Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Enhancing the Dispersion Stability of Exfoliated MoS2 Nanoflakes for Na⁺ Intercalation
- Jae Min Sung, Dong-Won Kyung, Ammad Ali, Kee-Ryung Park, Mi Hye Lee, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum Sung Kim, Haejin Hwang, Leeseung Kang, Yoseb Song
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00255
- 477 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
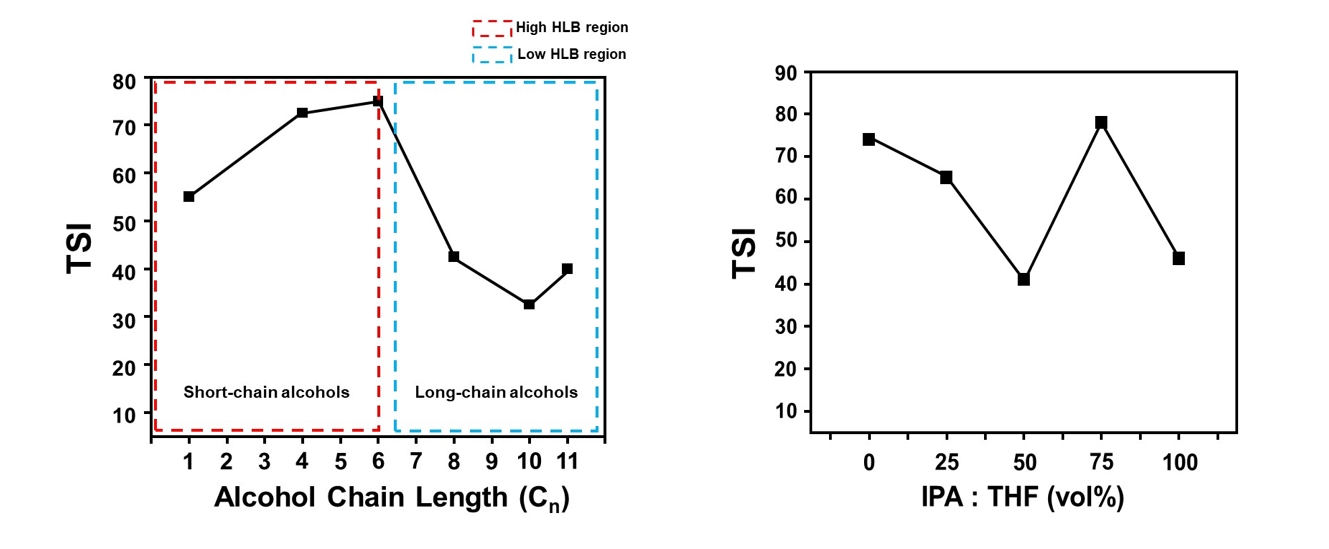
PDF - This study investigated the dispersion stability of exfoliated MoS₂ nanoflakes in various organic solvents and binary mixtures using a Turbiscan optical analyzer. Sedimentation behavior was quantitatively evaluated via transmittance variation (ΔT), backscattering variation (ΔBS), and the Turbiscan stability index (TSI). Alcohol-based solvents were categorized by hydrophilic-lipophilic balance values. Long-chain alcohols, such as 1-undecanol, showed increased stability due to high viscosity and strong hydrophobic affinity with MoS2 basal planes, while short-chain alcohols exhibited poor stabilization. Binary mixtures of isopropanol (IPA) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) were also assessed, with the 5:5 volume ratio showing the best stability profile, including the lowest TSI and minimal ΔT and ΔBS values. This improvement is attributed to synergistic interactions, as IPA stabilizes hydrophilic edge sites, while THF engages with hydrophobic basal surfaces. These findings highlight the importance of balancing physicochemical properties when selecting solvents to improve MoS2 dispersion for structural modification and electrocatalytic applications.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Surfactant on the Dispersion Stability of Slurry for Semiconductor Silicon CMP
- Hye Won Yun, Doyeon Kim, Do Hyung Han, Dong Wan Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):395-401. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.395
- 2,117 View
- 46 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The improvement of dispersion stability for the primary polishing slurry in a CMP process is achieved to prevent defects produced by agglomeration of the slurry. The dispersion properties are analyzed according to the physical characteristics of each silica sol sample. Further, the difference in the dispersion stability is confirmed as the surfactant content. The dispersibility results measured by Zeta potential suggest that the dispersion properties depend on the content and size of the abrasive in the primary polishing slurry. Moreover, the optimum ratio for high dispersion stability is confirmed as the addition content of the surfactant. Based on the aforementioned results, the long-term stability of each slurry is analyzed. Turbiscan analysis demonstrates that the agglomeration occurs depending on the increasing amount of surfactant. As a result, we demonstrate that the increased particle size and the decreased content of silica improve the dispersion stability and long-term stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
Seung-Hwan Oh, Hyeonmin Yim, Donghee Lee, Dong Hyeok Seo, Won Jin Kim, Ryun Na Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2022; 32(9): 396. CrossRef
- Surface Defect Properties of Prime, Test-Grade Silicon Wafers
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


