Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):509-516. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00339
- 584 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
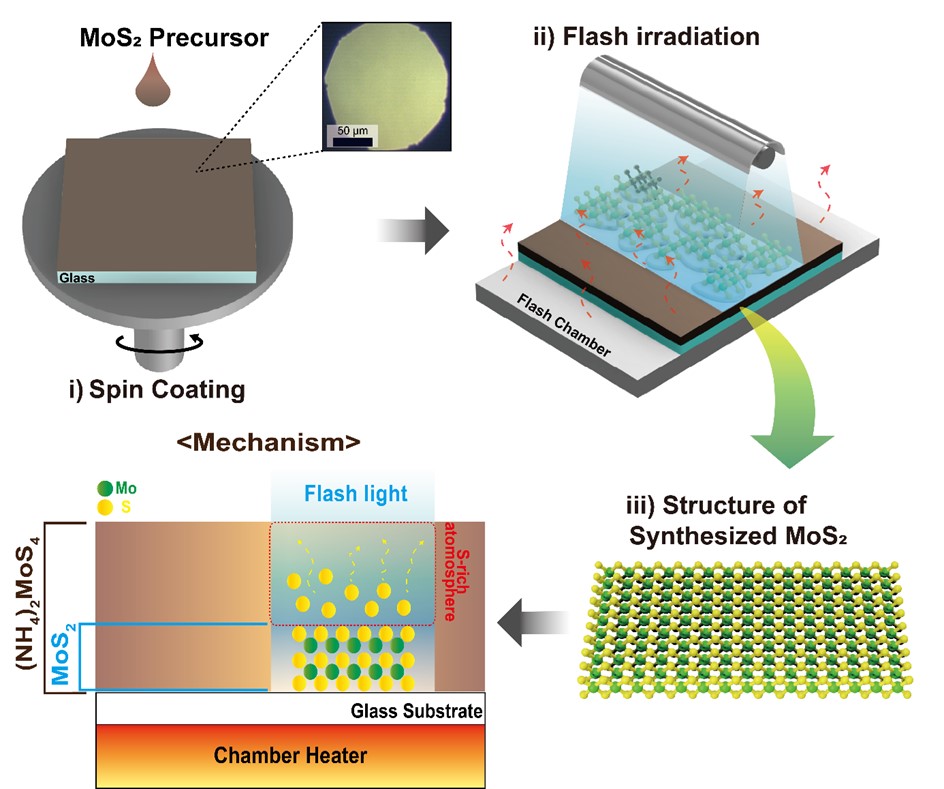
PDF - This study presents the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide (MoS₂) using flashlamp annealing and provides a comprehensive investigation of its structural and physical properties. The proposed flash-induced approach enables rapid production of high-quality MoS₂, offering superior process efficiency compared to conventional synthesis techniques. The structural, electronic, and thermal characteristics of the synthesized MoS₂ were systematically examined using multiple analytical methods, with particular attention to how synthesis conditions influence layer structure, crystallinity, and defect density. The results indicate that MoS₂ produced through this method exhibits material properties suitable for high-performance electronic devices and energy storage applications. Moreover, this work demonstrates the potential of flash-induced synthesis for scalable and practical fabrication of MoS₂-based nanomaterials, thereby contributing to the broader advancement of transition metal dichalcogenide technologies across diverse nanotechnology applications.
