Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Critical Review
- [Korean]
- Research Trends in Magneto-Mechano-Electric (MME) Energy Harvesting Devices
- So Ie Jeong, Geon-Tae Hwang
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):529-541. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00493
- 477 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
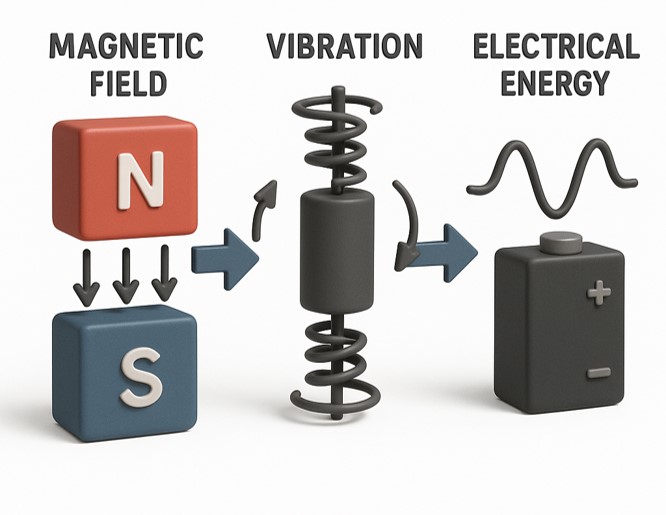
PDF - Magneto-mechano-electric (MME) energy harvesters have emerged as a promising solution for maintenance-free power generation in rapidly expanding Internet of Things (IoT) environments, where replacing or wiring batteries is impractical. MME devices convert weak alternating magnetic fields, ubiquitous around power infrastructures, into useful electrical energy through sequential magnetic, mechanical, and electrical transduction processes. This review summarizes recent advances across triboelectric-, piezoelectric-, and hybrid MME architectures. Triboelectric MME generators employing nano-engineered polymer surfaces, flash-induced surface modification, and nanoscale pattern replication demonstrate low-cost fabrication routes while achieving significantly enhanced voltage and current outputs. Piezoelectric MME systems based on Mn-doped PMN-PZT single crystals highlight strategies for improving mechanical quality factors and resonance-driven power generation. Further, hybrid MME designs that integrate piezoelectric and electromagnetic induction mechanisms enable high-power outputs exceeding tens of milliwatts, sufficient to operate multifunctional IoT platforms and charge practical energy-storage devices. Collectively, these studies illustrate a transition of MME harvesting technologies from laboratory concepts to application-ready self-powered systems. Future opportunities lie in broadband resonance design, modular harvester integration, advanced power management, and multi-source hybridization for robust long-term operation in real environments.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


