Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Aqueous Synthesis and Luminescent Characteristics of Cu:ZnSe Quantum Dots by Internal Doping Method
- Geum Ji Back, Hyun Seon Hong
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):370-375. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.370
- 852 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
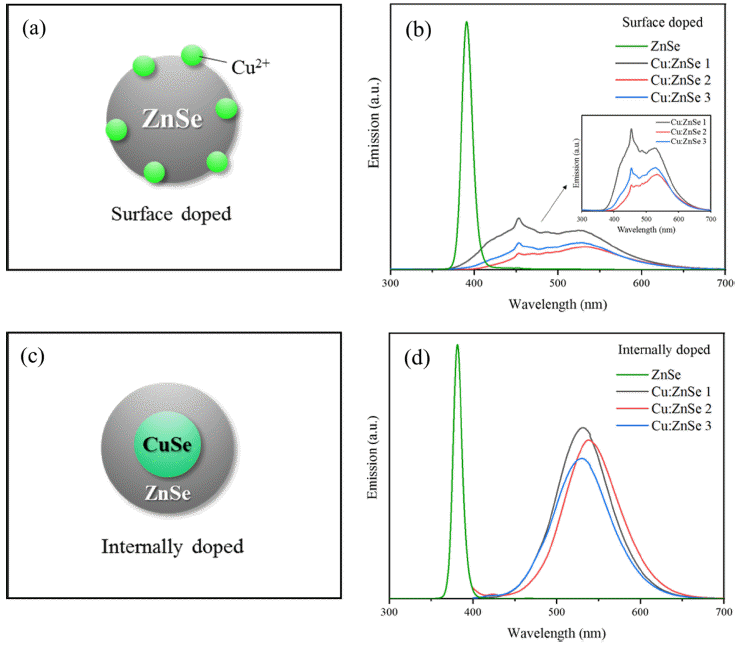
PDF Cu-doped ZnSe quantum dots were successfully synthesized in an aqueous solution using an internal doping method. The effects of ligand type, CuSe synthesis temperature, and heating time on Cu-doped ZnSe synthesis were systematically investigated. Of MPA, GSH, TGA, and NAC used as ligands, MPA was the optimal ligand as determined by PL spectrum analysis. In addition, the emission wavelength was found to depend on the synthesis temperature of the internal doping core of CuSe. As the temperature increased, the doping of Cu2+ was enhanced, and the emission wavelength band was redshifted; accordingly, the emission peaks moved from blue to green (up to 550 nm). Thus, the synthesis of Cu:ZnSe using internal doping in aqueous solutions is a potential method for ecomanufacturing of colortuned ZnSe quantum dots for display applications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
Hyun Seon Hong, Yerin Kim, Jea Hyung Kim, Hyeon Seon Ryu, Dahye Song
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2025; 62(3): 472. CrossRef
- Synthesis and luminescence characteristics of manganese-doped ZnSe quantum dots synthesized in aqueous solution through internal doping
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


