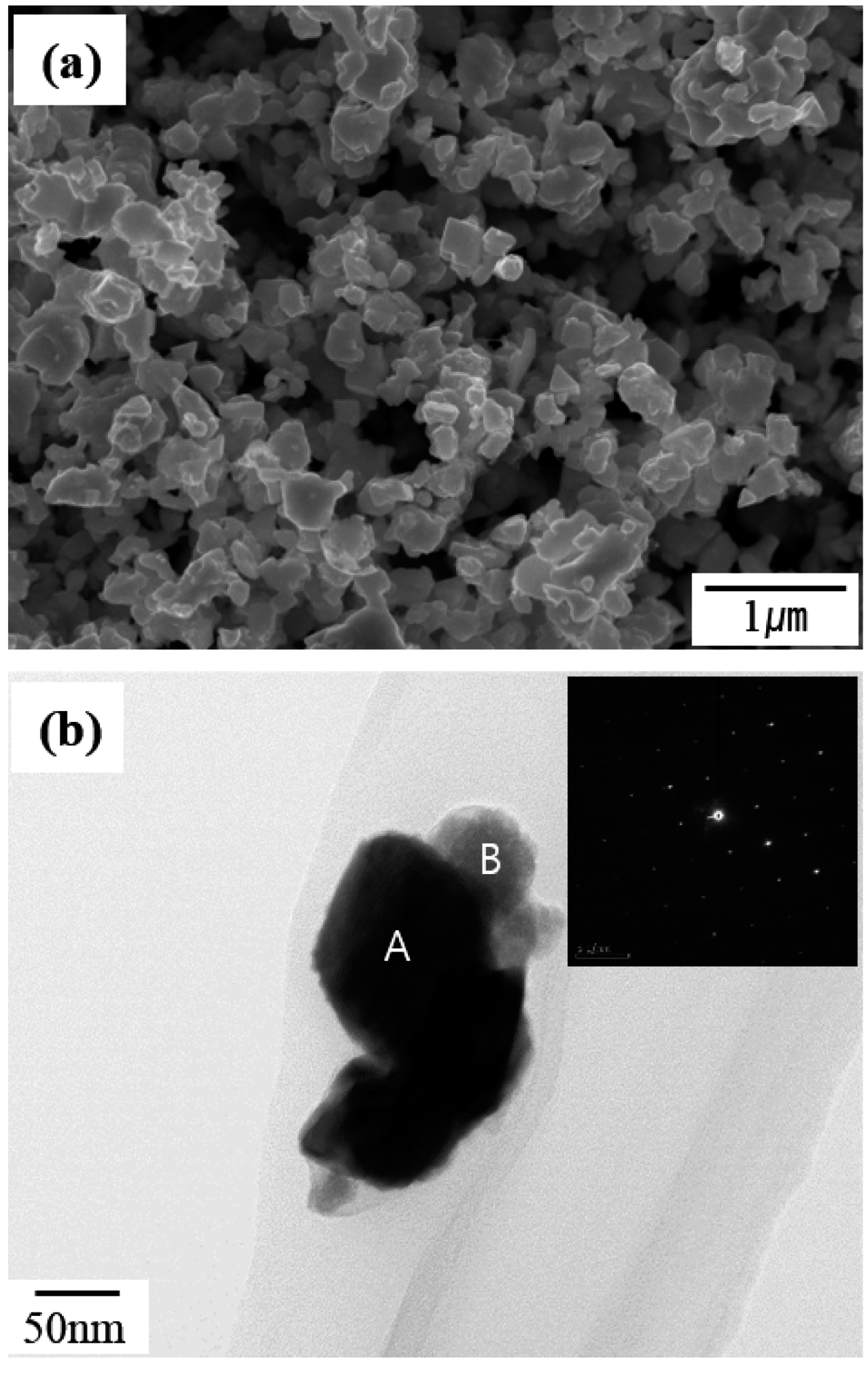
- Fabrication of WC/Co composite powder from oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap by carbothermal reduction process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Young Soo Lim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):240-245. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.240
- 741 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study focuses on the fabrication of a WC/Co composite powder from the oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap using solid carbon in a hydrogen gas atmosphere for the recycling of WC/Co hardmetal. Mixed powders are manufactured by mechanically milling the oxide powder of WC-13 wt% Co hardmetal scrap and carbon black with varying powder/ball weight ratios. The oxide powder of WC-13 wt% Co hardmetal scrap consists of WO3 and CoWO4. The mixed powder mechanically milled at a lower powder/ball weight ratio (high mechanical milling energy) has a more rapid carbothermal reduction reaction in the formation of WC and Co phases compared with that mechanically milled at a higher powder/ball weight ratio (lower mechanical milling energy). The WC/Co composite powder is fabricated at 900°C for 6 h from the oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap using solid carbon in a hydrogen gas atmosphere. The fabricated WC/Co composite powder has a particle size of approximately 0.25-0.5 μm.
- [Korean]
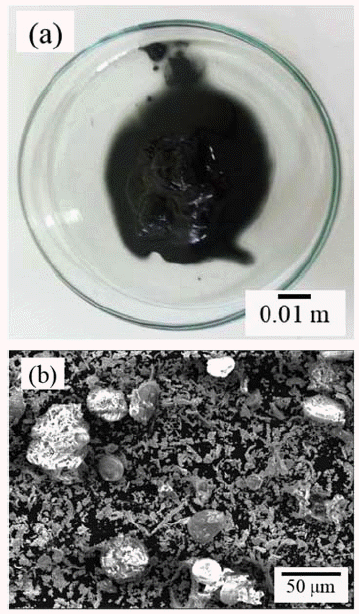
- Recovery of Tungsten from WC/Co Hardmetal Sludge by Alkaline Leaching Hydrometallurgy Process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Ji-Eun Kwon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):372-378. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.372
- 839 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study focuses on the development of an alkaline leaching hydrometallurgy process for the recovery of tungsten from WC/Co hardmetal sludge, and an examination of the effect of the process parameters on tungsten recovery. The alkaline leaching hydrometallurgy process has four stages, i.e., oxidation of the sludge, leaching of tungsten by NaOH, refinement of the leaching solution, and precipitation of tungsten. The WC/Co hardmetal sludge oxide consists of WO3 and CoWO4. The leaching of tungsten is most affected by the leaching temperature, followed by the NaOH concentration and the leaching time. About 99% of tungsten in the WC/Co hardmetal sludge is leached at temperatures above 90°C and a NaOH concentration above 15%. For refinement of the leaching solution, pH control of the solution using HCl is more effective than the addition of Na2S·9H2O. The tungsten is precipitated as high-purity H2WO4·H2O by pH control using HCl. With decreasing pH of the solution, the tungsten recovery rate increases and then decrease. About 93% of tungsten in the WC/Co hardmetal sludge is recovered by the alkaline leaching hydrometallurgy process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of tungsten oxide powder from WC–Co cemented carbide scraps by oxidation behaviour
Min Soo Park, Jong-Min Gwak, Kyeong-mi Jang, Gook-Hyun Ha
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 688. CrossRef
- Fabrication of tungsten oxide powder from WC–Co cemented carbide scraps by oxidation behaviour
- [Korean]
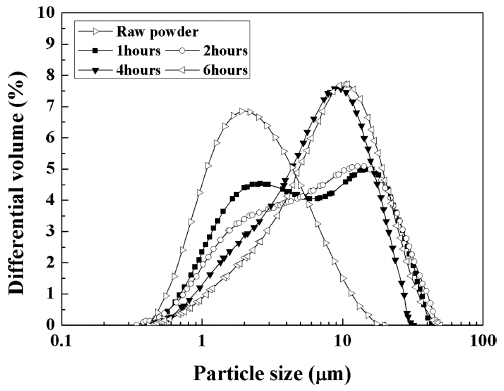
- Fabrication of Silver Flake Powder by the Mechanical Milling Process
