Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Powder Metall Inst > Volume 21(6); 2014 > Article
-
ARTICLE
전기선폭발법으로 제조된 텅스텐 분말의 산소 조성이 방전플라즈마소결 거동에 미치는 영향 - 김철희, 이성a, 김병기b, 김지순b,*
- Effect of Oxygen Content in the Tungsten Powder Fabricated by Electrical Explosion of Wire Method on the Behavior of Spark-Plasma Sintering
- Cheol-Hee Kim, Seong Leea, Byung-Kee Kimb, Ji Soon Kimb,*
-
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute 2014;21(6):447-453.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.6.447
Published online: November 30, 2014
덕산하이메탈,
국방과학연구소,
b울산대학교 첨단소재공학부
Duksan Hi-Metal Co. Ltd., Ulsan 683-804, Korea
aAgency for Defense Development, Daejon 305-600, Korea
bSchool of Materials Science & Engineering, University of Ulsan, Ulsan 680-749, Korea
- *Corresponding Author : Ji Soon Kim, TEL: +82-52-259-2244, FAX: +82-52-259-1688, E-mail: jskim@ulsan.ac.kr
© Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 650 Views
- 2 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
- Effect of oxygen content in the ultrafine tungsten powder fabricated by electrical explosion of wire method on the behvior of spark plasma sintering was investigated. The initial oxygen content of 6.5 wt% of as-fabricated tungsten powder was reduced to 2.3 and 0.7 wt% for the powders which were reduction-treated at 400°C for 2 hour and at 500°C for 1h in hydrogen atmosphere, respectively. The reduction-treated tungsten powders were spark-plasma sintered at 1200-1600°C for 100-3600 sec. with applied pressure of 50 MPa under vacuum of 0.133 Pa. Maximun sindered density of 97% relative density was obtained under the condition of 1600°C for 1h from the tungsten powder with 0.7 wt% oxygen. Sintering activation energy of 95.85 kJ/mol−1 was obtained, which is remarkably smaller than the reported ones of 380~460 kJ/mol−1 for pressureless sintering of micron-scale tungsten powders.
- 텅스텐은 높은 밀도(19.26 g/cm3), 고융점(3410°C)의 특 성을 가지며, 우수한 내아크 특성 및 높은 내열 충격성 등 고온에서의 열적 특성이 우수한 재료이다. 또한 고온 강도 및 고온 내마모성 등 기계적 특성이 우수하여 고열 용접봉 재, 고부하 전기접점재, 군사로켓용 노즐재료 등에 널리 응 용되고 있다. 텅스텐의 높은 융점으로 말미암아 마이크론 크기의 상용 순수 텅스텐 분말의 경우, 소결 온도를 1900°C 이상으로 높여도 고밀도의 소결체를 얻기 어렵기 때문에 미량의 천이금속 원소 등을 첨가하는 활성소결 방 법이 사용되고 있으나, 첨가된 천이금속원소들의 입계 편 석 등으로 기계적 특성이 저하하는 문제가 있다.
- 최근 다양한 물리적, 화학적 방법으로 텅스텐을 나노크 기 분말로 제조할 수 있게 되었는데, 나노 텅스텐 분말의 경우 높은 비표면적으로 인해 기존의 마이크론 크기 분말 이 갖지 못하는 우수한 기계적 물성을 나타낼 수 있을 뿐 아니라, 소결온도를 낮추는 효과도 기대할 수 있다[1-3]. 그 러나 나노크기 금속 분말은 높은 비표면적에 따른 표면 활 성의 증가로 대기 중에 노출 시 폭발적 산화 등 취급이 어 렵기 때문에 제조 과정에서 입자 분말 표면에 산화막을 형 성시키기 위한 부동태처리를 하게 된다. 금속 분말의 경우 입자 표면의 이러한 부동태 산화막은 소결성을 저하시키는 것으로 알려져 있다. 또한 나노 금속분말의 경우 소결 과 정에서 입자성장을 억제하면서 고밀도의 소결체를 얻는 것 이 중요하다. 방전플라즈마소결(Spark-Plasma Sintering, SPS)은 기존 소결법에 비해 매우 낮은 온도에서 짧은 시간 동안 소결함으로써 입자성장을 효과적으로 억제할 수 있는 것으로 보고되고 있다[4-5].
- 본 연구에서는 전기선폭발법(Electrical Explosion of Wire Method, EEW)으로 제조된 초미세 텅스텐 분말을 환원 처 리하여 부동태로 인한 산화막을 제거함으로써 산소 조성을 변화 시킨 후, 방전플라즈마소결법으로 치밀화하여 텅스텐 분말 내 산소 양의 변화가 소결성과 입자성장, 소결 활성 화에너지에 어떠한 영향을 미치는지 조사하였다.
