Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Correlation of Sintering Parameters with Density and Hardness of Nano-sized Titanium Nitride reinforced Titanium Alloys using Neural Networks
- A. K. Maurya, P. L Narayana, Hong In Kim, N. S. Reddy
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(5):365-372. Published online October 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.5.365
- 1,453 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
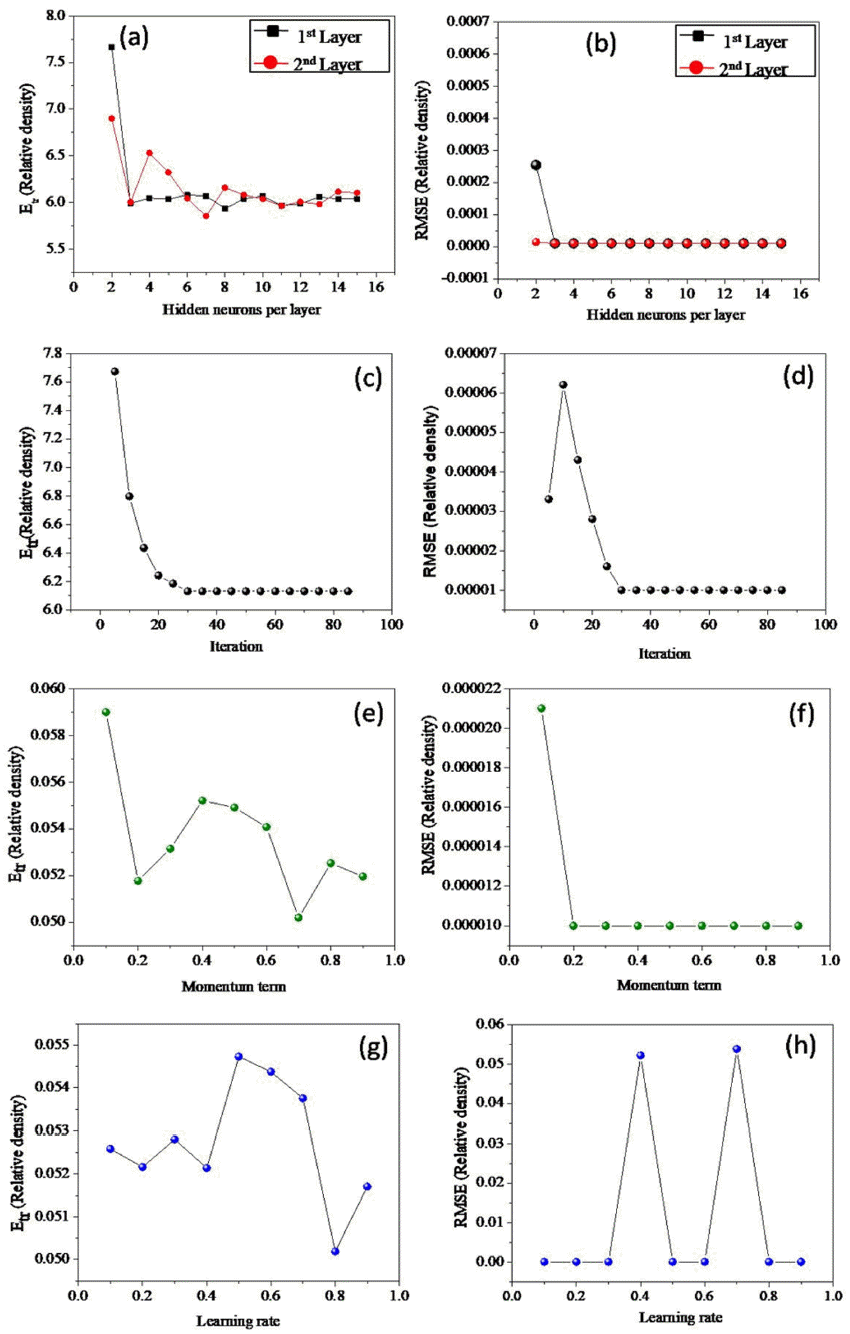
PDF Predicting the quality of materials after they are subjected to plasma sintering is a challenging task because of the non-linear relationships between the process variables and mechanical properties. Furthermore, the variables governing the sintering process affect the microstructure and the mechanical properties of the final product. Therefore, an artificial neural network modeling was carried out to correlate the parameters of the spark plasma sintering process with the densification and hardness values of Ti-6Al-4V alloys dispersed with nano-sized TiN particles. The relative density (%), effective density (g/cm3), and hardness (HV) were estimated as functions of sintering temperature (°C), time (min), and composition (change in % TiN). A total of 20 datasets were collected from the open literature to develop the model. The high-level accuracy in model predictions (>80%) discloses the complex relationships among the sintering process variables, product quality, and mechanical performance. Further, the effect of sintering temperature, time, and TiN percentage on the density and hardness values were quantitatively estimated with the help of the developed model.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of Machine Learning Algorithms and SHAP for Prediction and Feature Analysis of Tempered Martensite Hardness in Low-Alloy Steels
Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee, Minsu Jung
Metals.2021; 11(8): 1159. CrossRef
- Application of Machine Learning Algorithms and SHAP for Prediction and Feature Analysis of Tempered Martensite Hardness in Low-Alloy Steels
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