- Hae-Young Jeong, Gil-Geun Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):54-60. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.54
- 693 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study focuses on fabricating silver flake powder by a mechanical milling process and investigating the formation of flake-shaped particles during milling. The silver flake powder is fabricated by varying the mechanical milling parameters such as the amount of powder, ball size, impeller rotation speed, and milling time of the attrition ballmill. The particle size of the silver flake powder decreases with increasing amount of powder; however, it increases with increasing impeller rotation speed. The change in the particle size of the silver flake powder is analyzed based on elastic collision between the balls, taking energy loss of the balls due to the powder into consideration. The change in the particle size of the silver flake powder with mechanical milling parameters is consistent with the change in the diameter of the elastic deformation contact area of the ball, due to the collision between the balls, with milling parameters. The flake-shaped silver particles are formed at the elastic deformation contact area of the ball due to the collision.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of WC/Co composite powder from oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap by carbothermal reduction process
Gil-Geun Lee, Young Soo Lim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 240. CrossRef
- Fabrication of WC/Co composite powder from oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap by carbothermal reduction process
- [Korean]
- Effect of Mechanical Milling Parameters on the Particle Size of Silver Flake
- Gil-Geun Lee, Hae-Young Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):307-312. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.307
- 680 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study is focused on investigating the relation between the particle size of silver flake powder and mechanical milling parameters. Mechanical milling parameters such as ball size, impeller rotation speed and milling time of the attrition ball-mill were controlled to produce silver flake powder. The particle size of the silver flake powder increased with increasing ball size and impeller rotation speed. The change of the particle size of the silver flake powder with mechanical milling parameters was analyzed based on balls motion in the mill container of the attrition ballmill. The silver flake particles were formed at the elastic deformation area of the ball due to the collision between balls. The change of the particle size of the silver flake powder with mechanical milling parameters well consists with the change of the collision energy of ball with parameters mentioned above.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Silver Flake Powder by the Mechanical Milling Process
Hae-Young Jeong, Gil-Geun Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 54. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Silver Flake Powder by the Mechanical Milling Process
- [Korean]
- Effect of Added B4C on the Mechanical Properties of WC/Ni-Si Hardmetal
- Gil-Geun Lee, Gook-Hyun Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(5):366-370.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.5.366

