- [Korean]
- Fabrication of CNT dispersed Cu matrix composites by wet mixing and spark plasma sintering process
-
Seungchan Cho, Ilguk Jo, Sang-Bok Lee, Sang-Kwan Lee, Moonhee Choi, Jehong Park, Hansang Kwon, Yangdo Kim
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):158-164. Published online April 1, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.158
-
-
971
View
-
18
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)–copper (Cu) composites are successfully fabricated by a combination of a binder-free wet mixing and spark plasma sintering (SPS) process. The SPS is performed under various conditions to investigate optimized processing conditions for minimizing the structural defects of CNTs and densifying the MWCNT–Cu composites. The electrical conductivities of MWCNT–Cu composites are slightly increased for compositions containing up to 1 vol.% CNT and remain above the value for sintered Cu up to 2 vol.% CNT. Uniformly dispersed CNTs in the Cu matrix with clean interfaces between the treated MWCNT and Cu leading to effective electrical transfer from the treated MWCNT to the Cu is believed to be the origin of the improved electrical conductivity of the treated MWCNT–Cu composites. The results indicate the possibility of exploiting CNTs as a contributing reinforcement phase for improving the electrical conductivity and mechanical properties in the Cu matrix composites. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Proposing Machine Learning Models Suitable for Predicting Open Data Utilization
Junyoung Jeong, Keuntae Cho
Sustainability.2024; 16(14): 5880. CrossRef
- [English]
- Dispersion Behavior and Size Analysis of Thermally Purified High Pressure-high Temperature Synthesized Nanodiamond Particles
-
Hansang Kwon, Jehong Park, Marc Leparoux
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):216-222. Published online June 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.216
-
-
1,389
View
-
4
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
Synthesized monocrystalline nanodiamond (nD) particles are heat-treated at various temperatures to produce highly structured diamond crystals. The heat-treated nDs show different weight loss ratios during thermogravimetric analysis. The crystallinities of the heat-treated nDs are analyzed using Raman spectroscopy. The average particle sizes of the heat-treated nDs are measured by a dynamic light scattering (DLS) system and direct imaging observation methods. Moreover, individual dispersion behaviors of the heat-treated nD particles are investigated based on ultrasonic dispersion methods. The average particle sizes of the dispersed nDs according to the two different measurement methods show very similar size distributions. Thus, it is possible to produce highly crystallized nD powder particles by a heattreatment process, and the nD particles are relatively easy to disperse individually without any dispersant. The heattreated nDs can lead to potential applications such as in nanocomposites, quantum dots, and biomedical materials. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Two extreme crystal size scales of diamonds, large single crystal and nanocrystal diamonds: Synthesis, properties and their mutual transformation
Yang Wang, Wei-hua Wang, Shi-lin Yang, Guo-yang Shu, Bing Dai, Jia-qi Zhu
New Carbon Materials.2021; 36(3): 512. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Spark Plasma Sintering Behavior and Heat Dissipation Characteristics of the Aluminum Matrix Composite Materials with the Contents of Graphite
-
Hansang Kwon, Jehong Park, Sungwook Joo, Sanghwui Hong, Jihoon Mun
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):195-201. Published online June 1, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.195
-
-
1,034
View
-
4
Download
-
2
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
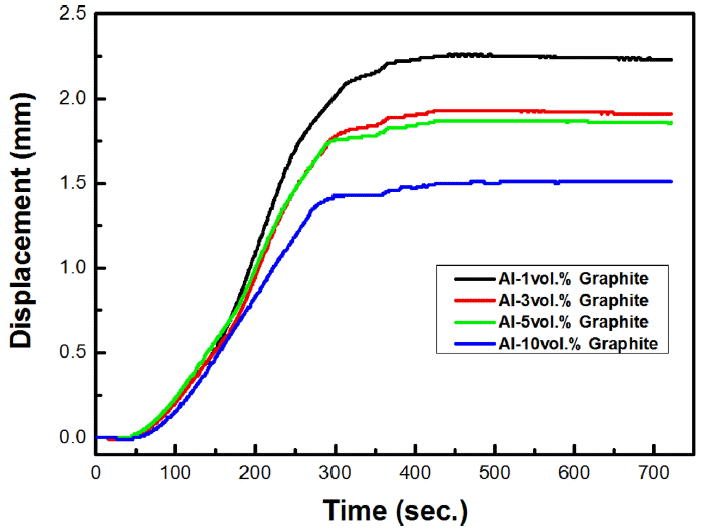
Composite materials consisting of pure aluminum matrix reinforced with different amounts of graphite particles are successfully fabricated by mechanical ball milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS) processes. The shrinkage rates of the composite powders vary with the amount of graphite particles and the lowest shrinkage value is observed for the composite with the highest amount of graphite particles. The current slopes of time increase with increase in the amount of graphite particles whereas the current slopes of temperature show the opposite trend. The highest thermal conductivity is achieved for the composite with the least amount of graphite particles. Therefore, the thermal properties of the composite materials can be controlled by controlling the amount of the graphite particles during the SPS process. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Sintering Behavior and Thermal Properties of Cu-Graphite Materials by a Spark Plasma Sintering Method
Min-hyeok Yang, Bum-soon Park, Hyoung-seok Moon, Jae-cheol Park, Hyun-kuk Park
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2024; 62(6): 411. CrossRef - Effect of processing parameters on the microstructural and mechanical properties of aluminum–carbon nanotube composites produced by spark plasma sintering
B. Sadeghi, M. Shamanian, P. Cavaliere, F. Ashrafizadeh
International Journal of Materials Research.2018; 109(10): 900. CrossRef
|