Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Abnormal Grain Growth on Ionic Conductivity in LATP
- Hyungik Choi, Yoonsoo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.23
- 2,814 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
Shu-Ting Ko, Chaojie Du, Huiming Guo, Hasti Vahidi, Jenna L. Wardini, Tom Lee, Yi Liu, Jingjing Yang, Francisco Guzman, Timothy J. Rupert, William J. Bowman, Shen J. Dillon, Xiaoqing Pan, Jian Luo
Journal of Advanced Ceramics.2025; 14(3): 9221047. CrossRef - Effect of bimodal particle size distribution on Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolytes: Microstructures and electrochemical properties
Gi Jeong Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Seul Ki Choi, Jong Won Bae, Kun-Jae Lee, Minho Yang
Powder Technology.2025; 466: 121407. CrossRef
- Temperature-dependent microstructural evolution in a compositionally complex solid electrolyte: The role of a grain boundary transition
- [Korean]
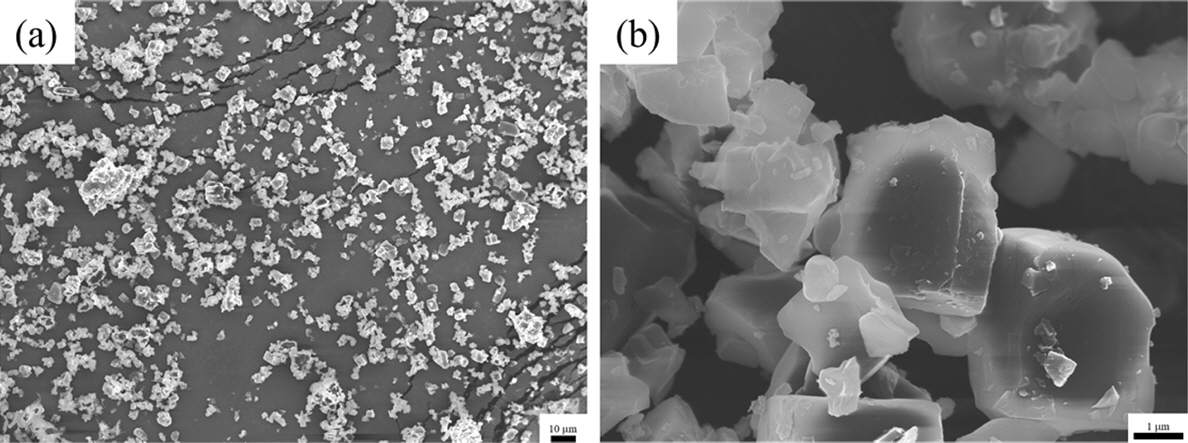
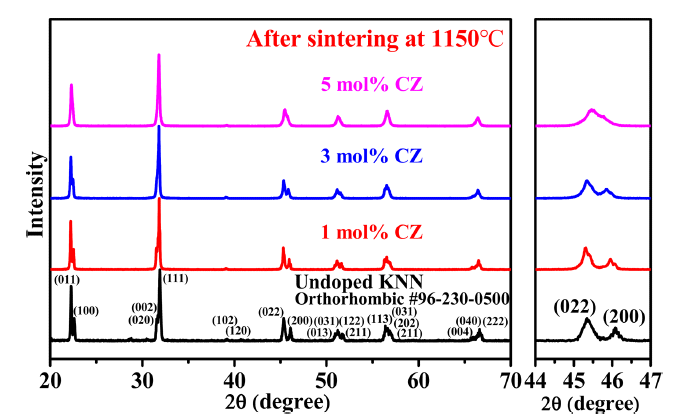
- Grain Shape and Grain Growth Behavior in the (K0.5Na0.5)NbO3-CaZrO3 System
- Chul-Lee Lee, Kyoung-Seok Moon
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):110-117. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.110
- 451 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The grain growth behavior in the (1-x)K0.5Na0.5NbO3-
x CaZrO3 (KNNCZ-x) system is studied as a function of the amount of CZ and grain shape. The (1-x)K0.5Na0.5NbO3-x CaZrO3 (KNNCZ-x) powders are synthesized using a conventional solid-state reaction method. A single orthorhombic phase is observed atx = 0 – 0.03. However, rhombohedral and orthorhombic phases are observed atx = 0.05. The grain growth behavior changes from abnormal grain growth to the suppression of grain growth as the amount of CaZrO3 (CZ) increases. With increasing CZ content, grains become more faceted, and the step-free energy increases. Therefore, the critical growth driving force increases. The grain size distribution broadens with increasing sintering time in KNNCZ-0.05. As a result, some large grains with a driving force larger than the critical driving force for growth exhibit abnormal grain growth behavior during sintering. Therefore, CZ changes the grain growth behavior and microstructure of KNN. Grain growth at the faceted interface of the KNNCZ system occurs via two-dimensional nucleation and growth.
