Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of WC/Co composite powder from oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap by carbothermal reduction process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Young Soo Lim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):240-245. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.240
- 746 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
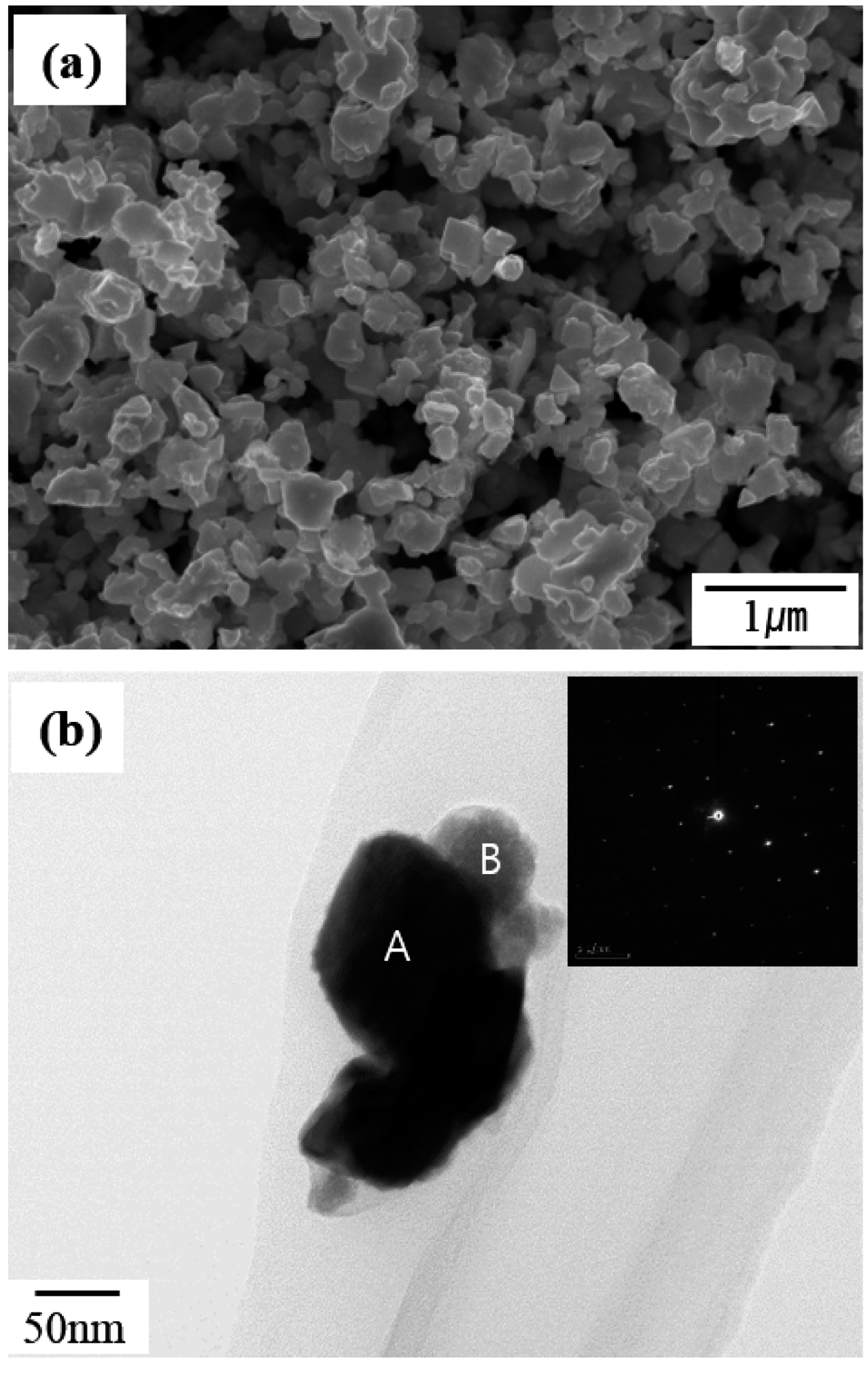
PDF This study focuses on the fabrication of a WC/Co composite powder from the oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap using solid carbon in a hydrogen gas atmosphere for the recycling of WC/Co hardmetal. Mixed powders are manufactured by mechanically milling the oxide powder of WC-13 wt% Co hardmetal scrap and carbon black with varying powder/ball weight ratios. The oxide powder of WC-13 wt% Co hardmetal scrap consists of WO3 and CoWO4. The mixed powder mechanically milled at a lower powder/ball weight ratio (high mechanical milling energy) has a more rapid carbothermal reduction reaction in the formation of WC and Co phases compared with that mechanically milled at a higher powder/ball weight ratio (lower mechanical milling energy). The WC/Co composite powder is fabricated at 900°C for 6 h from the oxide of WC/Co hardmetal scrap using solid carbon in a hydrogen gas atmosphere. The fabricated WC/Co composite powder has a particle size of approximately 0.25-0.5 μm.
- [Korean]
- Recovery of Tungsten from WC/Co Hardmetal Sludge by Alkaline Leaching Hydrometallurgy Process
- Gil-Geun Lee, Ji-Eun Kwon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):372-378. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.372
- 854 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study focuses on the development of an alkaline leaching hydrometallurgy process for the recovery of tungsten from WC/Co hardmetal sludge, and an examination of the effect of the process parameters on tungsten recovery. The alkaline leaching hydrometallurgy process has four stages, i.e., oxidation of the sludge, leaching of tungsten by NaOH, refinement of the leaching solution, and precipitation of tungsten. The WC/Co hardmetal sludge oxide consists of WO3 and CoWO4. The leaching of tungsten is most affected by the leaching temperature, followed by the NaOH concentration and the leaching time. About 99% of tungsten in the WC/Co hardmetal sludge is leached at temperatures above 90°C and a NaOH concentration above 15%. For refinement of the leaching solution, pH control of the solution using HCl is more effective than the addition of Na2S·9H2O. The tungsten is precipitated as high-purity H2WO4·H2O by pH control using HCl. With decreasing pH of the solution, the tungsten recovery rate increases and then decrease. About 93% of tungsten in the WC/Co hardmetal sludge is recovered by the alkaline leaching hydrometallurgy process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of tungsten oxide powder from WC–Co cemented carbide scraps by oxidation behaviour
Min Soo Park, Jong-Min Gwak, Kyeong-mi Jang, Gook-Hyun Ha
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 688. CrossRef
- Fabrication of tungsten oxide powder from WC–Co cemented carbide scraps by oxidation behaviour
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


