- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Oxygen Reduction and Surface Chemical State of Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb Powder by Ca Vapor
-
Taeheon Kim, Hanjung Kwon, Jae-Won Lim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(1):31-37. Published online February 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.1.31
-
-
1,109
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
This study explores reducing the oxygen content of a commercial Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb powder to less than 400 ppm by deoxidation in the solid state (DOSS) using Ca vapor, and investigates the effect of Ca vapor on the surface chemical state. As the deoxidation temperature increases, the oxygen concentration of the Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb powder decreases, achieving a low value of 745 ppm at 1100°C. When the deoxidation time is increased to 2 h, the oxygen concentration decreases to 320pp m at 1100°C, and the oxygen reduction rate is approximately 78% compared to that of the raw material. The deoxidized Ti-48Al-2Cr-2nb powder maintains a spherical shape, but the surface shape changes slightly owing to the reaction of Ca and Al. The oxidation state of Ti and Al on the surface of the Ti-48Al-2Cr-2Nb powder corresponds to a mixture of TiO2 and Al2O3. As a result, the peaks of metallic Ti and Ti suboxide intensify as TiO2 and Al2O3 in the surface oxide layer are reduced by Ca vapor deposition -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Production of spherical TiAl alloy powder by copper-assisted spheroidization
Jin Qian, Bo Yin, Dashun Dong, Geng Wei, Ming Shi, Shaolong Tang
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 25: 1860. CrossRef - Ca-Mg Multiple Deoxidation of Ti-50Al-2Cr-2Nb Intermetallic Compound Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Seongjae Cho, Taeheon Kim, Jae-Won Lim
ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology.2022; 11(4): 045008. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Lattice Deformation and Improvement Oxidation Resistance of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Powders Prepared by Hydrogen Added Argon Heat Treatment
-
Gye-Hoon Cho, Jung-Min Oh, Jae-Won Lim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.126
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
In the present work, a new hydrogen added argon heat treatment process that prevents the formation of hydrides and eliminates the dehydrogenation step, is developed. Dissolved hydrogen has a good effect on sintering properties such as oxidation resistance and density of greens. This process can also reduce costs and processing time. In the experiment, commercially available Ti-6Al-4V powders are used. The powders are annealed using tube furnace in an argon atmosphere at 700°C and 900°C for 120 min. Hydrogen was injected temporarily during argon annealing to dissolve hydrogen, and a dehydrogenation process was performed simultaneously under an argon-only atmosphere. Without hydride formation, hydrogen was dissolved in the Ti-6Al-4V powder by X-ray diffraction and gas analysis. Hydrogen is first solubilized on the beta phase and expanded the beta phases’ cell volume. TGA analysis was carried out to evaluate the oxidation resistance, and it is confirmed that hydrogen-dissolved Ti-6Al-4V powders improves oxidation resistance more than raw materials.
- [Korean]
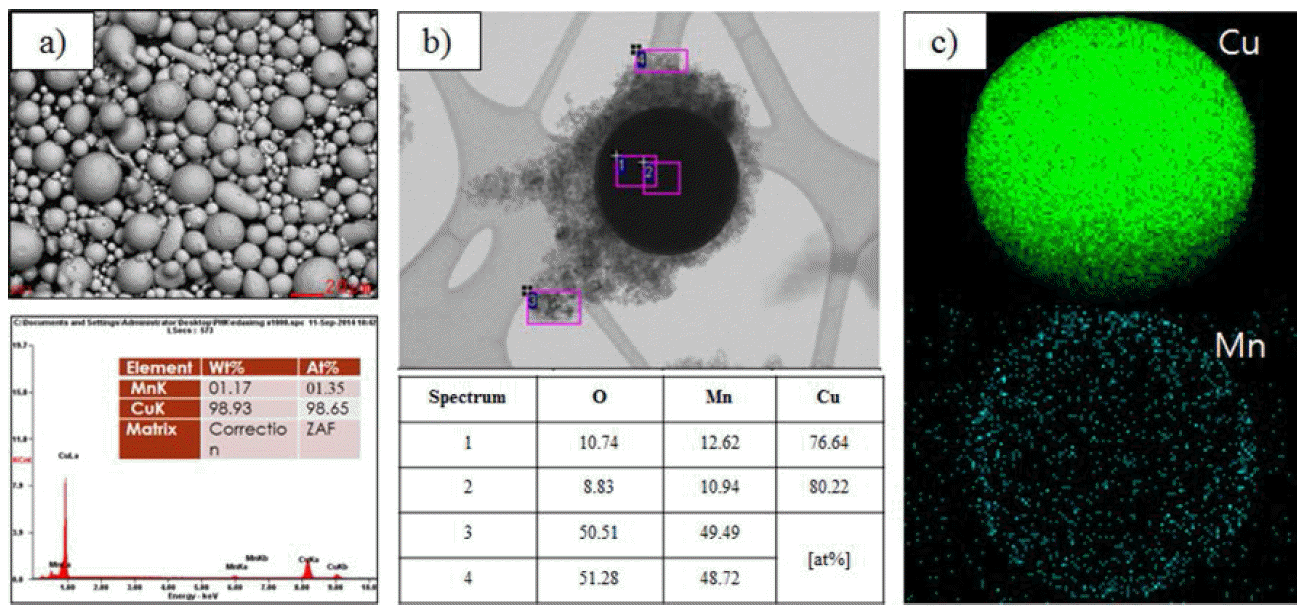
- Fabrication and Property Evaluation of Cu-Mn Compacts for Sputtering Target Application by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Method
-
Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Jae-Won Lim, Hyun-Kuk Park
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):1-7. Published online February 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.1
-
-
1,155
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Cu-Mn compacts are fabricated by the pulsed current activated sintering method (PCAS) for sputtering target application. For fabricating the compacts, optimized sintering conditions such as the temperature, pulse ratio, pressure, and heating rate are controlled during the sintering process. The final sintering temperature and heating rate required to fabricate the target materials having high density are 700°C and 80°C/min, respectively. The heating directly progresses up to 700°C with a 3 min holding time. The sputtering target materials having high relative density of 100% are fabricated by employing a uniaxial pressure of 60 MPa and a sintering temperature of 700°C without any significant change in the grain size. Also, the shrinkage displacement of the Cu-Mn target materials considerably increases with an increase in the pressure at sintering temperatures up to 700°C. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 302. CrossRef
|