서 론
- 초미세 텅스텐 분말은 전기선폭발장치를 이용하여 표 1 의 조건으로 제조하였다[5]. 전기선폭발은 아르곤 가스 분 위기에서 20 kV의 전압으로 하였으며, 사용된 텅스텐 와이 어의 직경은 0.3 mm이었다. 제조된 분말은 레이저입도분 석기, 전계방사주사전자현미경, 투과전자현미경, 열중량분 석기, X선회절분석기를 이용하여 분말의 입도와 조성, 형 상, 환원 반응온도, 형성된 상 등을 조사하였다. 제조된 분 말의 산소 조성을 변화시키기 위해 환원처리를 하였으며, 관상로를 이용하여 수소분위기에서 각각 400°C-2h, 500°C- 1h의 조건으로 행하였다. 환원 처리한 분말에 대해서도 위 의 분석 장치 등을 이용하여 분말의 형상과 조성, 상분석 을 실시하였다. 방전플라즈마소결은 0.133 Pa의 진공에서 직경 10 mm의 흑연 다이를 사용하여 승온 속도 20°C/min 과 50 MPa의 압력으로 1200, 1400, 1500, 1600°C의 온도 로 가열하여 100, 1000, 3600초(1시간) 동안 유지하여 실 시하였다. 승온 과정을 포함한 전 소결 과정의 길이 변화 를 자동 데이터 저장장치로 기록하여 그 결과로부터 소 결 과정의 수축율, 치밀화율, 상대 밀도를 구하였다. 최종 소결체의 밀도는 수중밀도계를 이용하여 측정하였고, 소 결체의 미세조직을 전계방사주사전자현미경으로 관찰하 여 소결 특성 결과와 함께 소결성을 논의하고, 시간 변화 에 따른 소결 데이터들로부터 소결 활성화에너지를 구하 였다.
실험방법
- 3.1. 전기선폭발법으로 제조된 텅스텐 분말의 특성
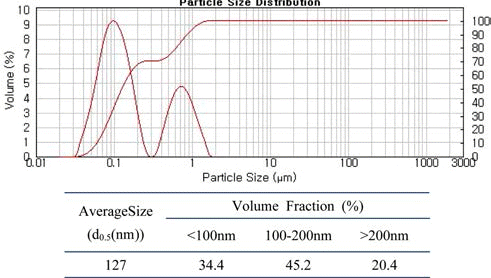
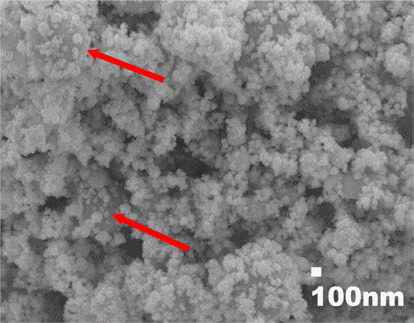
- 전기선폭발장치로 제조된 분말의 형상과 입도분석 결과 는 이미 보고한 바 있으며[5], 그림 1과 2에 그 결과를 다 시 나타내었다. 그림 1에서 보는 바와 같이, 제조된 텅스텐 분말은 구형을 하고 있으며, 화살표로 나타낸 부분에서처 럼 불균일 폭발로 인한 조대 분말과 100 nm 이하의 초미 세 분말이 혼재되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다. 조대 분말 의 경우, 수μm의 크기를 갖는 것도 있으며, 수십 nm 크기 의 미세분말들이 분산 또는 응집되어 있음을 알 수 있다. 그림 2의 입도 분석 결과에서 이러한 관찰 결과를 다시 확 인할 수 있는데, 1 μm대 크기의 조대 분말과 100 nm대 크기 의 초미세 분말이 혼재하는 bimodal 분포를 나타내고 있다.
- Results of laser particle-size analysis for the ultrafine tungsten powders fabricated by EEW in this study.
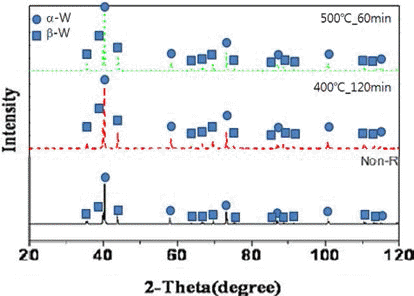
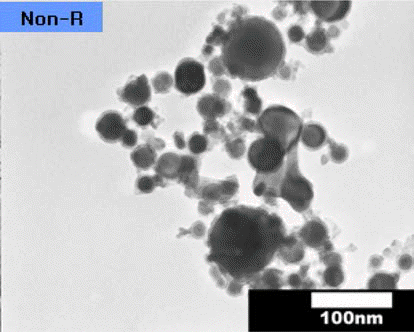
- 전기선폭발법으로 제조한 초미세 텅스텐 분말은 제조 과 정에서 부동태 처리를 거쳐 표면에 산화막을 형성시키게 되는데, 그림 3은 부동태 처리된 초미세 텅스텐 분말의 투 과전자현미경 관찰 결과를 나타낸 것이다. 그림 4는 제조 된 분말과 환원 처리 후 분말들의 X선 회절분석 결과를 나 타낸 것으로, 가장 하단의 곡선이 전기선폭발법으로 제조 된 초미세 텅스텐 분말의 분석 결과이다. 안정한 α-W상과 준안정 β-W상이 혼재되어 있음을 확인할 수 있으며, 산소 조성을 EDS 면분석으로 조사한 결과, 6.5 wt%로 확인되었 다(표 2). 이는 원자량 퍼센트로 44.4 at%에 달하는 양으로 서, 알려져 있는 텅스텐 산화물들(W2O3, WO2, W2O5, WO3) 중에서 시료 중의 텅스텐이 모든 산소와 반응하여 W2O3를 형성했다고 가정하면 전체 분말 중에서 산화물의 중량은 43.7%, WO3가 형성되었다고 가정하면 전체 분말 중 31.4%의 텅스텐 산화물이 형성된 결과로 계산되나, X 선 회절 분석 결과에서는 검출이 되지 않아 보다 정밀한 조사, 분석이 필요하다고 판단된다.
