Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and analysis CdSe/ZnS quantum dot with a Core/shell Continuous Synthesis System Using a Microfluidic Reactor
- Myung Hwan Hong, So Young Joo, Lee-Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):132-136. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.132
- 1,932 View
- 10 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
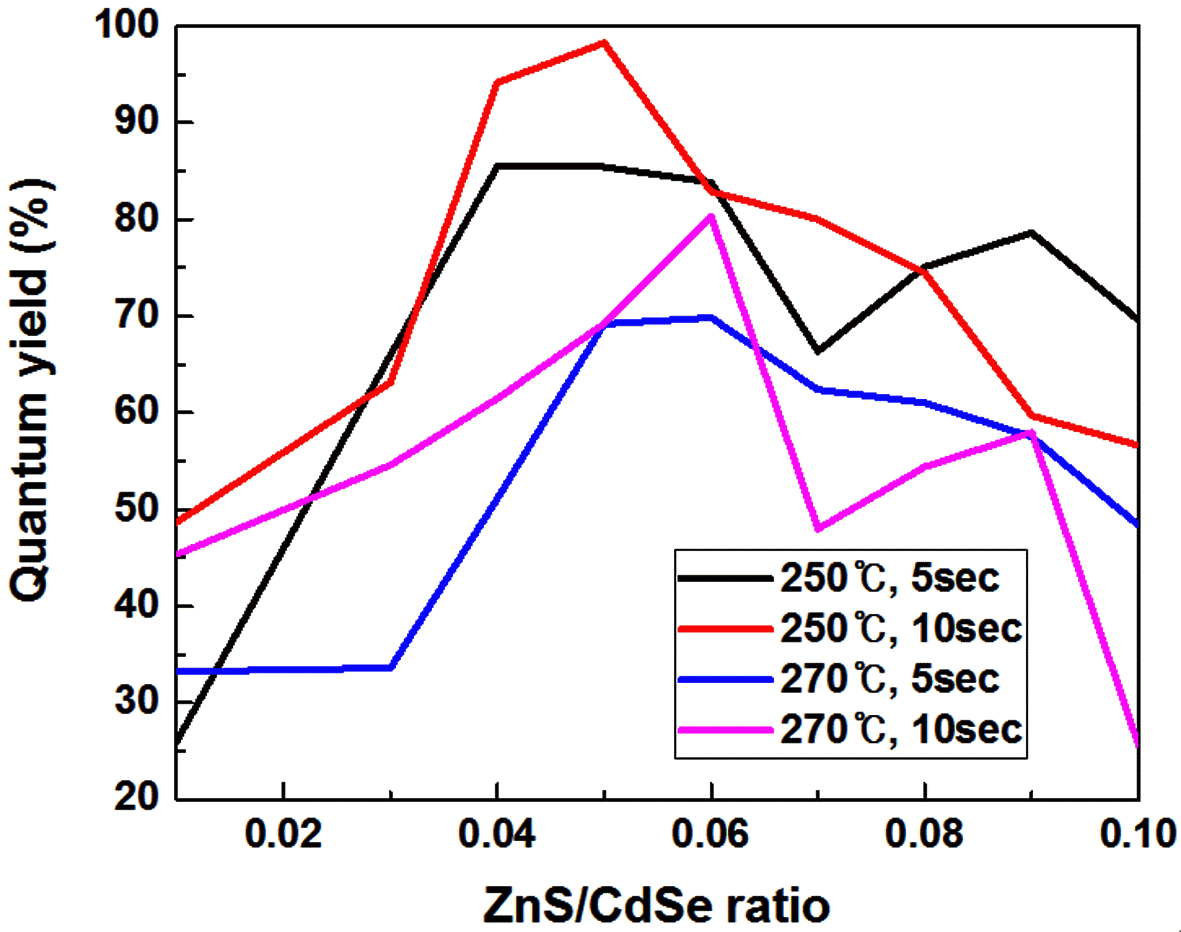
PDF Core/shell CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs) are synthesized by a microfluidic reactor-assisted continuous reactor system. Photoluminescence and absorbance of synthesized CdSe/ZnS core/shell QDs are investigated by fluorescence spectrophotometry and online UV-Vis spectrometry. Three reaction conditions, namely; the shell coating reaction temperature, the shell coating reaction time, and the ZnS/CdSe precursor volume ratio, are combined in the synthesis process. The quantum yield of the synthesized CdSe QDs is determined for each condition. CdSe/ZnS QDs with a higher quantum yield are obtained compared to the discontinuous microfluidic reactor synthesis system. The maximum quantum efficiency is 98.3% when the reaction temperature, reaction time, and ZnS/CdSe ratio are 270°C, 10 s, and 0.05, respectively. Obtained results indicate that a continuous synthesis of the Core/shell CdSe/ZnS QDs with a high quantum efficiency could be achieved by isolating the reaction from the external environment.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and analysis CdSe Quantum dot with a Microfluidic Reactor Using a Combinatorial Synthesis System
- Myung Hwan Hong, Duk-Hee Lee, Lee-Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Nam-Hoon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):143-148. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.143
- 881 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
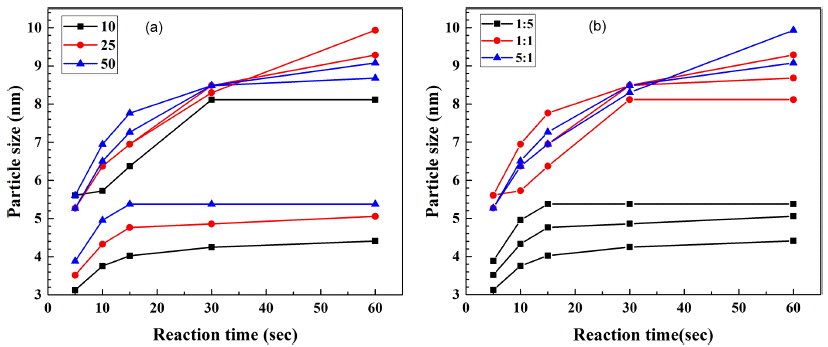
PDF A microfluidic reactor with computer-controlled programmable isocratic pumps and online detectors is employed as a combinatorial synthesis system to synthesize and analyze materials for fabricating CdSe quantum dots for various applications. Four reaction condition parameters, namely, the reaction temperature, reaction time, Cd/Se compositional ratio, and precursor concentration, are combined in synthesis condition sets, and the size of the synthesized CdSe quantum dots is determined for each condition. The average time corresponding to each reaction condition for obtaining the ultraviolet–visible absorbance and photoluminescence spectra is approximately 10 min. Using the data from the combinatorial synthesis system, the effects of the reaction conditions on the synthesized CdSe quantum dots are determined. Further, the data is used to determine the relationships between the reaction conditions and the CdSe particle size. This method should aid in determining and selecting the optimal conditions for synthesizing nanoparticles for diverse applications.
- [English]
- Materials Flow Analysis of Metallic Cobalt and Its Powder in Korea
- Hyun Seon Hong, Lee-Seung Kang, Hong-Yoon Kang, Han-Gil Suk
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):235-240. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.235

