Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
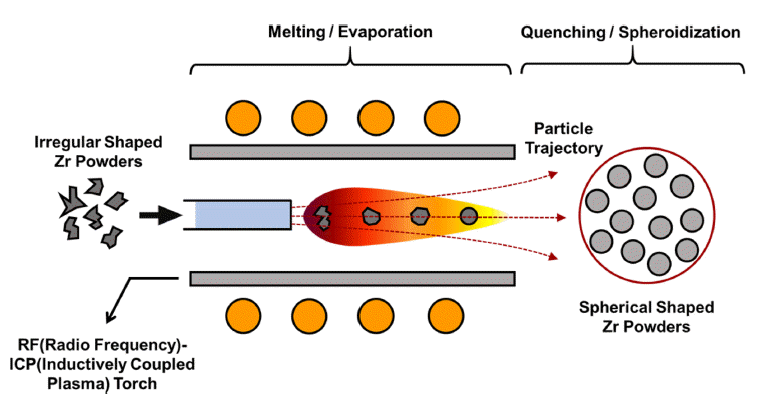
- Property of the Spheroidized Zr Powder by Radio Frequency Plasma Treatment
- Yukyeong Lee, Mi-Sun Choi, Eon Byeong Park, Jeong Seok Oh, Taehyun Nam, Jung Gi Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):97-102. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.97
- 855 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Powder quality, including high flowability and spherical shape, determines the properties of additively manufactured products. Therefore, the cheap production of high-quality powders is critical in additive manufacturing. Radio frequency plasma treatment is an effective method to fabricate spherical powders by melting the surface of irregularly shaped powders; in the present work, mechanically milled Zr powders are spheroidized by radio frequency plasma treatment and their properties are compared with those of commercial Zircaloy-2 alloy powder. Spherical Zr particles are successfully fabricated by plasma treatment, although their flowability and impurity contents are poorer than those of the commercial Zircaloy-2 alloy powder. This result shows that radio-frequency plasma treatment with mechanically milled powders requires further research and development for manufacturing low-cost powders for additive manufacturing.
- [Korean]
- Spheroidization of Enamel Powders by Radio Frequency Plasma Treatment and Application to Additive Manufacturing
- Ki-Bong Kim, Dong-Yeol Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Jungho Choe, Ji-Na Kwak, Woo-Hyung Jung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):388-393. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.388

- 762 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The enamel powders used traditionally in Korea are produced by a ball-milling process. Because of their irregular shapes, enamel powders exhibit poor flowability. Therefore, polygonal enamel powders are only used for handmade cloisonné crafts. In order to industrialize or automate the process of cloisonné crafts, it is essential to control the size and shape of the powder. In this study, the flowability of the enamel powders was improved using the spheroidization process, which employs the RF plasma treatment. In addition, a simple grid structure and logo were successfully produced using the additive manufacturing process (powder bed fusion), which utilizes spherical enamel powders. The additive manufacturing technology of spherical enamel powders is expected to be widely used in the field of cloisonné crafting in the future.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