- Result of EDS analysis for oxygen content in the ultrafine tungsten powders studied in this study
- Result of XRD analysis for ultrafine tungsten powders (Bottom: as-produced, middle: reduction-treated at 400°C for 2h, top: reduction-treated at 500°C for 1h).
- 3.2. 환원 처리 텅스텐 분말의 특성
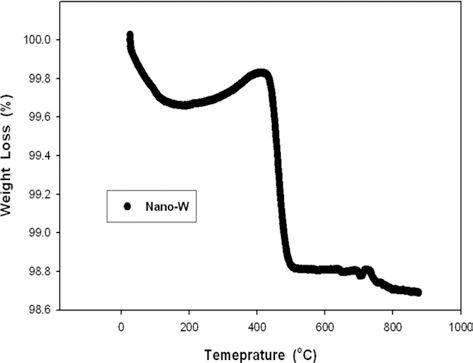
- 그림 5는 초미세 텅스텐 분말의 환원 온도 조건을 찾기 위해 수소 분위기에서 열중량분석을 실시한 결과를 나타낸 것이다. 400-500°C의 온도 범위에서 급격한 무게 변화가 일어나는 것을 확인할 수 있으며, 이러한 무게 변화는 분 말표면의 산화막과 분위기 가스인 수소가 반응하는 환원 반응에 의한 것으로 판단된다. 문헌에 의하면, 마이크론 크 기의 텅스텐 분말에 대한 환원 온도는 800°C 이상인 것으 로 알려져 있으나[6], 이보다 훨씬 낮은 온도에서 환원 반 응이 관찰된 것은 초미세 텅스텐 분말의 높은 표면적으로 환원 반응온도가 낮아질 수 있었기 때문으로 판단된다.
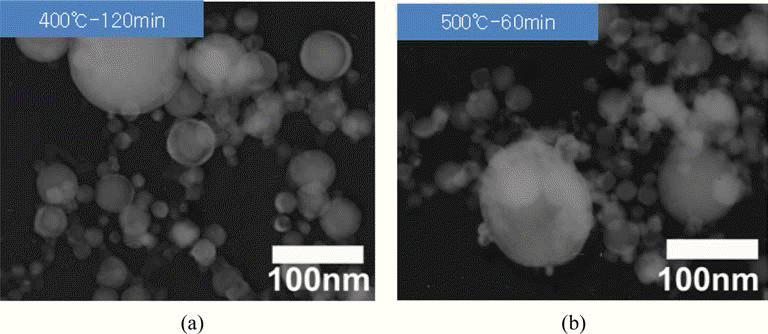
- 앞서 그림 3에서 관찰한 전기선폭발법으로 제조한 초미 세 텅스텐 분말을 다시 각각 400°C-2시간, 500°C-1시간의 조건으로 환원 처리한 분말의 TEM 관찰 결과를 그림 6에 나타내었다. 환원 전과 마찬가지로 조대한 입자와 미세한 입자들이 혼재하고 있음을 확인할 수 있다. 표 2에서 제시 했던 EDS에 의한 산소 조성 분석 결과에서, 전기선폭발법 으로 제조한 부동태 처리 분말은 6.5 wt%의 산소를 포함 하고 있었던 반면, 환원 처리 후 초미세 텅스텐 분말들의 산소 조성은 400°C-2시간 처리 후 2.3 wt%, 500°C-1시간 처리 후 0.7 wt%로 급격히 감소하였다. 그림 4의 X선 회 절 결과에서는 환원 처리 후 β-W peak에 대한 α-W의 peak 강도비가 상대적으로 증가한 것을 확인할 수 있다. 여기서 0.7 wt%로 감소된 산소 조성이 모두 W2O3 또는 WO3를 형 성했다고 가정하면, 이는 각각 전체 중량의 6.1%와 3.4%에 해당하나, X선 회절 분석 결과에서는 확인되지 않아 이 역 시 추가 조사가 필요한 부분이라 사료된다.
- TEM dark-field image of the ultrafine tungsten powders produced by EEW after reduction-treatment in hydrogen atmosphere. (a) at 400°C for 2h and (b) at 500°C for 1h.
