Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Electrochemical Behavior of Well-dispersed Catalysts on Ruthenium Oxide Nanofiber Supports
- Geon-Hyoung An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(2):96-101. Published online April 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.2.96
- 912 View
- 3 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
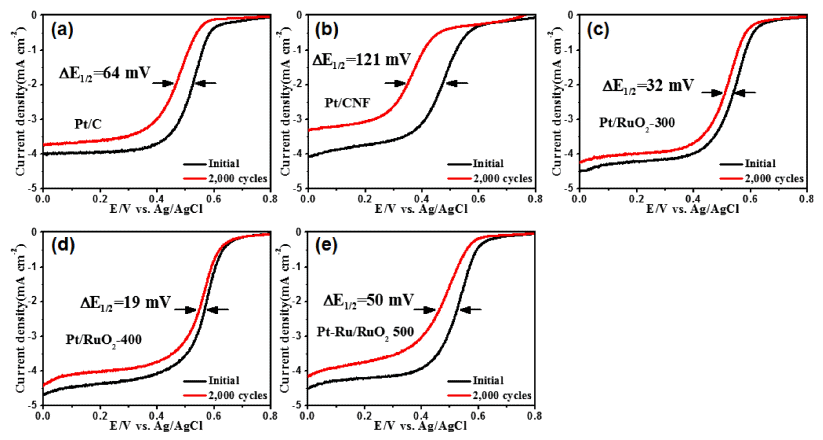
PDF Well-dispersed platinum catalysts on ruthenium oxide nanofiber supports are fabricated using electrospinning, post-calcination, and reduction methods. To obtain the well-dispersed platinum catalysts, the surface of the nanofiber supports is modified using post-calcination. The structures, morphologies, crystal structures, chemical bonding energies, and electrochemical performance of the catalysts are investigated. The optimized catalysts show well-dispersed platinum nanoparticles (1-2 nm) on the nanofiber supports as well as a uniform network structure. In particular, the well-dispersed platinum catalysts on the ruthenium oxide nanofiber supports display excellent catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reactions with a half-wave potential (E1/2) of 0.57 V and outstanding long-term stability after 2000 cycles, resulting in a lower E1/2 potential degradation of 19 mV. The enhanced electrochemical performance for oxygen reduction reactions results from the well-dispersed platinum catalysts and unique nanofiber supports.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Porous Electrodes for Zinc-Ion Supercapacitors with Improved Energy Storage Performance
Geon-Hyoung An
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2019; 29(8): 505. CrossRef - Surface tailoring of zinc electrodes for energy storage devices with high-energy densities and long cycle life
Geon-Hyoung An, SeungNam Cha, Jung Inn Sohn
Applied Surface Science.2019; 467-468: 1157. CrossRef - Synthesis of Nitrogen Doped Protein Based Carbon as Pt Catalysts Supports for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Young-geun Lee, Geon-hyeong An, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2018; 28(3): 182. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Porous Electrodes for Zinc-Ion Supercapacitors with Improved Energy Storage Performance
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Pt@TiO2 Nano-composite via Photochemical Reduction Method
- Ji Young Kim, Jong Min Byun, Jin Woo Kim, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):119-123. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.119
- 827 View
- 3 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Pt has been widely used as catalyst for fuel cell and exhausted gas clean systems due to its high catalytic activity. Recently, there have been researches on fabricating composite materials of Pt as a method of reducing the amount of Pt due to its high price. One of the approaches for saving Pt used as catalyst is a core shell structure consisting of Pt layer on the core of the non-noble metal. In this study, the synthesis of Pt shell was conducted on the surface of TiO2 particle, a non-noble material, by applying ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Anatase TiO2 particles with the average size of 20~30 nm were immersed in the ethanol dissolved with Pt precursor of H2PtCl6∙6H2O and exposed to UV irradiation with the wavelength of 365 nm. It was confirmed that Pt nano-particles were formed on the surface of TiO2 particles by photochemical reduction of Pt ion from the solution. The morphology of the synthesized Pt@TiO2 nano-composite was examined by TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
Jong Min Byun, Chun Woong Park, Young In Kim, Young Do Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(3): 257. CrossRef - Synthesis and Photo Catalytic Activity of 10 wt%, 20 wt%Li-TiO2 Composite Powders
Hyeong-Chul Kim, Jae-Kil Han
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 33. CrossRef
- Photocatalytic activity of rutile TiO2 powders coupled with anatase TiO2 nanoparticles using surfactant
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


