Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Influence of Powder Size on Properties of Selectively Laser-Melted- AlSi10Mg Alloys
- Yeong Seong Eom, Dong Won Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Sang Sun Yang, Jungho Choe, Injoon Son, Ji Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):103-110. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.103

- 1,132 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum (Al) - based powders have attracted attention as key materials for 3D printing because of their excellent specific mechanical strength, formability, and durability. Although many studies on the fabrication of 3Dprinted Al-based alloys have been reported, the influence of the size of raw powder materials on the bulk samples processed by selective laser melting (SLM) has not been fully investigated. In this study, AlSi10Mg powders of 65 μm in average particle size, prepared by a gas atomizing process, are additively manufactured by using an SLM process. AlSi10Mg powders of 45 μm average size are also fabricated into bulk samples in order to compare their properties. The processing parameters of laser power and scan speed are optimized to achieve densified AlSi10Mg alloys. The Vickers hardness value of the bulk sample prepared from 45 μm-sized powders is somewhat higher than that of the 65 μm-sized powder. Such differences in hardness are analyzed because the reduction in melt pool size stems from the rapid melting and solidification of small powders, compared to those of coarse powders, during the SLM process. These results show that the size of the powder should be considered in order to achieve optimization of the SLM process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser Soldering Process Optimization of MEMS Probe of Probe Card for Semiconductor Wafer Test
Myeongin Kim, Won Sik Hong, Mi-Song Kim
Journal of Welding and Joining.2022; 40(3): 271. CrossRef - Investigation on Interfacial Microstructures of Stainless Steel/Inconel Bonded by Directed Energy Deposition of alloy Powders
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Soo-Ho Jung, Jihun Yu, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Chul Yong Sim, Seung Jun An
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 219. CrossRef
- Laser Soldering Process Optimization of MEMS Probe of Probe Card for Semiconductor Wafer Test
- [Korean]
- Microstructures and Characterization of Al-Si-Mg Alloy Processed by Selective Laser Melting with Post-Heat-treatment
- Gi Seung Lee, Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Byoung Kee Kim, Ji Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):138-145. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.138

- 1,528 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, Al-Si-Mg alloys are additively manufactured using a selective laser melting (SLM) process from AlSi10Mg powders prepared from a gas-atomization process. The processing parameters such as laser scan speed and laser power are investigated for 3D printing of Al-Si-Mg alloys. The laser scan speeds vary from 100 to 2000 mm/s at the laser power of 180 and 270W, respectively, to achieve optimized densification of the Al-Si-Mg alloy. It is observed that the relative density of the Al-Si-Mg alloy reaches a peak value of 99% at 1600 mm/s for 180W and at 2000 mm/s for 270W. The