- 3.3. 환원 처리한 초미세 텅스텐 분말의 소결체 밀도
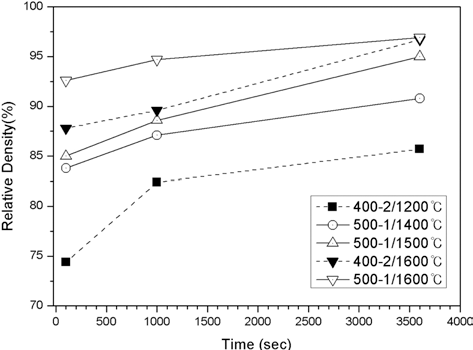
- 그림 7은 400°C-2시간, 500°C-1시간 환원 처리한 초미세 텅스텐 분말을 소결온도 1200, 1400, 1500, 1600°C에서 100- 3600초 동안 소결한 소결체의 밀도를 정리, 요약하여 나타낸 것이다. 소결온도와 소결시간 증가에 따라 소결밀도가 증가 하는 경향을 보였으며, 1600°C에서 1시간 소결하였을 때 두 분말 모두 상대밀도 97%의 최대 소결밀도를 나타내었다.
- Change in relative density of the ultrafine tungsten powder compacts sintered by SPS after reduction treatment at 400°C for 2h and at 500°C for 1h.
- 1600°C의 소결 온도에서 100, 1000, 3600초로 유지시간 을 변화시켰을 때, 400°C-2시간 환원 처리한 분말(산소 조 성 2.3 wt%)의 경우 각각 87.8, 89.6, 96.7%의 소결 밀도를 보였으며, 500°C-1시간 환원 처리한 분말(산소 조성 0.7 wt%)의 소결체는 각각 92.6, 94.7, 96.9%의 소결 밀도를 보여 산소 조성이 보다 낮은 500°C-1시간 환원 처리 분말 의 소결성이 더 우수함을 확인하였다. 이는 환원처리에 의 한 표면 산화막 제거에 따른 소결 과정에서의 확산 촉진에 기인한 것으로 판단된다. 소결체의 산소 조성을 EDS로 확 인한 결과 시편에 따라 산소 조성의 미세한 감소가 확인되 었으나, 그 차이가 크지 않아 방전플라즈마소결 과정에서 일어날 수 있다고 알려진 분말 표면 산화막의 환원 효과는 크지 않았던 것으로 판단된다.
- 3.4. 환원 처리한 초미세 텅스텐 분말의 소결체 미세조직
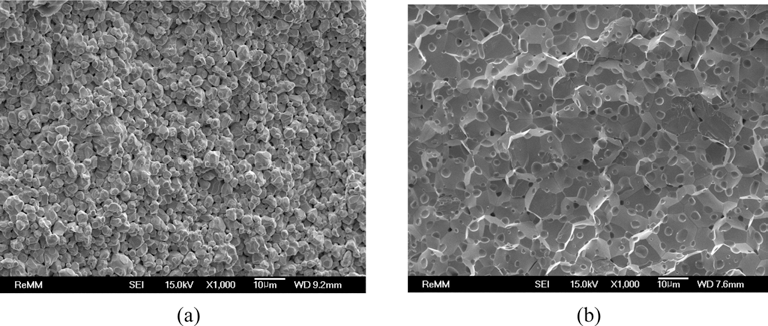
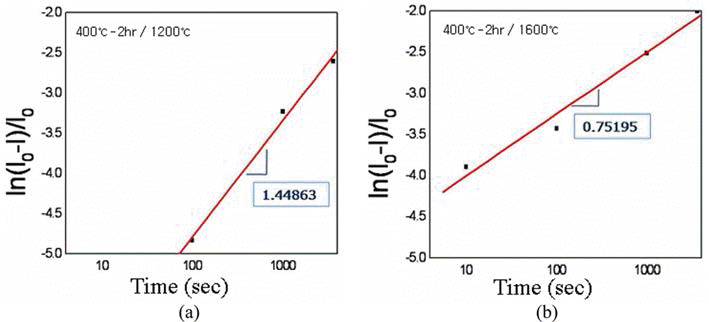
- 그림 8은 400°C-2시간 환원 처리 텅스텐 분말을 각각 소 결 온도 1200°C와 1600°C에서 3600초 동안 소결한 소결체 파면 미세조직을 전계방사주사전자현미경으로 관찰한 결 과이다. 1200°C에서 소결한 시편의 상대밀도는 85.7%로 그림 8(a)의 파면 미세조직에서 분말 입자 간의 결합이 이 미 이루어졌음을 알 수 있으나, 입자성장 단계에는 아직 도 달하지 않았음을 알 수 있다. 1600°C에서 소결한 시편의 상대밀도는 96.7%로 그림 8(b)에서 보는 바와 같이 고밀도 로 치밀화가 이루어졌으나, 입자성장이 상당히 진행되어 대부분의 입자들이 10 μm 크기 이상의 결정립들로 성장하 였음을 알 수 있다. 또한 텅스텐 입자 내부에 다수의 기공 들이 관찰되고 있어 치밀화에 이은 입자성장이 빠른 속도 로 진행되었음을 예상할 수 있다. 그림 9는 위의 소결 실 험 데이터들로부터 1200°C와 1600°C의 소결온도에서의 소 결시간에 대한 수축율을 나타낸 결과로서, 각 직선의 기울 기 값이 각각 1.45와 0.75로 상이한 결과를 보임으로써 온 도별로 주 소결기구가 서로 다를 것임을 예상할 수 있으나, 소결기구의 명확한 해석을 위해서는 확산 거동 등의 추가 연구가 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
- FE-SEM images of the fracture surface of ultrafine tungsten powder compacts after reduction treatment at 400°C for 2h and followed by spark-plasma sintering at (a) 1200°C (85.7% RD) and (b) 1600°C (96.7% RD) for 1h.
