Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
- Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):302-307. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.302
- 1,094 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
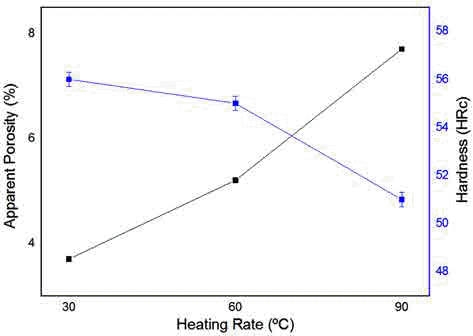
PDF In this study, Fe-Cu-C alloy is sintered by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The sintering conditions are 60 MPa pressure with heating rates of 30, 60 and 9°C/min to determine the influence of heating rate on the mechanical and microstructure properties of the sintered alloys. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the sintered Fe-Cu-C alloy is investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The temperature of shrinkage displacement is changed at 450°C with heating rates 30, 60, and 90°C/min. The temperature of the shrinkage displacement is finished at 650°C when heating rate 30°C/min, at 700°C when heating rate 60oC/min and at 800°C when heating rate 90oC/min. For the sintered alloy at heating rates of 30, 60, and 90oC/min, the apparent porosity is calculated to be 3.7%, 5.2%, and 7.7%, respectively. The hardness of the sintered alloys is investigated using Rockwell hardness measurements. The objective of this study is to investigate the densification behavior, porosity, and mechanical properties of the sintered Fe-Cu-C alloys depending on the heating rate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 126. CrossRef
- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Property Evaluation of Cu-Mn Compacts for Sputtering Target Application by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Method
- Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Jae-Won Lim, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):1-7. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.1
- 1,142 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
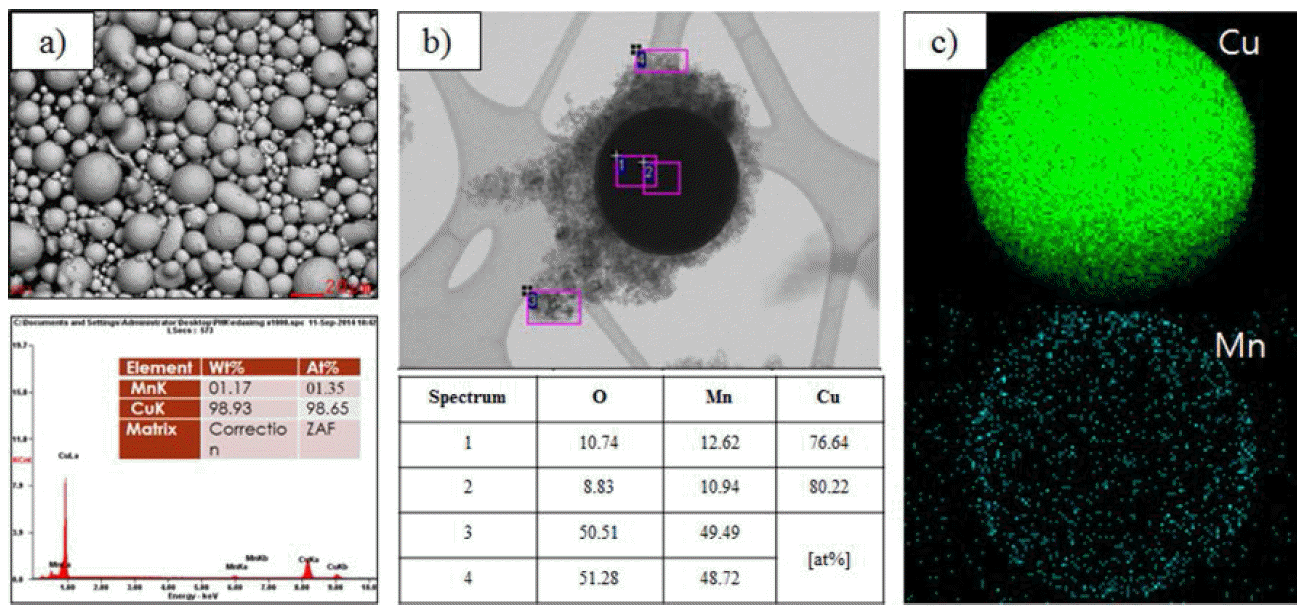
PDF Cu-Mn compacts are fabricated by the pulsed current activated sintering method (PCAS) for sputtering target application. For fabricating the compacts, optimized sintering conditions such as the temperature, pulse ratio, pressure, and heating rate are controlled during the sintering process. The final sintering temperature and heating rate required to fabricate the target materials having high density are 700°C and 80°C/min, respectively. The heating directly progresses up to 700°C with a 3 min holding time. The sputtering target materials having high relative density of 100% are fabricated by employing a uniaxial pressure of 60 MPa and a sintering temperature of 700°C without any significant change in the grain size. Also, the shrinkage displacement of the Cu-Mn target materials considerably increases with an increase in the pressure at sintering temperatures up to 700°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 302. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