- 1,780 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The basis of the cobalt demand analysis by use was established via the investigation and analysis of the cobalt materials flow, and the overall cobalt metal material and parts industry structure in Korea was examined to determine the cobalt material flow. The markets of the cobalt material for machinery were studied, including their interrelations, via market and study trends, and relevant plans were examined. The results of the study indicated that the advanced core technology for advanced industry and technology-intensive industry development is required to structurally innovate the parts materials and basic materials industries and to upgrade the catch-up industry structure to the new frontier structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the potential for improving material utilization efficiency to secure lithium supply for China's battery supply chain
Xin Sun, Han Hao, Yong Geng, Zongwei Liu, Fuquan Zhao
Fundamental Research.2024; 4(1): 167. CrossRef - Trade structure and risk transmission in the international automotive Li-ion batteries trade
Xiaoqian Hu, Chao Wang, Xiangyu Zhu, Cuiyou Yao, Pezhman Ghadimi
Resources, Conservation and Recycling.2021; 170: 105591. CrossRef
- Exploring the potential for improving material utilization efficiency to secure lithium supply for China's battery supply chain
- [Korean]
- Optimization of Wet Reduction Processing for Nanosized Cobalt Powder
- Hyun-Seon Hong, Hang-Chul Jung, Geon-Hong Kim, Lee-Seung Kang, Han-Gil Suk
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(3):191-196.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.3.191

- 799 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nano-sized cobalt powder was fabricated by wet chemical reduction method at room temperature. The effects of various experimental variables on the overall properties of fabricated nano-sized cobalt powders have been investigated in detail, and amount of NaOH and reducing agent and dropping speed of reducing agent have been properly selected as experimental variables in the present research. Minitab program which could find optimized conditions was adopted as a statistic analysis. 3D Scatter-Plot and DOE (Design of Experiments) conditions for synthesis of nano-sized cobalt powder were well developed using Box-Behnken DOE method. Based on the results of the DOE process, reproducibility test were performed for nano-sized cobalt powder. Spherical nano-sized cobalt powders with an average size of 70-100 nm were successfully developed and crystalline peaks for the HCP and FCC structure were observed without second phase such as Co(OH)_2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preparation of Spherical Cobalt Fine Powders by New Liquid Reduction Method
Dae Weon Kim, Ji-Hoon Kim, Yo-Han Choi, Hee Lack Choi, Jin-Ho Yoon
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.1970; 22(4): 260. CrossRef
- Preparation of Spherical Cobalt Fine Powders by New Liquid Reduction Method
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Li2MnSiO4 for Lithium Ion Battery Prepared by Amorphous Silica Precusor
- Yun-Ho Jin, Kun-Jae Lee, Lee-Seung Kang, Hang-Chul Jung, Hyun-Seon Hong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(3):210-214.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.3.210