- Plots of linear shrinkage vs. sintering time for the spark-plasma sintered ultrafine tungsten powders after reduction treatment at 400°C for 2h: (a) sintered at 1200°C and (b) 1600°C.
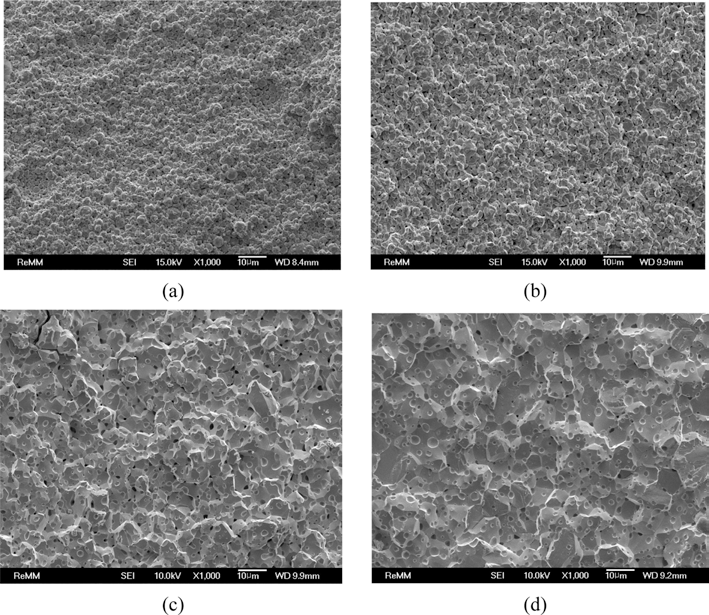
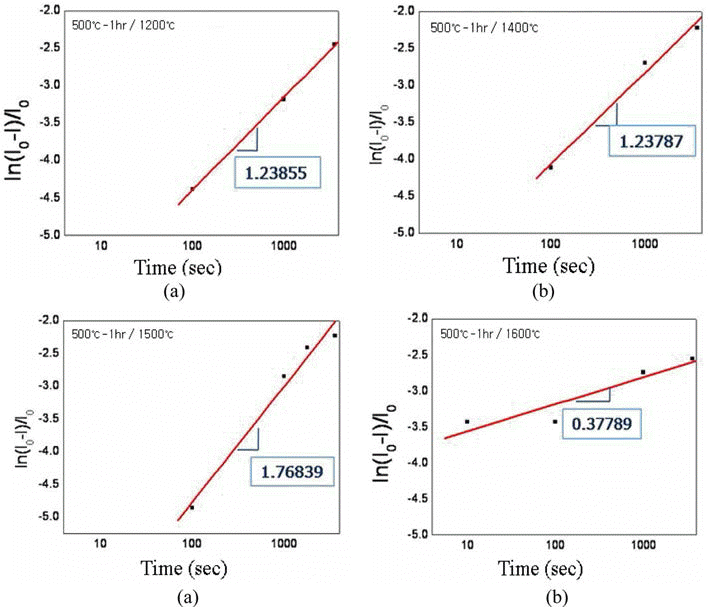
- 그림 10은 500°C-1시간 환원하여 산소 조성이 0.7 wt%인 초미세 텅스텐 분말을 각각 1200, 1400, 1500, 1600°C에서 1시간 동안 방전플라즈마소결한 소결체 파면을 전계방사주 사자현미경으로 관찰한 결과이다. 1200°C 소결체의 경우 (그림 10(a)), 입자 간 결합 형성이 약하게 이루어지고 있음 을 알 수 있으며, 파면으로부터 수 μm에서 10 μm이상의 크기를 갖는 입자들의 흔적을 확인할 수 있다. 소결밀도 90.8%를 나타낸 1400°C 소결체의 경우(그림 10(b))에는 치 밀화가 진행됨에 따라 입자 간의 결합이 더욱 뚜렷하여졌 음을 알 수 있으며, 입자 성장도 시작되었음을 확인할 수 있다. 1500°C로 소결온도를 증가시켜 밀도가 95.0%로 높 아지면서(그림 10(c)), 입자성장이 이미 과도히 일어난 것 을 알 수 있으며, 1600°C로 소결온도를 더욱 증가시킬 경 우 입자성장이 더욱 촉진되는 것을 확인하였다. 앞서 그림 9에서 나타내었던 것과 마찬가지로 소결시간에 대한 수축 율을 그림 11에 나타내었다. 1200°C와 1400°C의 소결온도 에서는 그래프의 기울기 값이 약 1.24로 거의 같아 동일한 기구에 의해 소결이 이루어졌을 것으로 판단된다. 1500°C 와 1600°C의 경우에는 각각 약 1.77과 0.38로 큰 차이를 보 여 서로 다른 기구에 의한 소결이 이루어졌을 것으로 예상된 다. 앞서 그림 9에서 400°C-2시간 환원 처리한 텅스텐 분말 의 1200°C 소결의 경우에는 기울기 값이 약 1.45로 다른 값 을 보였는데 이는 산소 조성 차이에 따른 것으로 사료된다.
