- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Ni-Cr-Al Metal Foam-Supported Catalysts for the Steam Methane Reforming (SMR), and its Mechanical Stability and Hydrogen Yield Efficiency
-
Kyu-Sik Kim, Tae-Hoon Kang, Man Sik Kong, Man-Ho Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Ji Hye Ahn, Kee-Ahn Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(3):201-207. Published online June 1, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.3.201
-
-
1,293
View
-
19
Download
-
1
Citations
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
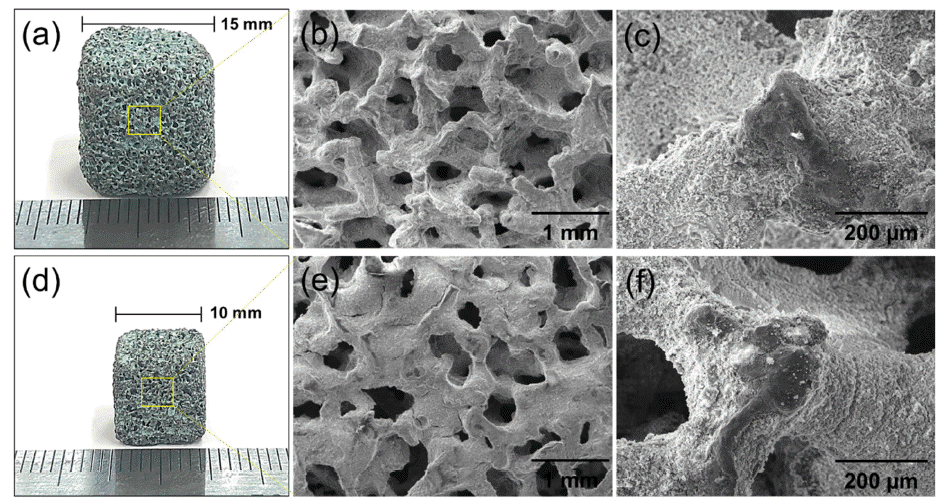
Ni–Cr–Al metal-foam-supported catalysts for steam methane reforming (SMR) are manufactured by applying a catalytic Ni/Al2O3 sol–gel coating to powder alloyed metallic foam. The structure, microstructure, mechanical stability, and hydrogen yield efficiency of the obtained catalysts are evaluated. The structural and microstructural characteristics show that the catalyst is well coated on the open-pore Ni–Cr–Al foam without cracks or spallation. The measured compressive yield strengths are 2–3 MPa at room temperature and 1.5–2.2 MPa at 750°C regardless of sample size. The specimens exhibit a weight loss of up to 9–10% at elevated temperature owing to the spallation of the Ni/Al2O3 catalyst. However, the metal-foam-supported catalyst appears to have higher mechanical stability than ceramic pellet catalysts. In SMR simulations tests, a methane conversion ratio of up to 96% is obtained with a high hydrogen yield efficiency of 82%. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Experimental Investigation of a 98% Hydrogen Peroxide Monopropellant Thruster Comprising the Metal-Foam-Supported Manganese Oxide Catalyst
Pawel Surmacz, Zbigniew Gut
Aerospace.2023; 10(3): 215. CrossRef
- [Korean]
- Structural Characteristics, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Cr-Al Metallic Foam Fabricated by Powder Alloying Process
-
Kyu-Sik Kim, Byeong-Hoon Kang, Man-Ho Park, Jung-Yeul Yun, Kee-Ahn Lee
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(1):37-43. Published online February 1, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.1.37
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
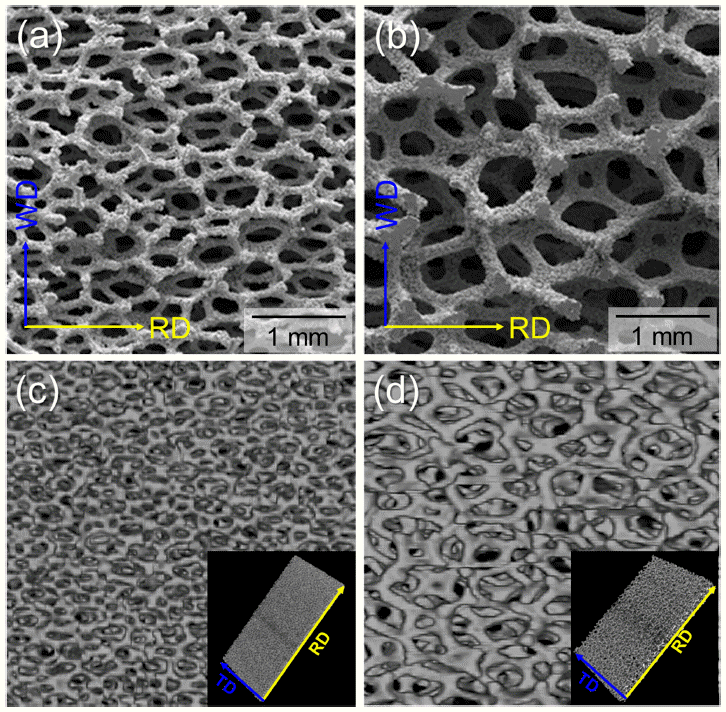
The Fe-22wt.%Cr-6wt.%Al foams were fabricated via the powder alloying process in this study. The structural characteristics, microstructure, and mechanical properties of Fe-Cr-Al foams with different average pore sizes were investigated. Result of the structural analysis shows that the average pore sizes were measured as 474 μm (450 foam) and 1220 μm (1200 foam). Regardless of the pore size, Fe-Cr-Al foams had a Weaire-Phelan bubble structure, and α-ferrite was the major constituent phase. Tensile and compressive tests were conducted with an initial strain rate of 10−3 /s. Tensile yield strengths were 3.4 MPa (450 foam) and 1.4 MPa (1200 foam). Note that the total elongation of 1200 foam was higher than that of 450 foam. Furthermore, their compressive yield strengths were 2.5 MPa (450 foam) and 1.1 MPa (1200 foam), respectively. Different compressive deformation behaviors according to the pore sizes of the Fe-Cr-Al foams were characterized: strain hardening for the 450 foam and constant flow stress after a slight stress drop for the 1200 foam. The effect of structural characteristics on the mechanical properties was also discussed.
|