Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Parametric Study of Selective Laser Melting Using Ti-6Al-4V Powder Bed for Concurrent Control of Volumetric Density and Surface Roughness
- Jeongmin Woo, Ji-Yoon Kim, Yongho Sohn, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(5):410-416. Published online October 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.5.410
- 1,303 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
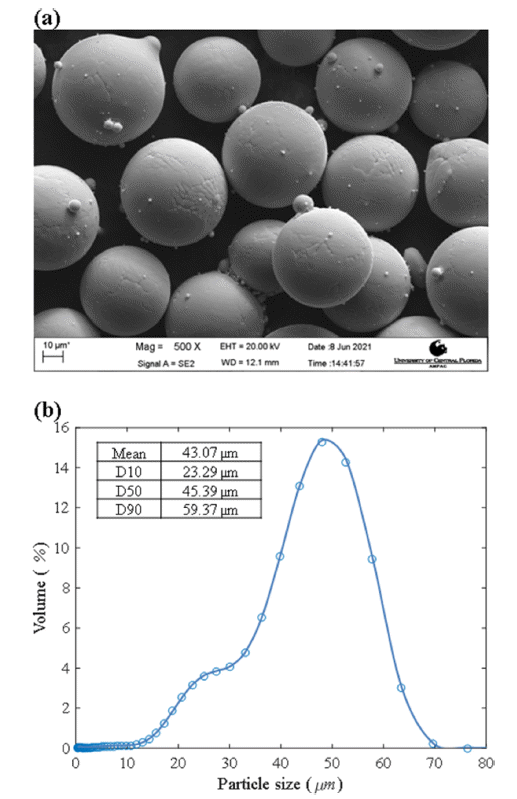
PDF Ti-6Al-4V alloy has a wide range of applications, ranging from turbine blades that require smooth surfaces for aerodynamic purposes to biomedical implants, where a certain surface roughness promotes biomedical compatibility. Therefore, it would be advantageous if the high volumetric density is maintained while controlling the surface roughness during the LPBF of Ti-6Al-4V. In this study, the volumetric energy density is varied by independently changing the laser power and scan speed to document the changes in the relative sample density and surface roughness. The results where the energy density is similar but the process parameters are different are compared. For comparable energy density but higher laser power and scan speed, the relative density remained similar at approximately 99%. However, the surface roughness varies, and the maximum increase rate is approximately 172%. To investigate the cause of the increased surface roughness, a nonlinear finite element heat transfer analysis is performed to compare the maximum temperature, cooling rate, and lifetime of the melt pool with different process parameters.
- [Korean]
- Electrospray and Thermal Treatment Process for Enhancing Surface Roughness of Fecralloy Coating Layer on a Large Sized Substrate
- Hye Moon Lee, Hye Young Koo, Sangsun Yang, Dahee Park, Sooho Jung, Jung-Yeul Yun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):46-52. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.46
- 385 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
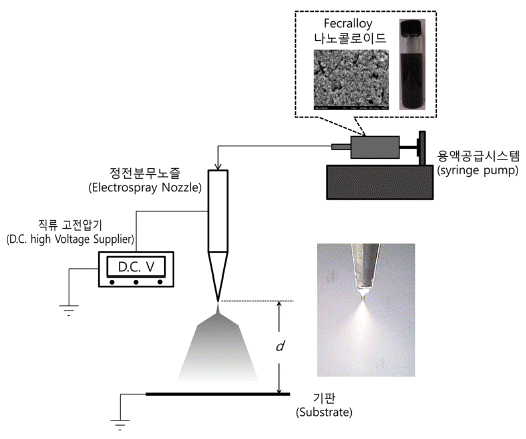
PDF Fecralloy coating layer with large surface area is suitable for use as a filter media for efficient removal of hot gaseous pollutants exhausted from combustion processes. For uniform preparation of a Fecralloy coating layer with large surface area and strong adhesion to substrate, electrospray coating and thermal treatment processes are experimentally optimized in this study. A nano-colloidal solution with 0.05 wt% Fecralloy nanoparticles is successfully prepared. Optimized electrospraying conditions are experimentally discovered to prepare a uniform coating layer of Fecralloy nanocolloidal solution on a substrate. Drying the electrospray coated Fecralloy nano-colloidal solution layer at 120°C and subsequent heating at 600°C are the best post-treatment for enhancing the adhesion force and surface roughness of the Fecralloy coating layer on a substrate. An electrospray coating system, consisting of several multi-groove nozzles, is also experimentally confirmed as a reasonable device for uniform coating of Fecralloy nano-colloid on a large area substrate.
- [Korean]
- Study on Surface Modification of Ti Substrate to Improve the Dispersion of Catalytic Metals on Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes
- Seoung Yeol Kwak, Ho Gyu Kim, Jong Min Byun, Ju Hyuk Park, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.28
- 894 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
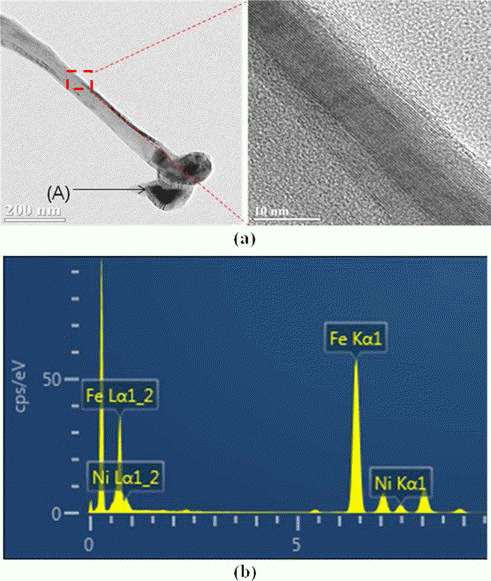
PDF This paper describes the surface modification effect of a Ti substrate for improved dispersibility of the catalytic metal. Etching of a pure titanium substrate was conducted in 50% H2SO4, 50°C for 1 h-12 h to observe the surface roughness as a function of the etching time. At 1 h, the grain boundaries were obvious and the crystal grains were distinguishable. The grain surface showed micro-porosities owing to the formation of micro-pits less than 1 μm in diameter. The depths of the grain boundary and micro-pits appear to increase with etching time. After synthesizing the catalytic metal and growing the carbon nano tube (CNT) on Ti substrate with varying surface roughness, the distribution trends of the catalytic metal and grown CNT on Ti substrate are discussed from a micro-structural perspective.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Solvent induced surface modifications on hydrogen storage performance of ZnO nanoparticle decorated MWCNTs
Madhavi Konni, Anima S. Dadhich, Saratchandra Babu Mukkamala
Sustainable Energy & Fuels.2018; 2(2): 466. CrossRef - Influence of nickel nanoparticles on hydrogen storage behaviors of MWCNTs
Ye-Ji Han, Soo-Jin Park
Applied Surface Science.2017; 415: 85. CrossRef - Spontaneous Formation of Titanium Nitride on the Surface of a Ti Rod Induced by Electro-Discharge-Heat-Treatment in an N2 Atmosphere
W.H. Lee, Y.H. Yoon, Y.H. Kim, Y.K. Lee, J.Y. Kim, S.Y. Chang
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1281. CrossRef - Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(2): 122. CrossRef
- Solvent induced surface modifications on hydrogen storage performance of ZnO nanoparticle decorated MWCNTs
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