- FE-SEM images of the fracture surface of ultrafine tungsten powder compacts after reduction treatment at 500°C for 1h and followed by spark-plasma sintering at (a) 1200°C (81.1%RD), (b) 1400°C (90.8%RD), (c) 1500°C (95.0%RD), and (d) 1600°C (96.9%RD) for 1h.
- Plots of linear shrinkage vs. sintering time for the spark-plasma sintered ultrafine tungsten powders after reduction treatment at 500°C for 1h.
- 3.5. 환원 처리한 초미세 텅스텐 분말의 소결 활성화 에너지
- 500°C-2시간 환원 처리한 초미세 텅스텐 분말을 1200, 1400, 1500, 1600°C의 온도에서 각각 소결하여 얻어진 데 이터와 다음 식으로부터 활성화 에너지를 구하였다[7-8].
- Y는 수축율, Δl/l0이며, C0는 물리적 변수를 포함하는 상 수, n은 지수이다. n값은 ln Y vs. ln t 그래프를 그려 그 기 울기로부터 얻을 수 있으며, 절편으로부터 C를 구하였다. 위의 식에서 절편을 나타내는 식은 아래와 같이 나타낼 수 있다.
- 이 식에서 C vs. n/T 플롯을 하여 기울기를 구하면 Q/R 으로부터 소결 활성화 에너지를 구할 수 있다.
- 위와 같은 과정을 거쳐 구한 소결 활성화 에너지는 95.85 kJ∙mol−1이었으며, 이 값은 기존에 마이크론 크기 분말을 상압소결로 소결한 다른 연구 결과들에서 보고된 소결 활 성화 에너지값이 380-460 kJ∙mol−1인 것에 비해 현저히 낮 은 값이다[9-11]. 이는 텅스텐 분말의 나노 크기에서 기인 한 높은 비표면적 효과와 함께 방전플라즈마소결의 소결 촉진 효과가 복합적으로 작용하였기 때문이라 예상된다. 그러나 보다 명확한 소결 기구를 해석하기 위해서는 텅스 텐 분말의 확산 기구별 활성화 에너지 값이 조사되어야 하 나, 아직 이에 대한 데이터가 충분히 알려져 있지 않아서 추가 조사와 연구가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
실혐 결과 및 고찰
| Specimen | wt% | at% |
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| As-produced by EEW | 6.5 | 44.4 |
| Reduced at 400°C for 120 min in H2 | 2.3 | 30.2 |
| Reduced at 500°C for 60 min in H2 | 0.7 | 7.5 |
(1)
- 전기선폭발법으로 제조된 초미세 텅스텐 분말을 수소 분 위기에서 환원 열처리 한 후 소결 첨가제 없이 방전플라즈 마소결하여 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
텅스텐 분말 내 산소 조성을 500°C에서 1시간 동안 수 소 분위기에서 환원 처리하여 0.7 wt%로 감소시켰을 때, 소결첨가제 없이 1600°C에서 1시간 동안 방전플라즈마소 결하여 상대밀도 97%의 고밀도 소결체를 얻을 수 있다.
초미세 텅스텐 분말의 산소 조성을 0.7 wt%로 제어한 경우, 입자 성장을 억제하면서 95% 이상의 고밀도를 얻기 위해서는 1500-1600°C 범위의 소결 온도에서 30분 이내의 소결 시간을 유지하여야 할 것으로 판단된다.
소결 수축율 데이터로부터 구한 초미세 텅스텐 분 말의 방전플라즈마소결 활성화 에너지는 95.85 kJ∙mol−1 이었다. 이는 마이크론 크기 텅스텐 분말을 상압소결로 소결하였을 때 조사, 보고된 활성화 에너지 값인 380- 460 kJ∙mol−1에 비해 현저히 낮은 값으로 텅스텐 나노분 말의 입자 크기에서 기인한 표면효과와 방전플라즈마소 결의 소결 촉진 효과가 복합적으로 작용했기 때문으로 사료된다.
결 론
-
Acknowledgements
- 본 연구는 국방과학연구소의 기초연구사업(ADD-03-09- 01)으로 수행되었으며, 이에 감사를 드립니다.
감사의 글
- 1. B. K Kim and C. J Choi, Trends in Metals and Materials Engineering. (2000) 13 26.
- 2. B. K Kim and C. J Choi, Trends in Metals and Materials Engineering. (2001) 14 45.
- 3. J. G Park and K. J Lee, Trends in Metals and Materials Engineering. (2000) 13 38.
- 4. Y. S Kwon, Y. H Kim, J. H Kang, M. J Seok, J. S Moon and H. T Kim, J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst. (2001) 8 61.
- 5. L. S Siegl, J. S Kim, W. H Gu, J. C Kim, S Lee, Y. D Kim and Y. S Kwon, (2009) In: 17th Plansee Seminar 2009 Proceedings of International Conference on High Performance P/M Materials Reutte Austria; 3 GT36.
