Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Optimization of Al2O3 Microchannels Using DLP-Based 3D Printing
- Jun-Min Cho, Yong-Jun Seo, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):59-66. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00346
- 994 View
- 32 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study focused on optimizing the digital light processing (DLP) 3D printing process for high-precision ceramic components using alumina-based slurries. Key challenges, such as cracking during debinding and precision loss due to slurry sedimentation, were addressed by evaluating the exposure time and the nano-to-micro alumina powder ratios. The optimal conditions—exposure time of 15 seconds and a 1:9 mixing ratio—minimized cracking, improved gas flow during debinding, and increased structural precision. Microchannels with diameters above 1.2 mm were successfully fabricated, but channels below 0.8 mm faced challenges due to slurry accumulation and over-curing. These results establish a reliable process for fabricating complex ceramic components with improved precision and structural stability. The findings have significant potential for applications in high-value industries, including aerospace, energy, and healthcare, by providing a foundation for the efficient and accurate production of advanced ceramic structures.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Deposition Parameter and Mixing Process of Raw Materials on the Phase and Structure of Ytterbium Silicate Environmental Barrier Coatings by Suspension Plasma Spray Method
- Ho-lim Ryu, Seon-A Choi, Sung-Min Lee, Yoon-Soo Han, Kyun Choi, Sahn Nahm, Yoon-Suk Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):437-443. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.437

- 793 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF SiC-based composite materials with light weight, high durability, and high-temperature stability have been actively studied for use in aerospace and defense applications. Moreover, environmental barrier coating (EBC) technologies using oxide-based ceramic materials have been studied to prevent chemical deterioration at a high temperature of 1300°C or higher. In this study, an ytterbium silicate material, which has recently been actively studied as an environmental barrier coating because of its high-temperature chemical stability, is fabricated on a sintered SiC substrate. Yb2O3 and SiO2 are used as the raw starting materials to form ytterbium disilicate (Yb2Si2O7). Suspension plasma spraying is applied as the coating method. The effect of the mixing method on the particle size and distribution, which affect the coating formation behavior, is investigated using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. It is found that the originally designed compounds are not effectively formed because of the refinement and vaporization of the raw material particles, i.e., SiO2, and the formation of a porous coating structure. By changing the coating parameters such as the deposition distance, it is found that a denser coating structure can be formed at a closer deposition distance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
Seong-June Youn, Young-Kyun Kim, Jae-Sung Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 333. CrossRef
- Fabrication, Microstructure and Adhesive Properties of BCuP-5 Filler Metal/Ag Plate Composite by using Plasma Spray Process
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Solid State Electrolyte Li7La3Zr2O12 thick Film by Tape Casting
