Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- High-Temperature Steam Oxidation Behavior of Silicide- or Aluminide- Coated Mo and Nb Refractory Metals
- Woojin Lim, Je-Kyun Baek, JaeJoon Kim, Hyun Gil Kim, Ho Jin Ryu
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):546-555. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00381
- 1,484 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
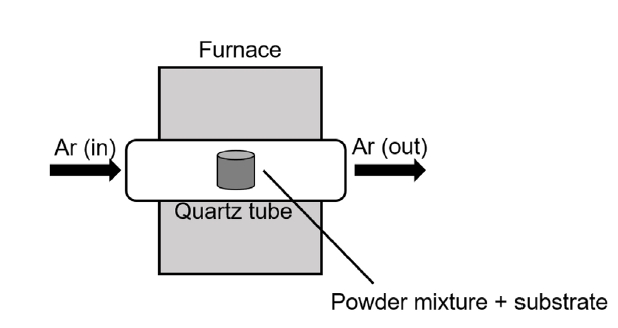
PDF - Refractory materials, such as molybdenum and niobium, are potential candidates for cladding material due to their high melting temperatures and desirable mechanical properties at higher temperatures than those of zirconium alloys. However, refractory materials have low resistance to oxidation at elevated temperatures. Therefore, this study examined silicide or aluminide surface coatings as protection against rapid oxidation of refractory materials at elevated temperatures for a potential accident-tolerant fuel cladding. Silicide or aluminide layers were formed on refractory metal substrates by using the pack cementation method. The steam oxidation behavior of both coated and uncoated samples was compared by thermogravimetric analysis at 1200°C. The weight changes of the coated samples were greatly reduced than those of uncoated samples. Microstructural analyses demonstrated that the silicide and aluminide layers were oxidized to form a protective surface oxide that prevented rapid oxidation of the refractory substrate at elevated temperatures.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