- 6. L Jiqiao, C Shaoyi, Z Zhiqiang, L Haibo and H Baiyun, International J. Refractory Metals and Hard Materials. (1999) 17 423.Article
- 7. G. C Kuczynski, J. Applied Physics. (1950) 21 632.ArticlePDF
- 8. L. C Pathak, S. K Mishra, D Bhattacharya and K. L Chopra, Materials Science and Engineering B. (2004) 110 119.Article
- 9. N. C. J Kothari, Less Common Metals. (1963) 5 140.Article
- 10. H. W Hayden and J. H. J Brophy, Less Common Metals. (1964) 6 214.Article
- 11. R. M German and Z.A Munir, Met. Trans. (1976) 7A 1873.
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Effect of Powder Mixing Process on the Characteristics of Hybrid Structure Tungsten Powders with Nano-Micro Size
Na-Yeon Kwon, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(5): 384. CrossRef
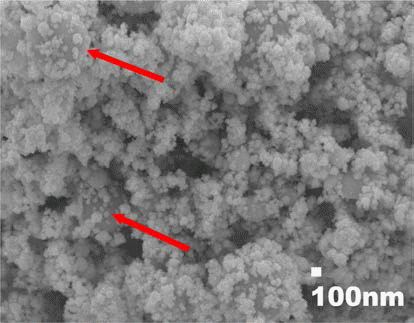
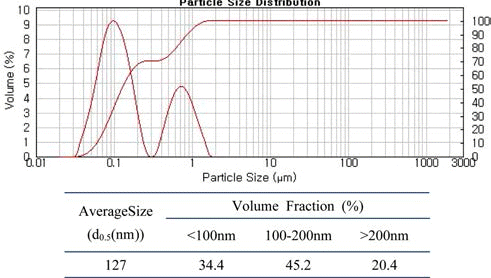
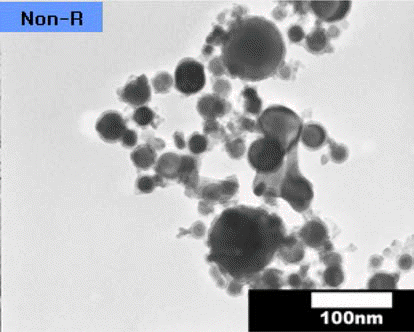
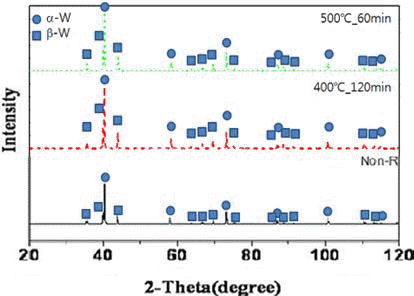
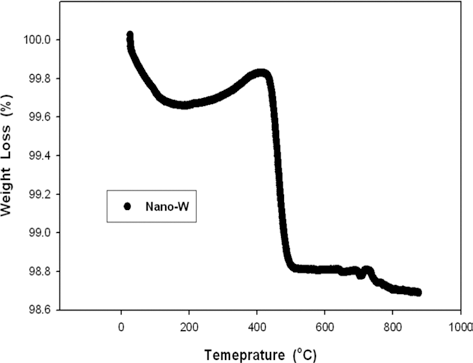