- Ran-Hee Shin, Samick Son, Sung-Soo Ryu, Hyung-Tae Kim, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):379-383. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.379
- 1,019 View
- 11 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
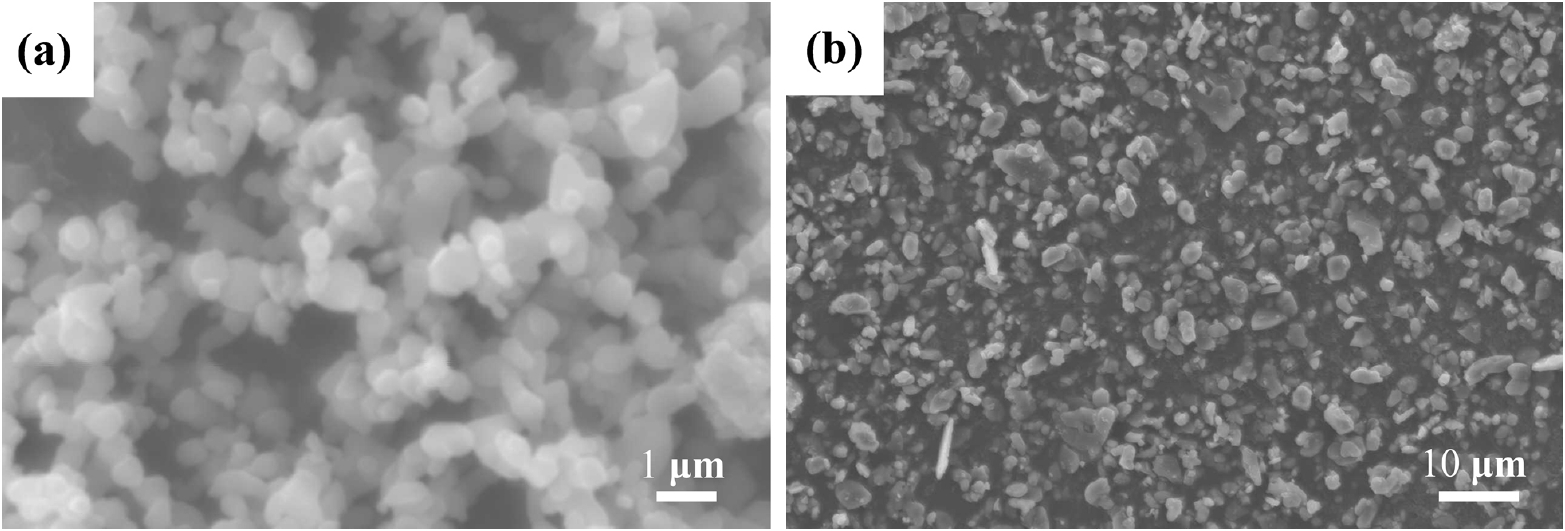
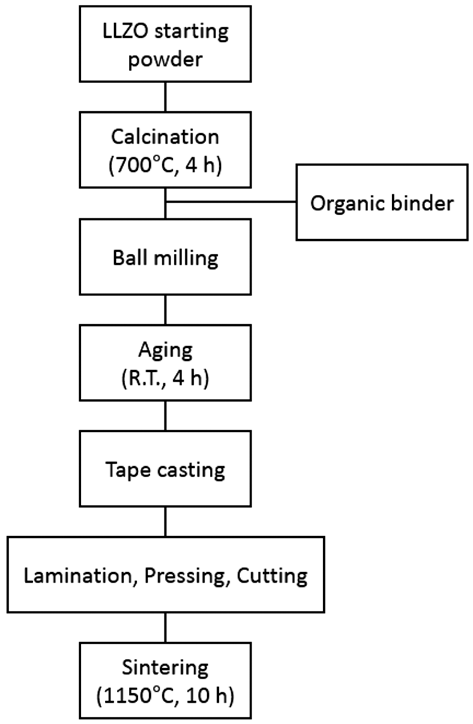
PDF A thick film of Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) solid-state electrolyte is fabricated using the tape casting process and is compared to a bulk specimen in terms of the density, microstructure, and ion conductivity. The final thickness of LLZO film after sintering is 240 μm which is stacked up with four sheets of LLZO green films including polymeric binders. The relative density of the LLZO film is 83%, which is almost the same as that of the bulk specimen. The ion conductivity of a LLZO thick film is 2.81 × 10−4 S/cm, which is also similar to that of the bulk specimen, 2.54 × 10−4 S/ cm. However, the microstructure shows a large difference in the grain size between the thick film and the bulk specimen. Although the grain boundary area is different between the thick film and the bulk specimen, the fact that both the ion conductivities are very similar means that no secondary phase exists at the grain boundary, which is thought to originate from nonstoichiometry or contamination.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Waste minimization in all-solid-state battery production via re-lithiation of the garnet solid electrolyte LLZO
Vivien Kiyek, Martin Hilger, Melanie Rosen, Jürgen Peter Gross, Markus Mann, Dina Fattakhova-Rohlfing, Ruth Schwaiger, Martin Finsterbusch, Olivier Guillon
Journal of Power Sources.2024; 609: 234709. CrossRef - Powder Aerosol Deposition as a Method to Produce Garnet‐Type Solid Ceramic Electrolytes: A Study on Electrochemical Film Properties and Industrial Applications
Tobias Nazarenus, Yanyan Sun, Jörg Exner, Jaroslaw Kita, Ralf Moos
Energy Technology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bum Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(6): 477. CrossRef
- Waste minimization in all-solid-state battery production via re-lithiation of the garnet solid electrolyte LLZO
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Porous Al2O3 Film by Freeze Tape Casting
- Ran-Hee Shin, Jun-Mo Koo, Young-Do Kim, Yoon-Soo Han
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(6):438-442. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.6.438

- 625 View
- 6 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Porous thick film of alumina which is fabricated by freeze tape casting using a camphene-camphor-acrylate vehicle. Alumina slurry is mixed above the melting point of the camphene-camphor solvent. Upon cooling, the camphene-camphor crystallizes from the solution as particle-free dendrites, with the Al2O3 powder and acrylate liquid in the interdendritic spaces. Subsequently, the acrylate liquid is solidified by photopolymerization to offer mechanical properties for handling. The microstructure of the porous alumina film is characterized for systems with different cooling rate around the melting temperature of camphor-camphene. The structure of the dendritic porosity is compared as a function of ratio of camphene-camphor solvent and acrylate content, and Al2O3 powder volume fraction in acrylate in terms of the dendrite arm width.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