- 411 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The effects of B_4C on the mechanical properties of WC/Ni-Si hardmetal were analyzed using sintered bodies comprising WC(70-x wt.%), Ni (28.5 wt.%), Si (1.5 wt.%), and B_4C (x wt.%), where 0leq_-xleq_-1.2 wt.%. Samples were prepared by a combination of mechanical milling and liquid-phase sintering. Phase and microstructure characterizations were conducted using X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, and electron probe X-ray micro analysis. The mechanical properties of the sintered bodies were evaluated by measuring their hardness and transverse rupture strength. The addition of B_4C improved the sinterability of the hardmetals. With increasing B_4C content, their hardness increased, but their transverse rupture strength decreased. The changes of sinterability and mechanical properties were attributed to the alloying reaction between B_4C and the binder metal (Ni, Si).
- [Korean]
- The Electric and Thermal Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3
- Gil-Geun Lee, Young-Hoon Choi, Gook-Hyun Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(4):285-290.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.4.285

- 504 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study was focused on the analysis of the electric and thermal properties of spark plasma sintered Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3 thermoelectric material. The crystal structure, microstructure, electric and thermal properties of the sintered body were evaluated by measuring XRD, SEM, electric resistivity, Hall effect and thermal conductivity. The Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3 sintered body showed anisotropic crystal structure. The c-axis of the Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3 crystal aligned in a parallel direction with applied pressure during spark plasma sintering. The degree of the crystal alignment increased with increasing sintering temperature and sintering time. The electric resistivity and thermal conductivity of the Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3 sintered body showed anisotropic characteristics result from crystal alignment.
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 Powder Synthesized by an Oxide-Reduction Process
- Bae-Gun Park, Gil-Geun Lee, Woo-Yeol Kim, Gook-Hyun Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(5):437-442.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.5.437

