Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Critical Review
- [English]
- Trends in Materials Modeling and Computation for Metal Additive Manufacturing
- Seoyeon Jeon, Hyunjoo Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):213-219. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00150

- 2,683 View
- 74 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a process that fabricates products by manufacturing materials according to a three-dimensional model. It has recently gained attention due to its environmental advantages, including reduced energy consumption and high material utilization rates. However, controlling defects such as melting issues and residual stress, which can occur during metal additive manufacturing, poses a challenge. The trial-and-error verification of these defects is both time-consuming and costly. Consequently, efforts have been made to develop phenomenological models that understand the influence of process variables on defects, and mechanical/electrical/thermal properties of geometrically complex products. This paper introduces modeling techniques that can simulate the powder additive manufacturing process. The focus is on representative metal additive manufacturing processes such as Powder Bed Fusion (PBF), Direct Energy Deposition (DED), and Binder Jetting (BJ) method. To calculate thermal-stress history and the resulting deformations, modeling techniques based on Finite Element Method (FEM) are generally utilized. For simulating the movements and packing behavior of powders during powder classification, modeling techniques based on Discrete Element Method (DEM) are employed. Additionally, to simulate sintering and microstructural changes, techniques such as Monte Carlo (MC), Molecular Dynamics (MD), and Phase Field Modeling (PFM) are predominantly used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Research Article
- [English]
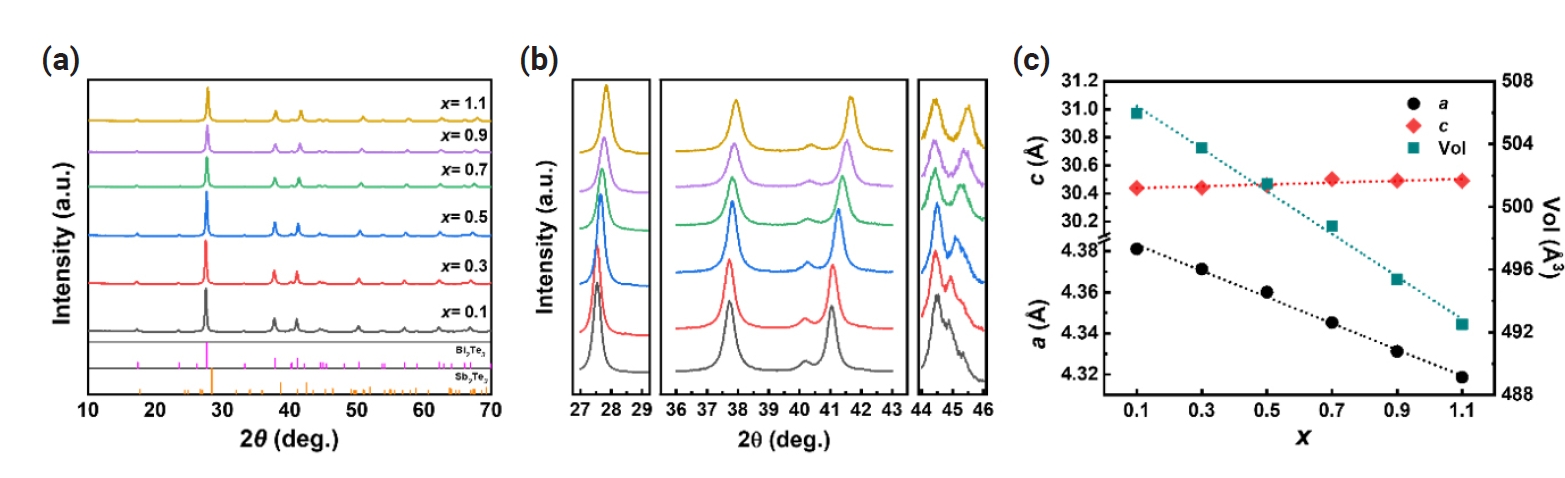
- Exploring Thermoelectric Transport Properties and Band Parameters of n-Type Bi2-xSbxTe3 Compounds Using the Single Parabolic Band Model
- Linh Ba Vu, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son, Seungki Jo
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):119-125. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00045
- 3,179 View
- 81 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The n-type Bi2-xSbxTe3 compounds have been of great interest due to its potential to achieve a high thermoelectric performance, comparable to that of p-type Bi2-xSbxTe3. However, a comprehensive understanding on the thermoelectric properties remains lacking. Here, we investigate the thermoelectric transport properties and band characteristics of n-type Bi2-xSbxTe3 (x = 0.1 – 1.1) based on experimental and theoretical considerations. We find that the higher power factor at lower Sb content results from the optimized balance between the density of state effective mass and nondegenerate mobility. Additionally, a higher carrier concentration at lower x suppresses bipolar conduction, thereby reducing thermal conductivity at elevated temperatures. Consequently, the highest zT of ~ 0.5 is observed at 450 K for x = 0.1 and, according to the single parabolic band model, it could be further improved by ~70 % through carrier concentration tuning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
Yeon-Joo Lee, Pil-Ryung Cha, Hyoung-Seop Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(1): 144. CrossRef - Enhanced energy harvesting performance of bendable thermoelectric generator enabled by trapezoidal-shaped legs
Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Cheol Min Kim, Hyejeong Choi, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Journal of Power Sources.2025; 631: 236254. CrossRef - Flexible hybrid thermoelectric films made of bismuth telluride-PEDOT:PSS composites enabled by freezing-thawing process and simple chemical treatment
Cheol Min Kim, Seoha Kim, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Bitna Bae, Momanyi Amos Okirigiti, Gwang Hyun Kim, Hyeon Jun Park, Haksu Jang, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kwi-Il Park
Materials Today Chemistry.2025; 44: 102532. CrossRef - Enhanced Electrical Properties of 3D Printed Bi2Te3-Based Thermoelectric Materials via Hot Isostatic Pressing
Seungki Jo
Ceramist.2025; 28(1): 126. CrossRef - Hot isostatic pressing-driven fine-tuning of electrical properties in p- and n-type (Bi,Sb)2Te3 thermoelectric materials
Seungki Jo, Jeong Min Park, Linh Ba Vu, Haeum Park, Soo Ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Jong Min Park, Jungho Choe, Kyung Tae Kim
Ceramics International.2025; 51(26): 51107. CrossRef - Compensation of increased carrier concentration and thermal conductivity in enhancing thermoelectric efficiency in Sn-doped Sb-In-Te alloys
Yunjae Kim, Seungwoo Ha, Gyujin Chang, Gwan Hyeong Lee, Jaewoo Park, Chanwoo Ju, Se Yun Kim, TaeWan Kim, Sang-il Kim
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Review of “Integrated Computer-Aided Process Engineering Session in the 17th International Symposium on Novel and Nano Materials (ISNNM, 14–18 November 2022)”
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


