Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
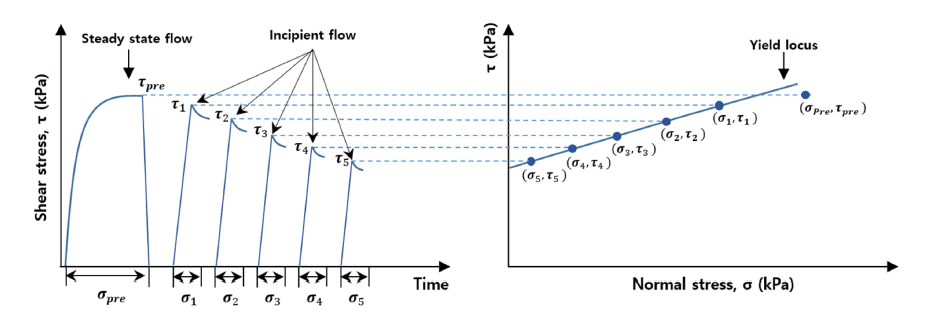
- Effect of Particle Sphericity on the Rheological Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Powders for Laser Powder Bed Fusion Process
- T. Y. Kim, M. H. Kang, J. H. Kim, J.K. Hong, J.H. Yu, J.I. Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):99-109. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.99
- 1,418 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder flowability is critical in additive manufacturing processes, especially for laser powder bed fusion. Many powder features, such as powder size distribution, particle shape, surface roughness, and chemical composition, simultaneously affect the flow properties of a powder; however, the individual effect of each factor on powder flowability has not been comprehensively evaluated. In this study, the impact of particle shape (sphericity) on the rheological properties of Ti-6Al-4V powder is quantified using an FT4 powder rheometer. Dynamic image analysis is conducted on plasma-atomized (PA) and gas-atomized (GA) powders to evaluate their particle sphericity. PA and GA powders exhibit negligible differences in compressibility and permeability tests, but GA powder shows more cohesive behavior, especially in a dynamic state, because lower particle sphericity facilitates interaction between particles during the powder flow. These results provide guidelines for the manufacturing of advanced metal powders with excellent powder flowability for laser powder bed fusion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A fully computational approach for the prediction of melt pool generation of the directed energy deposition process
Mingyu Chung, Kang-Hyun Lee, Jaeeun Park, Yoon Sun Lee, Gun Jin Yun
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2025; 39(11): 6847. CrossRef - Enhanced Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy with Vanadium Carbide Coating via Directed Energy Deposition
Ui Jun Ko, Ju Hyeong Jung, Jung Hyun Kang, Kyunsuk Choi, Jeoung Han Kim
Materials.2024; 17(3): 733. CrossRef - Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy through Selective Laser Melting: Comprehensive Study on the Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Gargi Roy, Raj Narayan Hajra, Woo Hyeok Kim, Jongwon Lee, Sangwoo Kim, Jeoung Han Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef
- A fully computational approach for the prediction of melt pool generation of the directed energy deposition process
- [Korean]
- Effect of Magnetic properties and Microstructure of Hydrogenation stage in HDDR process
- S.H. Lee, J.H. Yu, Y.D. Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(5):443-448.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.5.443

- 553 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The HDDR(hydrogenation-disproportionation-desorption-recombination) process can be used as an effective way of converting no coercivity Nd-Fe-B material, with a coarse Nd_2Fe_14B grain structure to a highly coercive one with a fine grain. Careful control of the HDDR process can lead to an anisotropic Nd_2Fe_14B without any post aligning process. In this study, the effect of hydrogen gas input at various temperature in range of 200sim500°C of hydrogenation stage (named Modified-solid HDDR, MS-HDDR) on the magnetic properties has been investigated. The powder from the modified-solid HDDR process exhibits Br of 11.7 kG and iHc of 10.7 kOe, which are superior to those of the powder prepared using the normal HDDR process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Dehydrogenation Speed on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Magnets Prepared by HDDR Process
Hee-Ryoung Cha, Ji-Hun Yu, Youn-Kyoung Baek, Hae-Woong Kwon, Yang-Do Kim, Jung-Goo Lee
Journal of Magnetics.2014; 19(1): 49. CrossRef
- The Influence of Dehydrogenation Speed on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Magnets Prepared by HDDR Process
- [Korean]
- Improvement of Microstructural Anisotropy of Nd-Fe-B-Ga-Nb Alloy by the Control of Hydrogen Reaction
- S.H. Lee, D.H. Kim, J.H. Yu, D.W. Lee, B.K. Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(1):23-28.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.1.023

- 337 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - HDDR treated anisotropic Nd-Fe-B powders have been widely used for the sheet motors and the sunroof motors of hybrid or electric vehicles, due to their excellent magnetic properties. Microstructural alignment of HDDR treated powders are mostly depending on the hydrogen reaction in disproportionation step, so the specific method to control hydrogenation reaction is required for improving magnetic properties. In disproportionation step, hydrogenation pressure and reaction time were controlled in the range of 0.15~1.0 atm for 15~180 min in order to control the micorstructural alignment of Nd_2Fe_14B phase and, at the same time, to improve remanence of HDDR treated magnet powders. In this study, we could obtain a well aligned anisotropic Nd-Fe-B-Ga-Nb alloy powder having high remanence of 12 kG by reducing hydrogen pressure down to 0.3 atm in disproportionation step.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Homogenization Treatment on Magnetic Properties of HDDR Treated Nd-Fe-Ga-Nb-B Alloy
- J.H. Yu, S.H. Lee, D.H. Kim, D.W. Lee, B.K. Kim, M.H. Choi, Y.D. Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(4):285-290.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.4.285

- 391 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - HDDR treated anisotropic Nd-Fe-B powders have been widely used, due to their excellent magnetic properties, especially for sheet motors and sunroof motors of hybrid and electric vehicles. Final microstructure and coercivity of such Nd-Fe-B powders depend on the state of starting mother alloys, so additional homogenization treatment is required for improving magnetic properties of them. In this study, a homogenization treatment was performed at 900sim1140°C in order to control the grain size and Nd-rich phase distribution, and at the same time to improve coercivity of the HDDR treated magnetic powders. FE-SEM was used for observing grain size of the HDDR treated powder and EPMA was employed to observe distribution of Nd-rich phase. Magnetic properties were analyzed with a vibrating sample magnetometer.
- [Korean]
- 자성 나노입자를 이용한 온열치료 기술
- J.H. Yu, D.W. Lee, Y.J. Kim, Y.H. Choa
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(4):309-314.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.4.309

- 409 View
- 2 Download
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


