Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Research Article
- [English]
- A Self-Powered Cationic Microfiber-Based Triboelectric Air Filter for High-Speed Particulate Matter Removal and Smart Monitoring
- Tae-hyung Kim, Jin-Kyeom Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(6):481-491. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00465
- 503 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
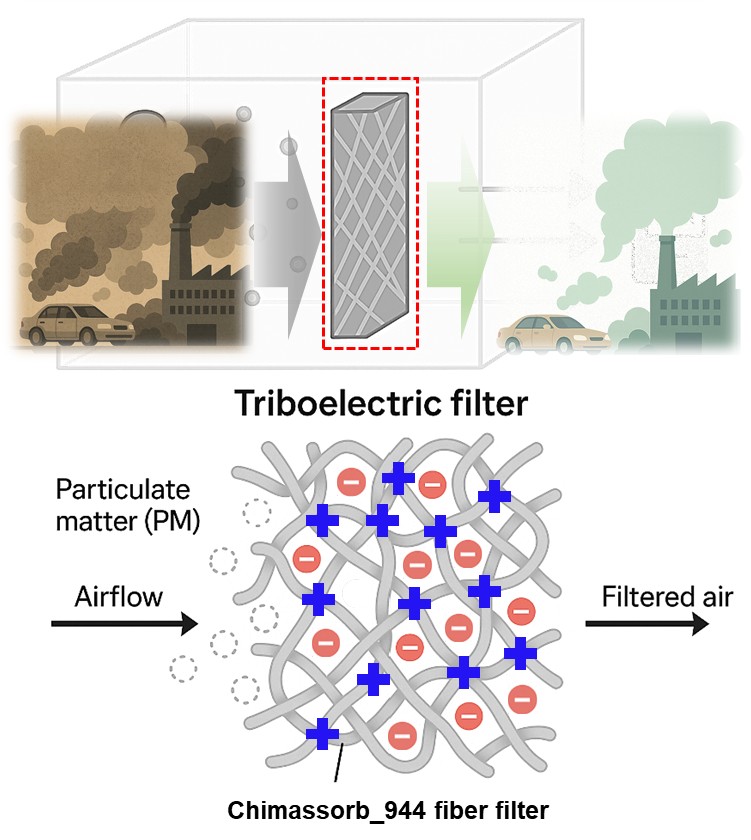
PDF - Particulate matter (PM) pollution demands air filters that combine high efficiency with low pressure drop. Here, we report a self-powered electrostatic filter based on an electrospun cationic microfiber web of Chimassorb 944 (C-fiber). The C-fiber functions as a triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), generating a surface charge density of 85.8 85.8 μC/m2 when paired with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), which creates a strong electrostatic field for capturing sub-micron particles, including the most penetrating particle size (MPPS). As a result, the triboelectrically charged C-fiber filter maintains >80% filtration efficiency at a high wind speed of 60 cm/s, far exceeding uncharged mechanical filters (<20%) while retaining low air resistance. Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) visualizes the surface-potential change after particle capture, and the gradual decay of TENG output provides a built-in indicator of dust loading. This strategy offers a promising platform for next-generation smart air purification systems.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 First
First Prev
Prev