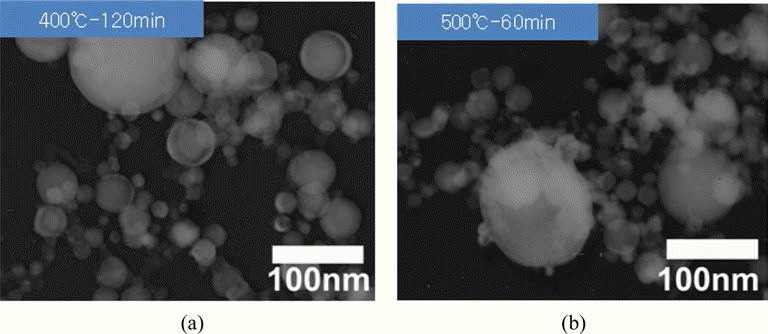
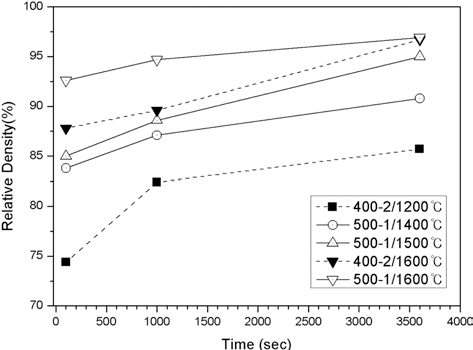
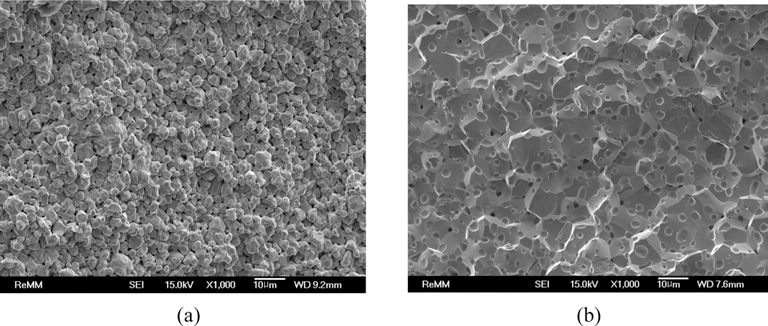
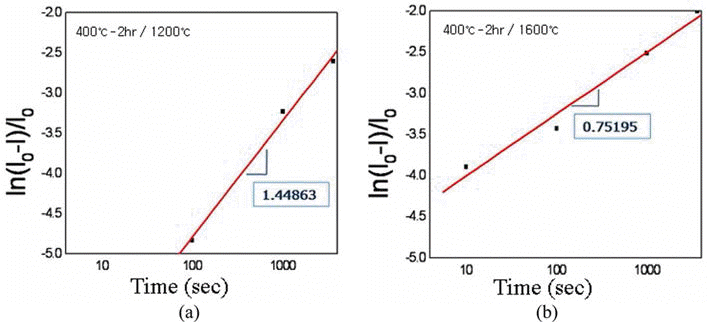
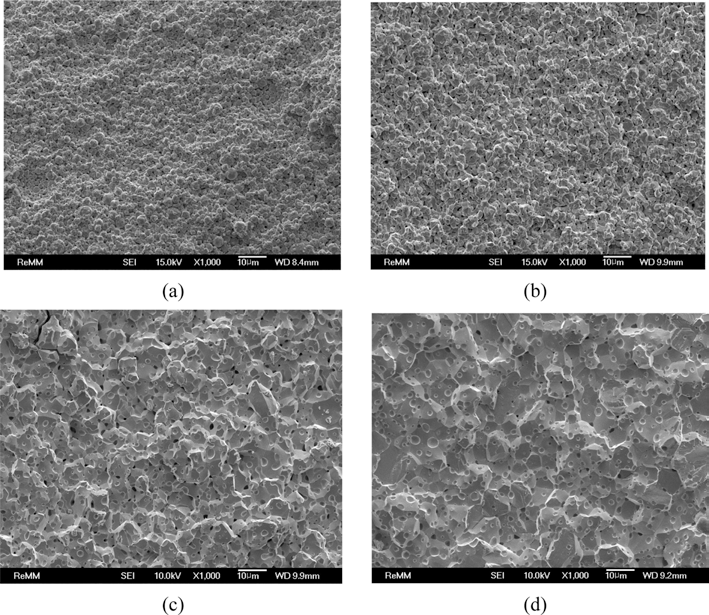
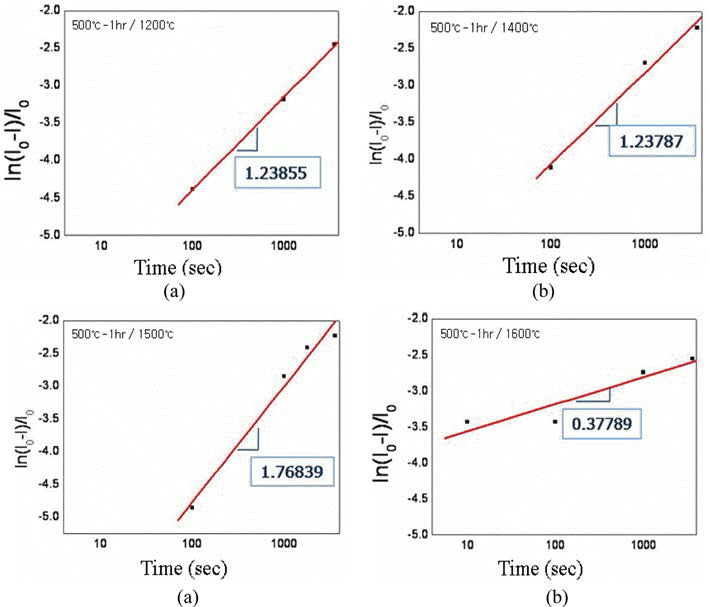
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
Fig. 5.
Fig. 6.
Fig. 7.
Fig. 8.
Fig. 9.
Fig. 10.
Fig. 11.
| Circuit | Capacitance | 2.2~3.2 mF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charging Voltage | 20 kV | |||||||
| Wire | Materials | W | ||||||
| Diameter | 0.3 mm | |||||||
| Feeding Speed | 50 mm/s | |||||||
| Ambient Gas | Species | Ar | ||||||
| Pressure | 0.2 MPa | |||||||
| Equipment | Fan Speed | 3000 rpm (4.5~5m/s) | ||||||
| Specimen | wt% | at% |
|---|---|---|
| As-produced by EEW | 6.5 | 44.4 |
| Reduced at 400°C for 120 min in H2 | 2.3 | 30.2 |
| Reduced at 500°C for 60 min in H2 | 0.7 | 7.5 |
Table 1.
Table 2.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI

 Cite this Article
Cite this Article