- 646 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mass production-capable Li_2MnSiO_4 powder was synthesized for use as cathode material in state-of-the-art lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are main powder sources for high tech-end digital electronic equipments and electric vehicles in the near future and they must possess high specific capacity and durable charge-discharge characteristics. Amorphous silicone was quite superior to crystalline one as starting material to fabricate silicone oxide with high reactivity between precursors of sol-gel type reaction intermediates. The amorphous silicone starting material also has beneficial effect of efficiently controlling secondary phases, most notably Li_xSiO_x. Lastly, carbon was coated on Li_2MnSiO_4 powders by using sucrose to afford some improved electrical conductivity. The carbon-coated Li_2MnSiO_4 cathode material was further characterized using SEM, XRD, and galvanostatic charge/discharge test method for morphological and electrochemical examinations. Coin cell was subject to 1.5-4.8 V at C/20, where 74 mAh/g was observed during primary discharge cycle.
- [Korean]
- Preparation of the Nano Cobalt Powder by Wet Chemical Reduction Method
- Hyun-Seon Hong, Young-Dae Ko, Lee-Seung Kang, Geon-Hong Kim, Hang-Chul Jung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(3):244-249.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.3.244

- 839 View
- 7 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Spherical nanosized cobalt powder with an average size of 150-400 nm was successfully prepared at room temperature from cobalt sulfate heptahydrate (CoSO_4cdot7H_2O). Wet chemical reduction method was adopted to synthesize nano cobalt powder and hypophosphorous acid (H_3PO_2) was used as reduction agent. Both the HCP and the FCC Co phase were developed while CoSO_4cdot7H_2O concentration ranged from 0.7 M to 1.1 M. Secondary phase such as Co(OH)_2 and CO_3O_4 were also observed. Peaks for the crystalline Co phase having HCP and FCC structure crystallized as increasing the concentration of H_3PO_2, indicating that the amount of reduction agent was enough to reduce Co(OH)_2. Consequently, a homogeneous Co phase could be developed without second phase when the H_3PO_2/CoSO_4cdot7H_2O ratio exceeded 7.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First-principles calculations to investigate electrochemical performance, storage mechanism and magnetocaloric effect of LiFeBO3 for lithium-ion batteries and magnetic refrigerants
Othmane Mennaoui, Rachid Masrour, Ling Xu, El Kebir Hlil
Ionics.2024; 30(5): 2537. CrossRef - Spark plasma sintering of WC–Co tool materials prepared with emphasis on WC core–Co shell structure development
Sungkyu Lee, Hyun Seon Hong, Hyo-Seob Kim, Soon-Jik Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2015; 53: 41. CrossRef - Coating of Cobalt Over Tungsten Carbide Powder by Wet Chemical Reduction Method
Hyun-Seon Hong, Jin-Ho Yoon
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(2): 93. CrossRef - Optimization of Wet Reduction Processing for Nanosized Cobalt Powder
Hyun-Seon Hong, Hang-Chul Jung, Geon-Hong Kim, Lee-Seung Kang, Han-Gil Suk
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(3): 191. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of CoFe2O4/SiO2using Cobalt Precursors from Recycling Waste Cemented Carbide
Ri Yu, Jae-Hwan Pee, Yoo-Jin Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2011; 48(5): 454. CrossRef - Preparation of Spherical Cobalt Fine Powders by New Liquid Reduction Method
Dae Weon Kim, Ji-Hoon Kim, Yo-Han Choi, Hee Lack Choi, Jin-Ho Yoon
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.1970; 22(4): 260. CrossRef
- First-principles calculations to investigate electrochemical performance, storage mechanism and magnetocaloric effect of LiFeBO3 for lithium-ion batteries and magnetic refrigerants
- [Korean]
- Research and Development Status of Low-Cost Fe-based Cathode Materials for Lithium Secondary Batteries
- Hyun-Seon Hong, Young-Dae Ko, Lee-Seung Kang, Hang-Chul Jung, Geon-Hong Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(2):196-203.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.2.196

- 738 View
- 0 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Study of storage mechanism and the electrochemical performance of
LiMnBO
3
for lithium‐ion batteries
Othmane Mennaoui, Rachid Masrour, Abderrahim Jabar, El Kebir Hlil
International Journal of Energy Research.2022; 46(14): 19875. CrossRef - Solvent Extraction of Co, Ni and Mn from NCM Sulfate Leaching Solution of Li(NCM)O2 Secondary Battery Scraps
Hyun Seon Hong, Dae Weon Kim, Hee Lack Choi, Sung-Soo Ryu
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1011. CrossRef - Synthesis and characterization of LiMnBO3 cathode material for lithium ion batteries
Kun-Jae Lee, Lee-Seung Kang, Sunghyun Uhm, Jae Sik Yoon, Dong-Wan Kim, Hyun Seon Hong
Current Applied Physics.2013; 13(7): 1440. CrossRef
-
Study of storage mechanism and the electrochemical performance of
LiMnBO
3
for lithium‐ion batteries
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