surface morphologies of the both Al-Si-Mg alloy samples at these conditions show significantly reduced porosities compared to those of other samples. The increase in hardness of as-built Al-Si-Mg alloy with increasing scan speed and laser power is analyzed due to high relative density. Furthermore, it was found that cooling conditions after the heat-treatment for homogenization results in the change of dispersion status of Si phases in the Al-Si matrix but also affects tensile behaviors of Al-Si-Mg alloys. These results indicate that combination between SLM processing parameters and post-heat treatment should be considered a key factor to achieve optimized Al-Si alloy performance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Dong Won Kim, Soo ho Jung, Jung Woo Nam, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Ji Hun Yu, Injoon Son
Powder Metallurgy.2021; 64(3): 198. CrossRef - Investigation on Interfacial Microstructures of Stainless Steel/Inconel Bonded by Directed Energy Deposition of alloy Powders
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Soo-Ho Jung, Jihun Yu, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Chul Yong Sim, Seung Jun An
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 219. CrossRef - Influence of Powder Size on Properties of Selectively Laser-Melted- AlSi10Mg Alloys
Yeong Seong Eom, Dong Won Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Sang Sun Yang, Jungho Choe, Injoon Son, Ji Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(2): 103. CrossRef
- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
- [English]
- Synthesis of Boron Nitride Nanotubes via inductively Coupled thermal Plasma process Catalyzed by Solid-state ammonium Chloride
- Mi Se Chang, Young Gyun Nam, Sangsun Yang, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji Hun Yu, Yong-Jin Kim, Jae Won Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):120-125. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.25.2.120
- 673 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
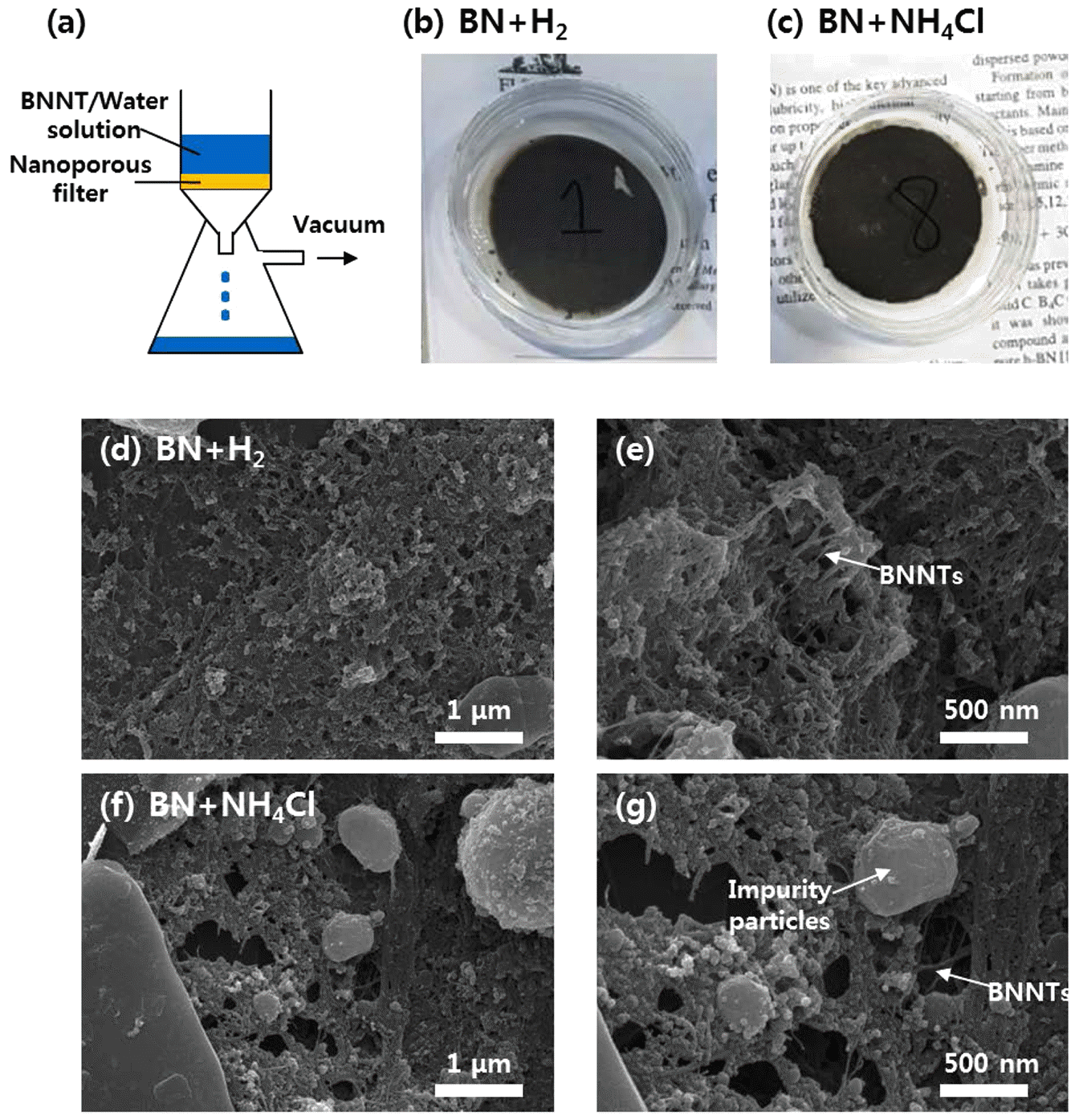
PDF Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) are receiving great attention because of their unusual material properties, such as high thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical resistance. However, high-throughput and highefficiency synthesis of BNNTs has been hindered due to the high boiling point of boron (~ 4000°C) and weak interaction between boron and nitrogen. Although, hydrogen-catalyzed plasma synthesis has shown potential for scalable synthesis of BNNTs, the direct use of H2 gas as a precursor material is not strongly recommended, as it is extremely flammable. In the present study, BNNTs have been synthesized using radio-frequency inductively coupled thermal plasma (RF-ITP) catalyzed by solid-state ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), a safe catalyst materials for BNNT synthesis. Similar to BNNTs synthesized from h-BN (hexagonal boron nitride) + H2, successful fabrication of BNNTs synthesized from h-BN+NH4Cl is confirmed by their sheet-like properties, FE-SEM images, and XRD analysis. In addition, improved dispersion properties in aqueous solution are found in BNNTs synthesized from h-BN +NH4Cl.
- [Korean]
- Study on Microstructures and Hardness of STS316L Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting
- Gi Hun Shin, Joon Phil Choi, Kyung Tae Kim, Byoung Kee Kim, Ji Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;24(3):210-215. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.210

- 957 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, STS316L powders prepared by gas atomization are used to manufacture bulk structures with dimensions of 10 × 10 × 10 mm3 using selective laser melting (SLM). The microstructures and hardness of the fabricated 316L stainless steel has been investigated with the laser beam overlap varied from 10% to 70%. The microstructures of the fabricated STS316L samples show a decrease in the balling and satellite of powders introducing defect in the bulk samples and the porosity caused by the gap between the molten metal pools disappearing as the overlap ratio increases, whereas a low overlap ratio results in significant balling and a large amount of isolated powders due to the increased gap between the melt pools. Furthermore, the highest value in Vickers hardness is obtained for the sample fabricated by 30% overlapped laser beams. These results show that the overlap ratio of laser beams in the SLM process should be considered as an important process parameter.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Dong Won Kim, Soo ho Jung, Jung Woo Nam, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Ji Hun Yu, Injoon Son
Powder Metallurgy.2021; 64(3): 198. CrossRef - Effect of laser remelting on the surface characteristics of 316L stainless steel fabricated via directed energy deposition
Seung Yeong Cho, Gwang Yong Shin, Do Sik Shim
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2021; 15: 5814. CrossRef - Investigation on Interfacial Microstructures of Stainless Steel/Inconel Bonded by Directed Energy Deposition of alloy Powders
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Soo-Ho Jung, Jihun Yu, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Chul Yong Sim, Seung Jun An
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 219. CrossRef - Influence of Powder Size on Properties of Selectively Laser-Melted- AlSi10Mg Alloys
Yeong Seong Eom, Dong Won Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Sang Sun Yang, Jungho Choe, Injoon Son, Ji Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(2): 103. CrossRef - Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of selective laser melted H13 tool steel under varying conditions
Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Junhyeok Park, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Im Doo Jung, Hyokyung Sung
Materials Characterization.2019; 155: 109817. CrossRef - Microstructures and Characterization of Al-Si-Mg Alloy Processed by Selective Laser Melting with Post-Heat-treatment
Gi Seung Lee, Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Byoung Kee Kim, Ji Hun Yu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 138. CrossRef - Correlation between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Additive Manufactured H13 Tool Steel
Woojin An, Junhyeok Park, Jungsub Lee, Jungho Choe, Im Doo Jung, Ji-Hun Yu, Sangshik Kim, Hyokyung Sung
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(11): 663. CrossRef
- Fabrication and mechanical properties of Al–Si-based alloys by selective laser melting process
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