- 690 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study focused on the synthesis of Bi-Te-Se-based powder by an oxide-reduction process, and analysis of the thermoelectric properties of the synthesized powder. The phase structure, chemical composition, and morphology of the synthesized powder were analyzed by XRD, EPMA and SEM. The synthesized powder was sintered by spark plasma sintering. The thermoelectric properties of the sintered body were evaluated by measuring its Seebeck coefficient, electrical resistivity, and thermal conductivity. Bi_2Te_2.7Se_0.3 powder was synthesized from a mixture of Bi_2O_3, TeO_2, and SeO_2 powders by mechanical milling, calcination, and reduction. The sintered body of the synthesized powder exhibited n-type thermoelectric characteristics. The thermoelectric properties of the sintered bodies depend on the reduction temperature. The Seebeck coefficient and electrical resistivity of the sintered body were increased with increasing reduction temperature. The sintered body of the Bi_2Te_2.7Se_0.3 powder synthesized at 360°C showed about 0.5 of the figure of merit (ZT) at room temperature.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Bi-Sb-Te-based Thermoelectric Powder by an Oxide-reduction Process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Sung-Hyun Kim, Gook-Hyun Ha, Kyung-Tae Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(4):336-341.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.4.336

- 829 View
- 2 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study focused on the synthesis of Bi-Sb-Te-based thermoelectric powder by an oxidereduction process. The phase structure, particle size of the synthesized powders were analyzed using XRD and SEM. The synthesized powder was sintered by the spark plasma sintering method. The thermoelectric property of the sintered body was evaluated by measuring the Seebeck coefficient and specific electric resistivity. The Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3 powder had been synthesized by a combination of mechanical milling, calcination and reduction processes using mixture of Bi_2O_3, Sb_2O_3 and TeO_2 powders. The sintered body of the Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3 powder synthesized by an oxide-reduction process showed p-type thermoelectric characteristics, even though it had lower thermoelectric properties than the sintered body of the Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3 thermoelectric powder synthesized by the conventional melting-crushing method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Bi2Te2.5Se0.5 by Combining Oxide-reduction and Compressive-forming Process and Its Thermoelectric Properties
Young Soo Lim, Gil-Geun Lee
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 50. CrossRef - Synthesis of N-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 Compounds through Oxide-Reduction Process and Related Thermoelectric Transport Properties
Young Soo Lim, Bae Gun Park, Gil-Geun Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2022; 60(6): 463. CrossRef - The Electric and Thermal Properties of Spark Plasma Sintered Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3
Gil-Geun Lee, Young-Hoon Choi, Gook-Hyun Ha
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(4): 285. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of (AgSbTe2)15(GeTe)85Thermoelectric Powder by Gas Atomization Process
Hyo-Seob Kim, Jin-Kyu Lee, Jar-Myung Koo, Byong-Sun Chun, Soon-Jik Hong
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(5): 449. CrossRef - Thermoelectric Properties of Bi2Te2.7Se0.3Powder Synthesized by an Oxide-Reduction Process
Bae-Gun Park, Gil-Geun Lee, Woo-Yeol Kim, Gook-Hyun Ha
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(5): 437. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Bi2Te2.5Se0.5 by Combining Oxide-reduction and Compressive-forming Process and Its Thermoelectric Properties
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of TiC/Co Composite Powder by the Carbothermal Reduction Process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Gook-Hyun Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(5):310-315.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.5.310