- [Korean]
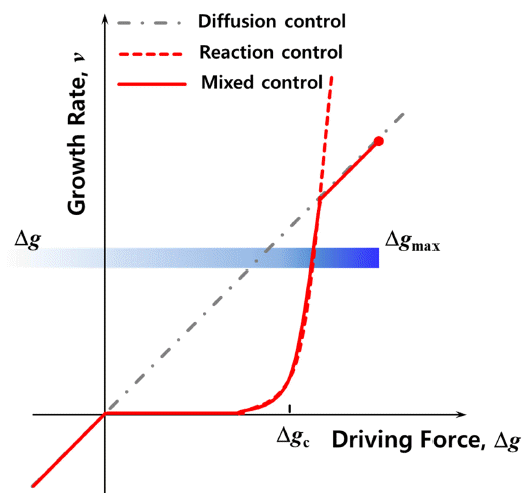
- Sintering Behavior of M-type Sr-Hexaferrite by MnCO3 Addition
- MinSeok Jeong, Changjae You, Jung Young Cho, Kyoung-Seok Moon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.126
- 570 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The grain growth behavior of M-type Sr hexaferrite (SrM) grains is investigated with the addition of MnCO3. First, the SrM powder is synthesized by a conventional solid-state reaction. The powder compacts of SrM are sintered at 1250°C for 2 h with various amounts of MnCO3 (0, 0.5, 1.0, and 4.0 mol%). There is no secondary solid phase in any of the sintered samples. Relative density increases when MnCO3 is added to the SrM. Obvious abnormal grain growth does not appear in any of the SrM samples with MnCO3. The average grain size increases when 0.5 mol% MnCO3 is added to the SrM. However, as the amount of MnCO3 increase to over 0.5 mol%, the average grain size decreases. These observations allow us to conclude that the growth of SrM grains is governed by the two-dimensional nucleation grain growth mechanism, and the critical driving force for the growth of a grain decreases as the amount of MnCO3 increases.
- [Korean]
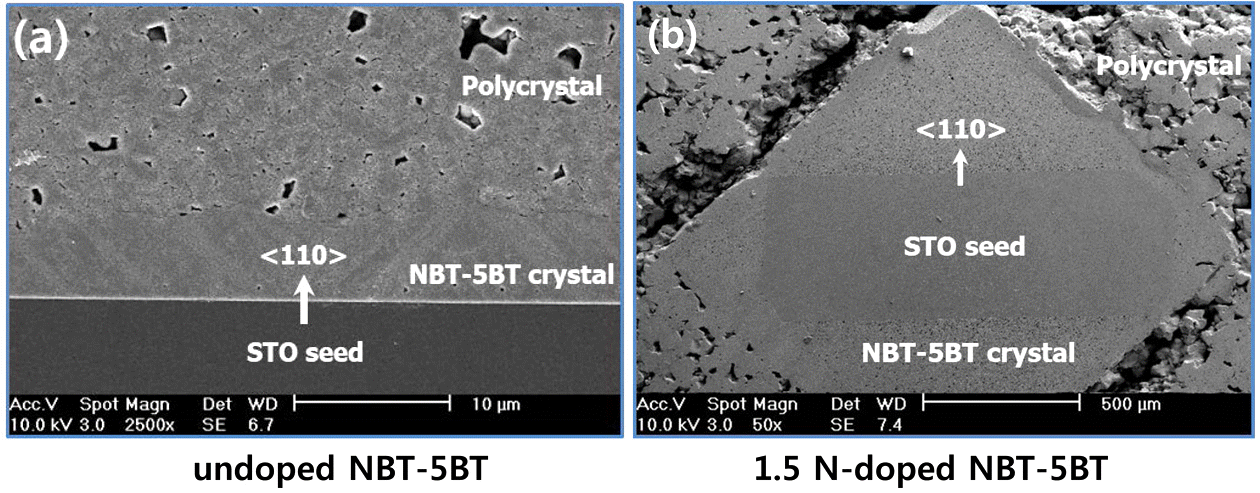
- Effect of Na2CO3 Addition on Grain Growth Behavior and Solid-state Single Crystal Growth in the Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-BaTiO3 System
- Kyoung-Seok Moon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):104-108. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.104
- 726 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Grain-growth behavior in the 95Na1/2Bi1/2TiO3-5BaTiO3 (mole fraction, NBT-5BT) system has been investigated with the addition of Na2CO3. When Na2CO3 is added to NBT-5BT, the growth rate is higher than desired and grains are already impinging each other during the initial stage of sintering. The grain size decreases as the sintering temperature increases. With the addition of Na2CO3, a liquid phase infiltrates the interfaces between grains during sintering. The interface structure can be changed to be more faceted and the interface migration rate can increase due to fast material transport through the liquid phase. As the sintering temperature increases, the impingement of abnormal grains increases because the number of abnormal grains increases. Therefore, the average grain size of abnormal grains can be decreased as the temperature increases. The phenomenon can provide evidence that grain coarsening in NBT-5BT with addition of Na2CO3 is governed by the growth of facet planes, which would occur via mixed control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Growth of single crystals in the (Na1/2Bi1/2)TiO3–(Sr1–xCax)TiO3 system by solid state crystal growth
Phan Gia Le, Huyen Tran Tran, Jong-Sook Lee, John G. Fisher, Hwang-Pill Kim, Wook Jo, Won-Jin Moon
Journal of Advanced Ceramics.2021; 10(5): 973. CrossRef - Sintering Behavior of M-type Sr-Hexaferrite by MnCO3 Addition
MinSeok Jeong, Changjae You, Jung Young Cho, Kyoung-Seok Moon
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(2): 126. CrossRef
- Growth of single crystals in the (Na1/2Bi1/2)TiO3–(Sr1–xCax)TiO3 system by solid state crystal growth
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


