Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [Korean]
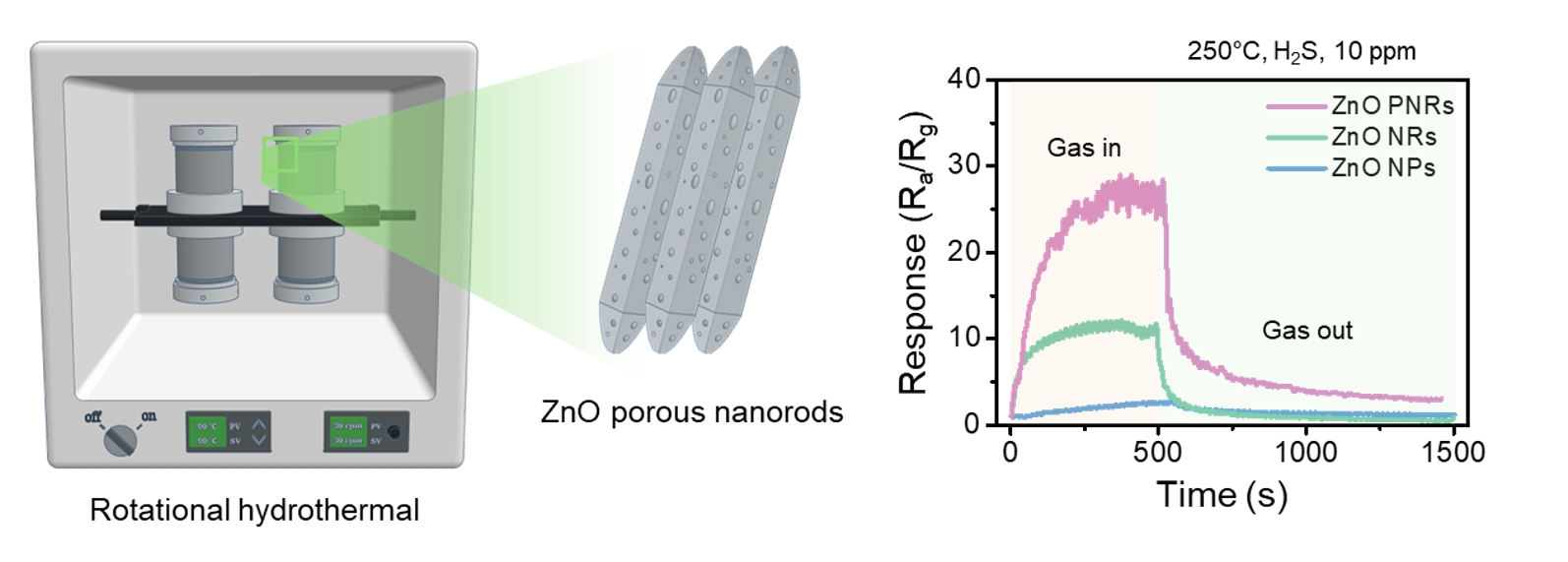
- Enhanced H2S Gas Sensing Using ZnO Porous Nanorod Synthesized via a Rotational Hydrothermal Method
- Jimyeong Park, Changyu Kim, Minseo Kim, Jiyeon Shin, Jae-Hyoung Lee, Myung Sik Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):406-415. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00262
- 414 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, ZnO porous nanorods were synthesised using a rotational hydrothermal process, and their performance as hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas sensors was analysed. Compared to commercial ZnO nanoparticles and conventionally hydrothermally synthesised ZnO nanorods, the ZnO porous nanorods exhibited a more uniform structure and improved crystal growth in the (002) plane, with surfaces rich in porosity and oxygen vacancies. These structural and chemical characteristics significantly improved the sensitivity toward H2S, showing high detection performance at 250°C across various concentrations of H2S gas. Additionally, the sensor demonstrated excellent selectivity against other gases such as C2H5OH, C6H6, C7H8, and NH3. This study indicated that the rotational hydrothermal process is an effective method for developing high-performance ZnO-based gas sensors and suggests its applicability to other metal oxide materials.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