- 442 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ultra-fine TiC/Co composite powder was synthesized by the carbothermal reduction process without wet chemical processing. The starting powder was prepared by milling of titanium dioxide and cobalt oxalate powders followed by subsequent calcination to have a target composition of TiC-15 wt.%Co. The prepared oxide powder was mixed again with carbon black, and this mixture was then heat-treated under flowing argon atmosphere. The changes in the phase, mass and particle size of the mixture during heat treatment were investigated using XRD, TG-DTA and SEM. The synthesized oxide powder after heat treatment at 700°C has a mixed phase of TiO_2 and CoTiO_3 phases. This composite oxide powder was carbothermally reduced to TiC/Co composite powder by the solid carbon. The synthesized TiC/Co composite powder at 1300°C for 9 hours has particle size of under about 0.4 mum.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Bi-Sb-Te Thermoelectric Nanopowder by the Plasma Arc Discharge Process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Dong-Youl Lee, Gook-Hyun Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(5):352-358.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.5.352

- 829 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study focused on the synthesis of a bismuth-antimony-tellurium-based thermoelectric nanopowders using plasma arc discharge process. The chemical composition, phase structure, particle size of the synthesized powders under various synthesis conditions were analyzed using XRF, XRD and SEM. The powders as synthesized were sintered by the plasma activated sintering. The thermoelectric properties of sintered body were analyzed by measuring Seebeck coefficient, specific electric resistivity and thermal conductivity. The chemical composition of the synthesized Bi-Sb-Te-based powders approached that of the raw material with an increasing DC current of the are plasma. The synthesized Bi-Sb-Te-based powder consist of a mixed phase structure of the Bi_0.5Sb_1.5Te_3, Bi_2Te_3 and Sb_2Te_3 phases. This powder has homogeneous mixing state of two different particles in an average particle size; about 100nm and about 500nm. The figure of merit of the sintered body of the synthesized 18.75 wt.%Bi-24.68 wt.%Sb-56.57 wt.%Te nanopowder showed higher value than one of the sintered body of the mechanically milled 12.64 wt.%Bi-29.47 wt.%Sb-57.89 wt.%Te powder.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of N-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 Compounds through Oxide-Reduction Process and Related Thermoelectric Transport Properties
Young Soo Lim, Bae Gun Park, Gil-Geun Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2022; 60(6): 463. CrossRef - Thermoelectric Properties of Bi2Te2.7Se0.3Powder Synthesized by an Oxide-Reduction Process
Bae-Gun Park, Gil-Geun Lee, Woo-Yeol Kim, Gook-Hyun Ha
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2011; 18(5): 437. CrossRef - Synthesis of Bi-Sb-Te-based Thermoelectric Powder by an Oxide-reduction Process
Gil-Geun Lee, Sung-Hyun Kim, Gook-Hyun Ha, Kyung-Tae Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2010; 17(4): 336. CrossRef
- Synthesis of N-type Bi2Te2.7Se0.3 Compounds through Oxide-Reduction Process and Related Thermoelectric Transport Properties
- [Korean]
- Consolidation of Binderless and Low-Binder WC hardmetal by Vacuum Sintering
- Byoung-June Min, Young-Ho Park, Gil-Geun Lee, Gook-Hyeon Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(5):315-319.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.5.315

- 500 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pure WC or WC with low Co concentration less than 0.5 wt.% is studied to fabricate high density WC/Co cemented carbide using vacuum sintering and post HIP process. Considering the high melting point of WC, it is difficult to consolidate it without the use of Co as binder. In this study, the effect of lower Co addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties evolution of WC/CO was investigated. By HIP process after vacuum sintering, hardness and density was sharply increased. The hardness values was 2,800kgf/mm2 using binderless WC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
Jong Min Gwak, Min Soo Park, Gook Hyun Ha, Nam Hyun Kang
Metals and Materials International.2025; 31(12): 3733. CrossRef
- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of TiB2 Dispersed Cu Matrix Composite Material by the Combination of the Mechanical Milling and Plasma Activated Sintering Process
- Kyong-Ju Kim, Gil-Geun Lee, Ik-Min Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(5):292-297.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.5.292

