Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Improvement of the Mechanical Property and Corrosion Resistivity of the Ni-/Fe-based Hybrid Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel Spraying by Heat Treatment
- Jungjoon Kim, Yeonjoo Lee, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Jae-hun Kim, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(3):240-246. Published online June 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.3.240
- 875 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
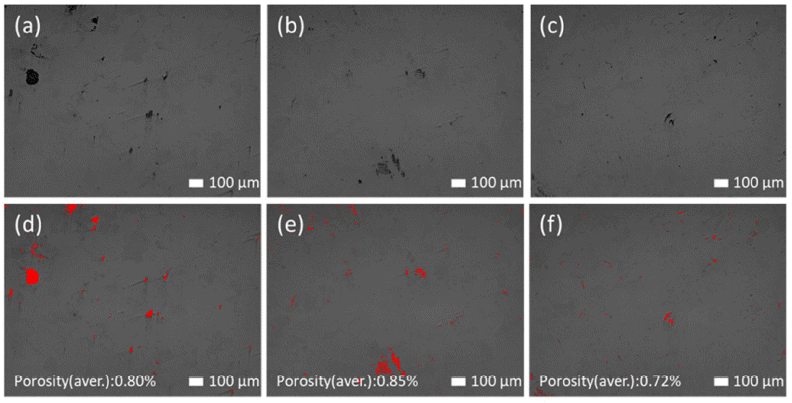
PDF Novel Ni- and Fe-based alloys are developed to impart improved mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The designed alloys are manufactured as a powder and deposited on a steel substrate using a high-velocity oxygen-fuel process. The coating layer demonstrates good corrosion resistance, and the thus-formed passive film is beneficial because of the Cr contained in the alloy system. Furthermore, during low-temperature heat treatment, factors that deteriorate the properties and which may arise during high-temperature heat treatment, are avoided. For the heattreated coating layers, the hardness increases by up to 32% and the corrosion resistance improves. The influence of the heat treatment is investigated through various methods and is considered to enhance the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the coating layer.
- [Korean]
- Development of Amorphous Iron Based Coating Layer using High-velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spraying
- Jungjoon Kim, Song-Yi Kim, Jong-Jae Lee, Seok-Jae Lee, Hyunkyu Lim, Min-Ha Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):483-490. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.483
- 681 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
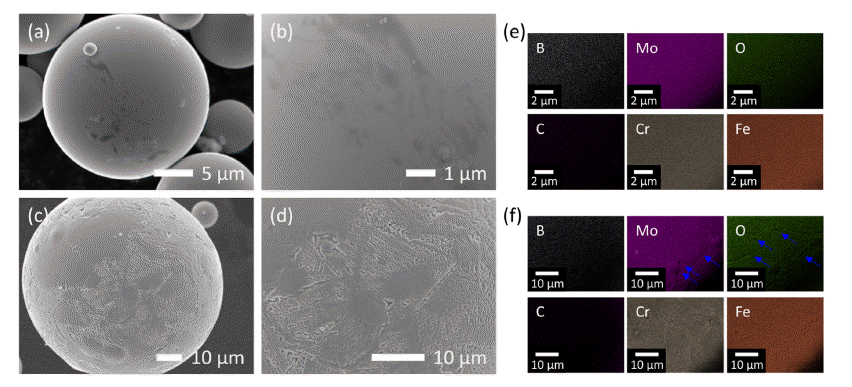
PDF A new Fe-Cr-Mo-B-C amorphous alloy is designed, which offers high mechanical strength, corrosion resistance as well as high glass-forming ability and its gas-atomized amorphous powder is deposited on an ASTM A213-T91 steel substrate using the high-velocity oxygen fuel (HVOF) process. The hybrid coating layer, consisting of nanocrystalline and amorphous phases, exhibits strong bonding features with the substrate, without revealing significant pore formation. By the coating process, it is possible to obtain a dense structure in which pores are hardly observed not only inside the coating layer but also at the interface between the coating layer and the substrate. The coating layer exhibits good adhesive strength as well as good wear resistance, making it suitable for coating layers for biomass applications.
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Characterization of Overlay Welding Layer using Fe-based Composite Powders
- Hong Min, Jong-Jae Lee, Jin Kyu Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):214-219. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.214
- 732 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
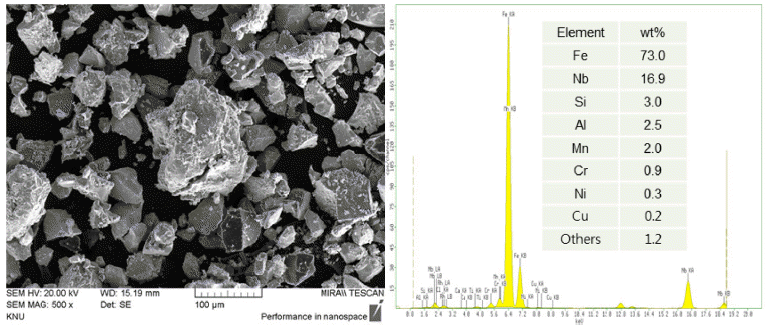
PDF In this study, the microstructure and characterization of an overlay welding layer using Fe-based composite powders are reported. The effects of the number of passes and composition of powders on the microstructure and mechanical properties are investigated in detail. The welding wire and powders are deposited twice on a stainless-steel rod using a laser overlay welding process. The microstructure and structural characterization are performed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The mechanical properties of the first and second overlay layers are analyzed through the micro-Vickers-hardness tester and abrasion wear tester. In the second overlay layer, the hardness and specific wear are approximately 840 Hv and 2.0 × 10−5 mm3/Nm, respectively. It is suggested that the increase of the volume fractions of (Cr,Fe)7C3 and NbC phases in the second welding layer enhances the hardness and wear resistance.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


