Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C Soft Magnetic Powders Prepared by High-Pressure Gas Atomization
- Jae Won Jeong, Dong-Yeol Yang, Ki Bong Kim, Junhong Lee, Young Ja Kim, Tae-Soo Lim, Sangsun Yang, Min Ha Lee, Hwi Jun Kim, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):391-396. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.391
- 830 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
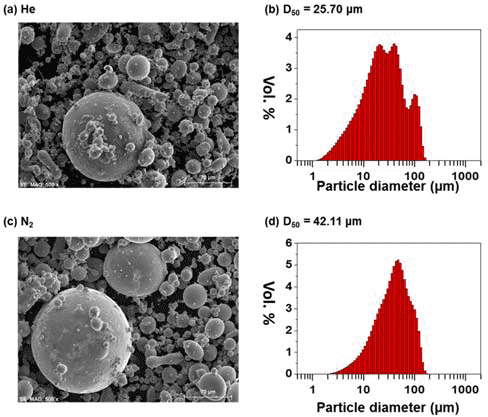
PDF In this study, ultra-fine soft-magnetic micro-powders are prepared by high-pressure gas atomization of an Fe-based alloy, Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C. Spherical powders are successfully obtained by disintegration of the alloy melts under high-pressure He or N2 gas. The mean particle diameter of the obtained powders is 25.7 μm and 42.1 μm for He and N2 gas, respectively. Their crystallographic structure is confirmed to be amorphous throughout the interior when the particle diameter is less than 45 μm. The prepared powders show excellent soft magnetic properties with a saturation magnetization of 164.5 emu/g and a coercivity of 9.0 Oe. Finally, a toroidal core is fabricated for measuring the magnetic permeability, and a μr of up to 78.5 is obtained. It is strongly believed that soft magnetic powders prepared by gas atomization will be beneficial in the fabrication of high-performance devices, including inductors and motors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
Jungjoon Kim, Dongchan Min, Suwon Park, Junhyub Jeon, Seok-Jae Lee, Youngkyun Kim, Hwi-Jun Kim, Youngjin Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2022; 63(10): 1304. CrossRef - Optimizing the magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous powder by adjusting atomic structures from vitrification at different temperatures
Song-Yi Kim, Hye-Ryeong Oh, Hyeon-Ah Kim, A-Young Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Sang-Sun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Il-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Gil Kim, Jürgen Eckert, Jong-Ryoul Kim, Min-Ha Lee
Journal of Applied Physics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline hybrid materials
Yeonjoo Lee, Jonggyu Jeon, Seungjin Nam, Teasuk Jang, Hwijun Kim, Minwoo Lee, Yongjin Kim, Dongyeol Yang, Kyeongsik Min, Hyunjoo Choi
Powder Technology.2018; 339: 440. CrossRef
- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Zr-Ti Alloy Powder by Magnesium Reduction
- Dong-Won Lee, Geun-Tae Park, Tae-Soo Lim, Hye-Moon Lee, Ji-Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(4):359-364.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.4.359

- 929 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Zr-Ti alloy powders were successfully synthesized by magnesium thermal reduction of metal chlorides. The evaporated and mixed gasses of ZrCl_4+TiCl_4 were injected to liquid magnesium and the chloride components were reduced by magnesium leading to the formation of MgCl_2. The released Zr and Ti atoms were then condensed to particle forms inside the mixture of liquid magnesium and magnesium chloride, which could be dissolved fully in post process by 1~5% HCl solution at room temperature. By the fraction-control of individually injected ZrCl_4 and TiCl_4 gasses, the final compositions of produced alloy powders were changed in the ranges of Zr-0 wt.%~20 wt.%Ti and their purity and particle size were about 99.4% and the level of several micrometers, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis of Vanadium Powder by Magnesiothermic Reduction
Dong Won Lee, Hak Sung Lee, Jung Yeul Yun, Young Ho Kim, Jei Pil Wang
Advanced Materials Research.2014; 1025-1026: 509. CrossRef - Extraction of Vanadium Powder by Metallothermic Reduction
Dong-Won Lee, Sang-Hyun Heo, Jong-Taek Yeom, Jei-Pil Wang
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(1): 43. CrossRef
- Synthesis of Vanadium Powder by Magnesiothermic Reduction
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of Nanostructured Ceria Powders for an Oxygen-sensor by Thermochemical Process
- Dong-Won Lee, Joon-Hwan Choi, Tae-Soo Lim, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2006;13(3):192-198.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2006.13.3.192

- 417 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The nanostructured cerium oxide powders were synthesized by spray thermal decomposition process for the use as the raw materials of resistive oxygen sensor. The synthesis routes consisted of 1) spray drying of water based organic solution made from cerium nitrate hydrate (Ce(NO_3)_36H_2O) and 2) heat treatment of spray dried precursor powders at 400°C in air atmosphere to remove the volatile components and identically to oxidize the cerium component. The produced powders have shown the loose structure agglomerated with extremely fine cerium oxide particles with about 15 nm and very high specific surface area (110m2/g). The oxygen sensitivity, n (LogproptoLog (P_O2/Po)-n and the response time, t_90 measured at 600°C in the sample sintered at 1000°C, were about 0.25 and 3 seconds, respectively, which had much higher performances than those known in micron or 100sim200nm sized sensors.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