- 423 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study was focused on the synthesis of a TiB_2 dispersed copper matrix composite material by the combination of the mechanical milling and plasma activated sintering processes. The Cu/TiB_2 mixed powder was prepared by the combination of the mechanical milling and reduction processes using the copper oxide and titanium diboride powder as the raw material. The synthesized Cu/TiB_2 mixed powder was sintered by the plasma activated sintering process. The hardness and electric conductivity of the sintered bodies were measured using micro vickers hardness and four probe method, respectively. The relative density of Cu/TiB_2 composite material sintered at 800°C showed about 98% of theoretical density. The Cu-1vol%TiB_2 composite material has a hardness of about 130Hv and an electric conductivity of about 85% IACS. The hardness and electric conductivity of Cu-3vol%TiB_2 composite material were about 140 Hv and about 45% IACS, respectively.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Zirconium-Based Nanopowder by the Plasma Arc Discharge Process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Kyong-Ju Kim, Je-Shin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(1):63-69.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.1.063

- 425 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study was focused on the synthesis of a zirconium-based alloyed nanopowder by the plasma arc discharge process. The chemical composition, phase structure, particle size and hydrogen sorption property of the synthesized powders under various synthesis conditions were analyzed using XRF, XRD, SEM, XPS and the ASTM-F798 method. The chemical composition of the synthesized Zr-V-Fe-based powders approached that of the raw material with an increasing hydrogen fraction in the powder synthesis atmosphere. The synthesized Zr_55V_29Fe_16 powder consist of a mixed phase structure of the Zr,;ZrH_2,;FeV;and;Zr(V_1-xFe_x)_2 phases. This powder has an average particle size of about 20 nm. The synthesized Zr_55V_29Fe_16 nanopowder showed getter characteristics, even though it had a lower hydrogen sorption speed than the Zr_57;V36;Fe_7 getter powder. However, the synthesized Zr nanopowder with an average particle size of 20 nm showed higher hydrogen sorption speed than the Zr_57;V36;Fe_7 getter powder.
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 Sintered Body Fabricated by Mechanical Grinding Process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Sung-Chul Shin, Woo-Yeol Kim, Gook-Hyun Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2006;13(5):313-320.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2006.13.5.313

- 570 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The present study is to analyze the thermoelectric properties of Bi_0.4Sb_1.6Te_3 thermoelectric materials fabricated by the mechanical grinding process. The Bi_0.4Sb_1.6Te_3 powders were prepared by the combination of mechanical milling and reduction treating methods using simply crushed pre-alloyed Bi_0.4Sb_1.6Te_3 powder. The mechanical milling was carried out using the tumbler-ball mill and planetary ball mill. The tumbler-ball milling had an effect on the carrier mobility rather than the carrier concentration, whereas, the latter on the carrier concentration. The specific electric resistivity and Seebeck coefficient decreased with increasing the reduction-heat-treatment time. The thermal conductivity continuously increased with increasing the reduction-heat-treatment time. The figure of merit of the Bi_0.4Sb_1.6Te_3 sintered body prepared by the mechanical grinding process showed higher value than one of the sintered body of the simply crushed powder.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cobalt Oxide on Carbothermal Reduction of Spray Dried Titanium-Cobalt-Oxygen Based Oxide Powder
- Gil-Geun Lee, Chan-Young Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(5):336-344.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.5.336

