Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- High Temperature Oxidation Behavior of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- Yu-Jin Hwang, Dong-Yeol Wi, Kyu-Sik Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):110-119. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.110
- 1,139 View
- 26 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
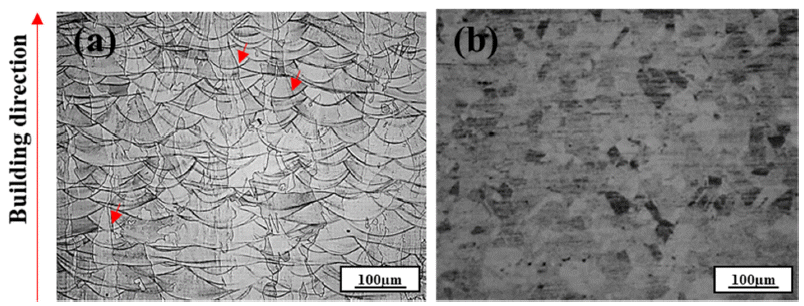
PDF In this study, the high-temperature oxidation properties of austenitic 316L stainless steel manufactured by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is investigated and compared with conventional 316L manufactured by hot rolling (HR). The initial microstructure of LPBF-SS316L exhibits a molten pool ~100 μm in size and grains grown along the building direction. Isotropic grains (~35 μm) are detected in the HR-SS316L. In high-temperature oxidation tests performed at 700°C and 900°C, LPBF-SS316L demonstrates slightly superior high-temperature oxidation resistance compared to HR-SS316L. After the initial oxidation at 700°C, shown as an increase in weight, almost no further oxidation is observed for both materials. At 900°C, the oxidation weight displays a parabolic trend and both materials exhibit similar behavior. However, at 1100°C, LPBF-SS316L oxidizes in a parabolic manner, but HR-SS316L shows a breakaway oxidation behavior. The oxide layers of LPBF-SS316L and HR-SS316L are mainly composed of Cr2O3, Febased oxides, and spinel phases. In LPBF-SS316L, a uniform Cr depletion region is observed, whereas a Cr depletion region appears at the grain boundary in HR-SS316L. It is evident from the results that the microstructure and the hightemperature oxidation characteristics and behavior are related.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
Hui Wang, Bo Yang, Tao Sun, Weilai Yao, Wei Jiang
Journal of Constructional Steel Research.2025; 235: 109930. CrossRef - Study of structural stability at high temperature of pseudo-single tube with double layer as an alternative method for accident-tolerant fuel cladding
Jong Woo Kim, Hyeong Woo Min, Jaehwan Ko, Yonghee Kim, Young Soo Yoon
Journal of Nuclear Materials.2022; 566: 153800. CrossRef
- Retention factor-based constitutive model of high-strength austenitic A4–80 bolts after fire exposure
- [Korean]
- Effect of Cell Size on the High Temperature Oxidation Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Powder Porous Metal Manufactured by Electro-spray Process
- Jae-Sung Oh, Young-Min Kong, Byoung-Kee Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):55-61. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.55

- 956 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Fe-Cr-Al powder porous metal was manufactured by using new electro-spray process. First, ultra-fine fecralloy powders were produced by using the submerged electric wire explosion process. Evenly distributed colloid (0.05~0.5% powders) was dispersed on Polyurethane foam through the electro-spray process. And then degreasing and sintering processes were conduced. In order to examine the effect of cell size (200 μm, 450 μm, 500 μm) in process, pre-samples were sintered for two hours at temperature of 1450°C, in H2 atmospheres. A 24-hour thermo gravimetric analysis test was conducted at 1000°C in a 79% N2 + 21% O2 to investigate the high temperature oxidation behavior of powder porous metal. The results of the high temperature oxidation tests showed that oxidation resistance increased with increasing cell size. In the 200 μm porous metal with a thinner strut and larger specific surface area, the depletion of the stabilizing elements such as Al and Cr occurred more quickly during the high-temperature oxidation compared with the 450, 500 μm porous metals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Open‐Cell Austenitic Stainless Steel Foam by Electrostatic Powder Spraying Process
Tae-Hoon Kang, Kyu-Sik Kim, Jung-Yeul Yun, Min-Jeong Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee
Advanced Engineering Materials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Behaviors of Fe-Ni Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering
Chae Hong Lim, Jong Seok Park, Sangsun Yang, Jung-Yeul Yun, Jin Kyu Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(1): 53. CrossRef - Effect of Al2O3 Inter-Layer Grown on FeCrAl Alloy Foam to Improve the Dispersion and Stability of NiO Catalysts
유진 이, 본율 구, 성호 백, 만호 박, 효진 안
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2015; 25(8): 391~397. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Open‐Cell Austenitic Stainless Steel Foam by Electrostatic Powder Spraying Process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


