Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Photocatalytic Properties of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by Electrodeposition Method
- Kwang-Mo Kang, Ji-Hye Jeong, Ga-In Lee, Jae-Min Im, Hyun-Jeong Cheon, Deok-Hyeon Kim, Yoon-Chae Nah
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):40-44. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.40
- 813 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
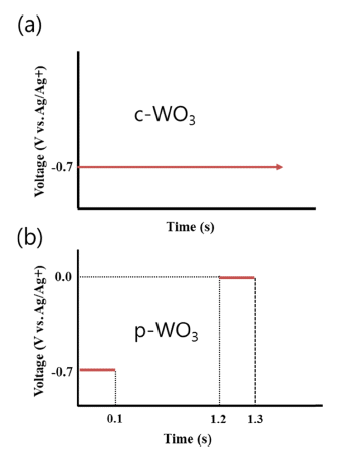
PDF Tungsten trioxide (WO3) is a promising candidate as a photocatalyst because of its outstanding electrical and optical properties. In this study, we prepare WO3 thin films by electrodeposition and characterize the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using these films. Depending on the voltage conditions (static and pulse), compact and porous WO3 films are fabricated on a transparent ITO/glass substrate. The morphology and crystal structure of electrodeposited WO3 thin films are investigated by scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and X-ray diffraction. An application of static voltage during electrodeposition yields a compact layer of WO3, whereas a highly porous morphology with nanoflakes is produced by a pulse voltage process. Compared to the compact film, the porous WO3 thin film shows better photocatalytic activities. Furthermore, a much higher reaction rate of degradation of methylene blue can be achieved after post-annealing of WO3 thin films.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advanced IGZO Phototransistor Arrays: Enhancing Visible Light Detection Through Selectively Electrohydrodynamic Jet‐Printed Photocatalytic Layer Formation
Jong Bin An, Byung Ha Kang, Sujin Jung, Kunho Moon, Jusung Chung, Seok Min Hong, Kyungho Park, Jong Hyuk Ahn, Hyun Jae Kim
Advanced Functional Materials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advanced IGZO Phototransistor Arrays: Enhancing Visible Light Detection Through Selectively Electrohydrodynamic Jet‐Printed Photocatalytic Layer Formation
- [Korean]
- Preparation and Characterization of Visible Light-Sensitive N-doped TiO2 Using a Sol-gel Method
- NaRi Lee, Ri Yu, Tae Kwan Kim, Jae-Hwan Pee, YooJin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):477-482. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.477

- 1,185 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide (N-doped TiO2) is attracting continuously increasing attention as a material for environmental photocatalysis. The N-atoms can occupy both interstitial and substitutional positions in the solid, with some evidence of a preference for interstitial sites. In this study, N-doped TiO2 is prepared by the sol–gel method using NH4OH and NH4Cl as N ion doping agents, and the physical and photocatalytic properties with changes in the synthesis temperature and amount of agent are analyzed. The photocatalytic activities of the N-doped TiO2 samples are evaluated based on the decomposition of methylene blue (MB) under visible-light irradiation. The addition of 5 wt% NH4Cl produces the best physical properties. As per the UV-vis analysis results, the N-doped TiO2 exhibits a higher visible-light activity than the undoped TiO2. The wavelength of the N-doped TiO2 shifts to the visible-light region up to 412 nm. In addition, this sample shows MB removal of approximately 81%, with the whiteness increasing to +97 when the synthesis temperature is 600oC. The coloration and phase structure of the N-doped TiO2 are characterized in detail using UV-vis, CIE
Lab color parameter measurements, and powder X-ray diffraction (XRD).
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