- [English]
- Investigation of the Thermal-to-Electrical Properties of Transition Metal-Sb Alloys Synthesized for Thermoelectric Applications
- Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Sooho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Kwi-Il Park, Kyung Tae Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):236-242. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00031
- 1,711 View
- 43 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
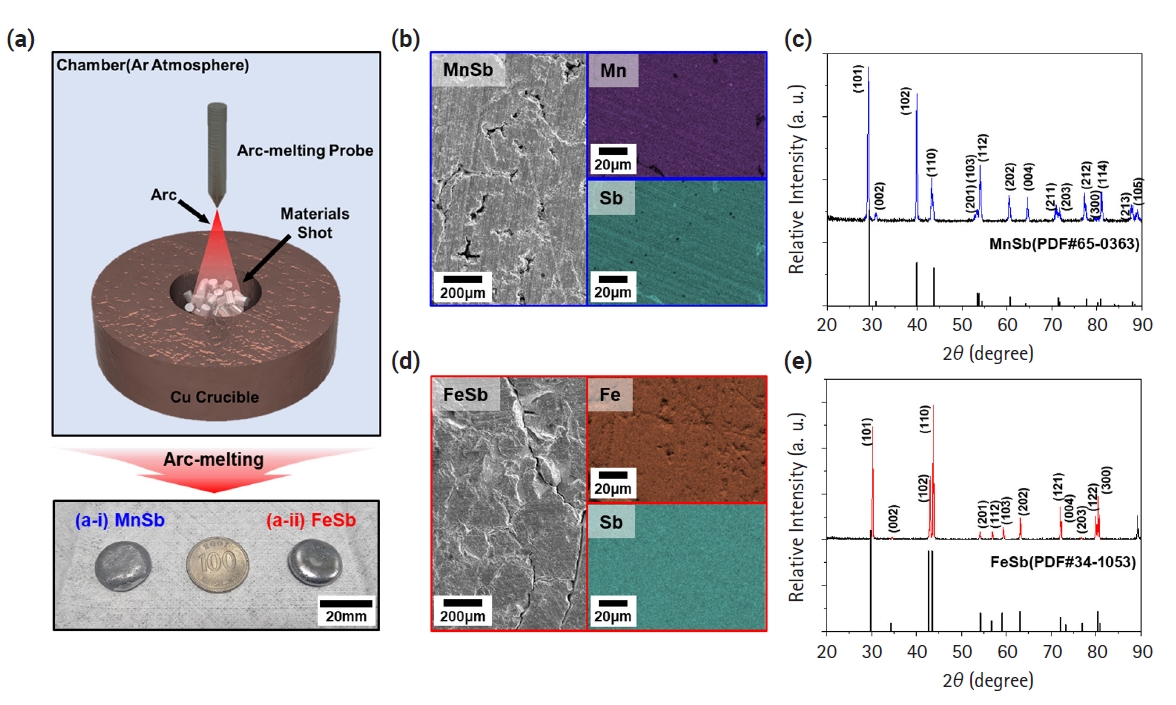
PDF - The development of thermoelectric (TE) materials to replace Bi2Te3 alloys is emerging as a hot issue with the potential for wider practical applications. In particular, layered Zintl-phase materials, which can appropriately control carrier and phonon transport behaviors, are being considered as promising candidates. However, limited data have been reported on the thermoelectric properties of metal-Sb materials that can be transformed into layered materials through the insertion of cations. In this study, we synthesized FeSb and MnSb, which are used as base materials for advanced thermoelectric materials. They were confirmed as single-phase materials by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns. Based on electrical conductivity, the Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity of both materials characterized as a function of temperature, the zT values of MnSb and FeSb were calculated to be 0.00119 and 0.00026, respectively. These properties provide a fundamental data for developing layered Zintl-phase materials with alkali/alkaline earth metal insertions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
Jong Min Park, Seungki Jo, Soo-ho Jung, Jinhee Bae, Linh Ba Vu, Jihun Yu, Kyung Tae Kim
Materials Letters.2025; 381: 137796. CrossRef - Highly deformable and hierarchical 3D composite sponge for versatile thermoelectric energy conversion
Jong Min Park, Changyeon Baek, Min-Ku Lee, Nagamalleswara Rao Alluri, Gyoung-Ja Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Kwi-Il Park
Applied Surface Science.2025; 692: 162730. CrossRef
- Improving thermoelectric properties of CuMnSb alloys via strategic alloying with magnetic MnSb and Cu
- [English]
- Research Trends in Electromagnetic Shielding using MXene-based Composite Materials
- Siyeon Kim, Jongmin Byun
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(1):57-76. Published online February 28, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2024.31.1.57
- 7,868 View
- 159 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
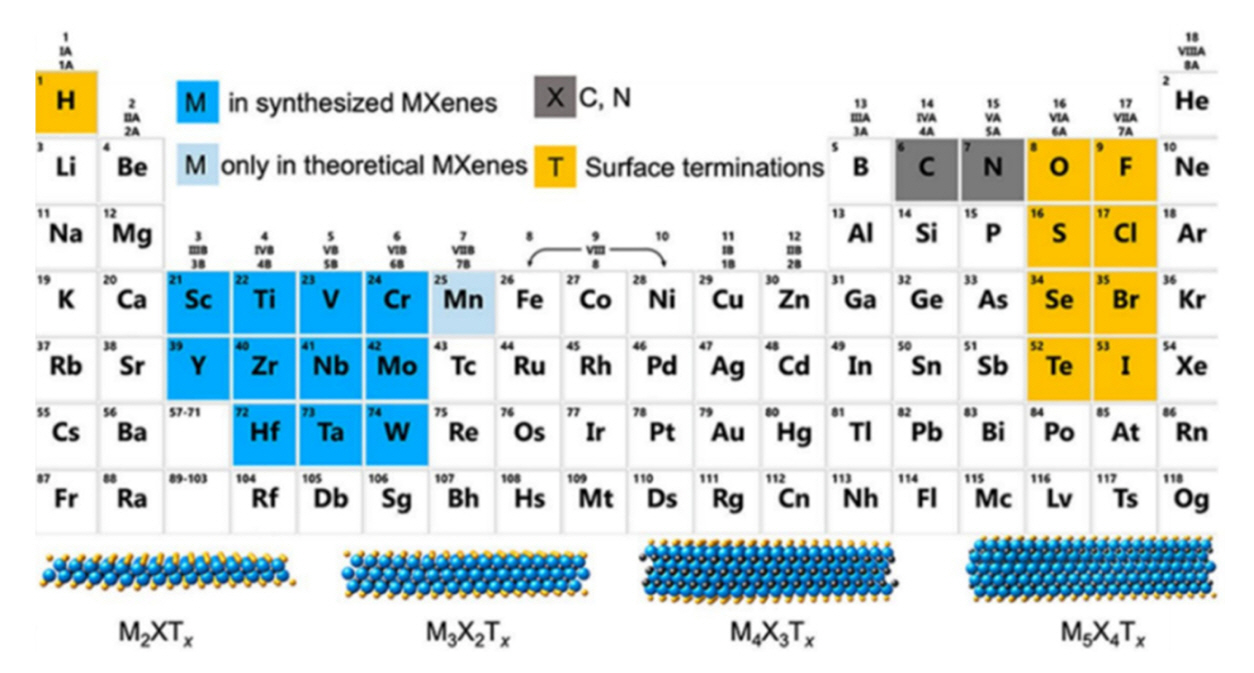
