Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of the Multi-layered SnO Nanoparticles and Enhanced Performance of Lithium-Ion Batteries by Heat treatment
- So Yi Lee, Yoon Myung, Kyu-Tae Lee, Jaewon Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):455-461. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.455

- 1,676 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, multilayered SnO nanoparticles are prepared using oleylamine as a surfactant at 165°C. The physical and chemical properties of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Interestingly, when the multilayered SnO nanoparticles are heated at 400°C under argon for 2 h, they become more efficient anode materials, maintaining their morphology. Heat treatment of the multilayered SnO nanoparticles results in enhanced discharge capacities of up to 584 mAh/g in 70 cycles and cycle stability. These materials exhibit better coulombic efficiencies. Therefore, we believe that the heat treatment of multilayered SnO nanoparticles is a suitable approach to enable their application as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and electrochemical properties of multi-layered SnO/rGO composite as anode materials for sodium ion batteries
So Yi Lee, Honggyu Seong, Geongil Kim, Youngho Jin, Joon Ha Moon, Wonbin Nam, Sung Kuk Kim, MinHo Yang, Jaewon Choi
Applied Surface Science.2023; 612: 155859. CrossRef
- Synthesis and electrochemical properties of multi-layered SnO/rGO composite as anode materials for sodium ion batteries
- [Korean]
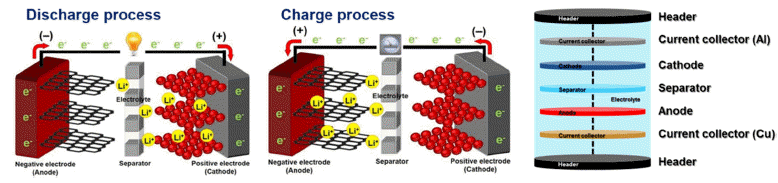
- Research Trends of Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries used in Electric Vehicles
- Dong-Yo Shin, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):58-69. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.58
- 987 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High performance lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have attracted considerable attention as essential energy sources for high-technology electrical devices such as electrical vehicles, unmanned drones, uninterruptible power supply, and artificial intelligence robots because of their high energy density (150-250 Wh/kg), long lifetime (> 500 cycles), low toxicity, and low memory effects. Of the high-performance LIB components, cathode materials have a significant effect on the capacity, lifetime, energy density, power density, and operating conditions of high-performance LIBs. This is because cathode materials have limitations with respect to a lower specific capacity and cycling stability as compared to anode materials. In addition, cathode materials present difficulties when used with LIBs in electric vehicles because of their poor rate performance. Therefore, this study summarizes the structural and electrochemical properties of cathode materials for LIBs used in electric vehicles. In addition, we consider unique strategies to improve their structural and electrochemical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Estimation of Representative Mechanical Property of Porous Electrode for Secondary Batteries with Homogenization Method
Changmin Pyo, Jaewoong Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers.2022; 21(9): 85. CrossRef
- Estimation of Representative Mechanical Property of Porous Electrode for Secondary Batteries with Homogenization Method
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