- 433 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the present study, the focus is on the effect of cobalt oxide powder in the carbothermal reduction of the titanium-cobalt-oxygen based oxide powder by solid carbon for the optimizing synthesis process of ultra fine TiC/Co composite powder. The titanium-cobalt-oxygen based oxide powder was prepared by the combination of the spray drying and desalting processes using the titanium dioxide powder and cobalt nitrate as the raw materials. The titanium-cobalt-oxygen based oxide powder was mixed with carbon black, and then this mixture was carbothermally reduced under flowing argon atmosphere. Changes in the phase structure and thermal gravity of the mixture during carbothermal reduction were analysed using XRD and TGA. Titanium-cobalt-oxygen based oxide powder desalted at 600°C had a mixture of TiO_2;and;Co_3O_4. And the one desalted at 800°C had a mixture of TiO_2;and;CoTiO_3. In the case of the former powder, the reduction of cobalt oxide powder in the titanium-cobalt-oxygen based oxide powder occurred at lower temperature than the latter one. However, the carbothermal reduction of titanium dioxide powder in the titanium-cobalt-oxygen based oxide powder with a mixture of TiO_2;and;Co_3O_4 occurred at higher temperature than the one with a mixture of TiO_2;and;CoTiO_3. And also, the former powder showed a lower TiC formation ability than the latter one.
- [Korean]
- Carbothermal Reduction of Oxide Powder Prepared from Waste WC/Co Hardmetal by Solid Carbon
- Gil-Geun Lee, Gook-Hyun Ha
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(2):112-116.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.2.112

- 748 View
- 2 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the present study, the focus is on the analysis of carbothermal reduction of oxide powder prepared from waste WC/Co hardmetal by solid carbon under a stream of argon for the recycling of the WC/Co hard-metal. The oxide powder was prepared by the combination of the oxidation and crushing processes using the waste WC-8 wt.%Co hardmetal as the raw material. This oxide powder was mixed with carbon black, and then this mixture was carbothermally reduced under a flowing argon atmosphere. The changes in the phase structure and gases discharge of the mixture during carbothermal reduction was analysed using XRD and gas analyzer. The oxide powder prepared from waste WC-8wt.%Co hardmetal has a mixture of WO_3 and CoWO_4. This oxide powder reduced at about 850°C, formed tungsten carbides at about 950°C, and then fully transformed to a mixed state of tungsten carbide (WC) and cobalt at about 1100°C by solid carbon under a stream of argon. The WC/Co composite powder synthesized at 1000°C for 6 hours from oxide powder of waste WC-8wt.%Co hardmetal has an average particle size of 0.3 µm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of mechanical milling on the carbothermal reduction of oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap
Gil-Geun Lee, Gook-Hyun Ha
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(2): 260. CrossRef - Recovery of Tungsten from WC/Co Hardmetal Sludge by Alkaline Leaching Hydrometallurgy Process
Gil-Geun Lee, Ji-Eun Kwon
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(5): 372. CrossRef - Recovery of tungsten carbide from hard material sludge by oxidation and carbothermal reduction process
Woo-Gwang Jung
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2014; 20(4): 2384. CrossRef - Trend on the Recycling Technologies for the used Tungsten Carbide(WC) by the Patent and Paper Analysis
Jin-Ki Jeong, Jae-Chun Lee, Sang-Woo Park, Kyung-Seok Kang
Journal of the Korean Institute of Resources Recycling.2012; 21(1): 82. CrossRef
- Effects of mechanical milling on the carbothermal reduction of oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap
- [Korean]
- Effect of Mold Dimensions on Temperature Distribution of Die during Plasma Activated Sintering
- Gil-Geun Lee, IK-Min Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2004;11(5):363-368.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2004.11.5.363

- 473 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the present study, the focus is on the analysis of the effect of the mold dimensions on the temperature distribution of a die during plasma activated sintering. The temperature distribution of a cylindrical mold with various dimensions was measured using K-type thermocouples. The temperature homogeneity of the die was studied based on the direction and dimensions of the die. A temperature gradient existed in the radial direction of the die during the plasma activated sintering. Also, the magnitude of the temperature gradient was increased with increasing sintering temperature. In the longitudinal direction, however, there was no temperature gradient. The temperature gradient of the die in the radial direction strongly depended on a ratio of die volume to punch area.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