PDF Recent advancements in electronic devices and wireless communication technologies, particularly the rise of 5G, have raised concerns about the escalating electromagnetic pollution and its potential adverse impacts on human health and electronics. As a result, the demand for effective electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials has grown significantly. Traditional materials face limitations in providing optimal solutions owing to inadequacy and low performance due to small thickness. MXene-based composite materials have emerged as promising candidates in this context owing to their exceptional electrical properties, high conductivity, and superior EMI shielding efficiency across a broad frequency range. This review examines the recent developments and advantages of MXene-based composite materials in EMI shielding applications, emphasizing their potential to address the challenges posed by electromagnetic pollution and to foster advancements in modern electronics systems and vital technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
Pramod D. Mhase, Varsha C. Pujari, Santosh S. Jadhav, Abdullah G. Al-Sehemi, Sarah Alsobaie, Sunil M. Patange
Composites Communications.2025; 54: 102284. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Fabrication of MOF@MXene composites via surface modification of MXene under acidic conditions
Ji-Haeng Jeong, Woong-Ryeol Yu
Functional Composites and Structures.2025; 7(2): 025006. CrossRef - V2CTx MXene@ZIF-8 composite as an efficient adsorbent for Pb(II) removal from aqueous solution
Sarina Khojasteh Fard, Golshan Mazloom, Manoochehr Sobhani, Mohsen Tamtaji
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(6): 120099. CrossRef
- Designing dual phase hexaferrite (SrFe12O19) – Perovskite (La0.5Nd0.5FeO3) composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and band gap modulation
- [Korean]
- Research trends of MXenes as the Next-generation Two-dimensional Materials
- Hojun Lee, Yejun Yun, Jinkwang Jang, Jongmin Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):150-163. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.150
- 3,405 View
- 101 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Interest in eco-friendly materials with high efficiencies is increasing significantly as science and technology undergo a paradigm shift toward environment-friendly and sustainable development. MXenes, a class of two-dimensional inorganic compounds, are generally defined as transition metal carbides or nitrides composed of few-atoms-thick layers with functional groups. Recently MXenes, because of their desirable electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties that emerge from conductive layered structures with tunable surface terminations, have garnered significant attention as promising candidates for energy storage applications (e.g., supercapacitors and electrode materials for Li-ion batteries), water purification, and gas sensors. In this review, we introduce MXenes and describe their properties and research trends by classifying them into two main categories: transition metal carbides and nitrides, including Ti-based MXenes, Mo-based MXenes, and Nb-based MXenes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Next-generation brackish water treatment: Exploring dual-ion capacitive deionization
Yize Li, Jing He, He Liu, Chao Yan
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering.2025; 13(2): 116037. CrossRef - Microstructure tailoring of Nb-based MAX phase by low temperature synthesis with layer-structured Nb2C powder and molten salt method
Chaehyun Lim, Wonjune Choi, Jongmin Byun
Materials Characterization.2025; 225: 115106. CrossRef - Review on 2D MXene and graphene electrodes in capacitive deionization
Hammad Younes, Ding Lou, Md. Mahfuzur Rahman, Daniel Choi, Haiping Hong, Linda Zou
Environmental Technology & Innovation.2022; 28: 102858. CrossRef
- Next-generation brackish water treatment: Exploring dual-ion capacitive deionization
- [Korean]
- Preparation of Cathode Materials for Lithium Rechargeable Batteries using Transition Metals Recycled from Li(Ni1-x-yCoxMny)O2 Secondary Battery Scraps
- Jae-won Lee, Dae Weon Kim, Seong Tae Jang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):131-136. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.131
- 581 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
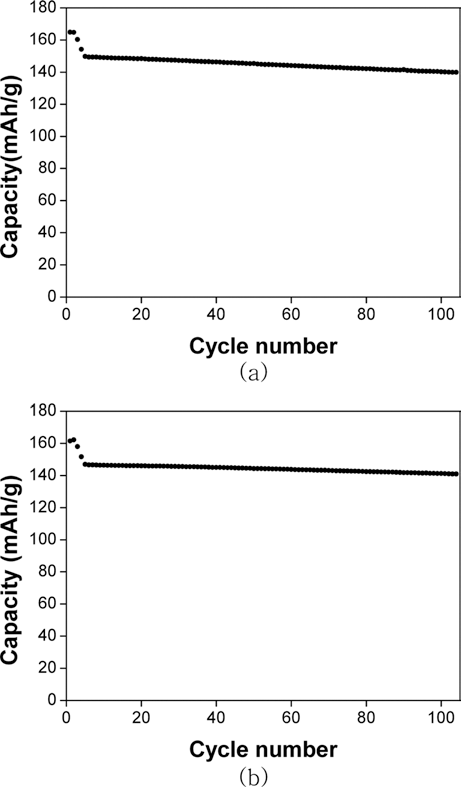
PDF Cathode materials and their precursors are prepared with transition metal solutions recycled from the the waste lithium-ion batteries containing NCM (nickel-cobalt-manganese) cathodes by a H2 and C-reduction process. The recycled transition metal sulfate solutions are used in a co-precipitation process in a CSTR reactor to obtain the transition metal hydroxide. The NCM cathode materials (Ni:Mn:Co=5:3:2) are prepared from the transition metal hydroxide by calcining with lithium carbonate. X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy analyses show that the cathode material has a layered structure and particle size of about 10 μm. The cathode materials also exhibited a capacity of about 160 mAh/g with a retention rate of 93~96% after 100 cycles.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


