- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of NiCo2O4/Ni Foam Electrode for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Water Splitting
-
Minsol Kwon, Jaeseong Go, Yesol Lee, Sungmin Lee, Jisu Yu, Hyowon Lee, Sung Ho Song, Dongju Lee
-
J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):411-417. Published online October 1, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.411
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
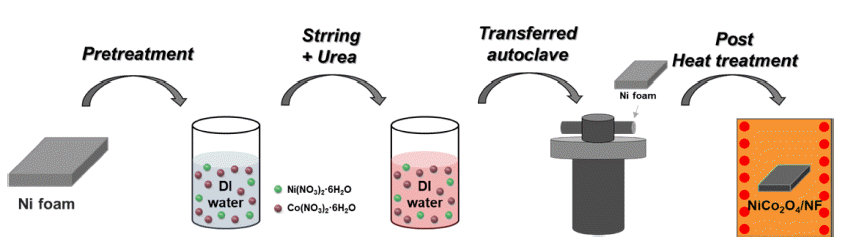
Environmental issues such as global warming due to fossil fuel use are now major worldwide concerns, and interest in renewable and clean energy is growing. Of the various types of renewable energy, green hydrogen energy has recently attracted attention because of its eco-friendly and high-energy density. Electrochemical water splitting is considered a pollution-free means of producing clean hydrogen and oxygen and in large quantities. The development of non-noble electrocatalysts with low cost and high performance in water splitting has also attracted considerable attention. In this study, we successfully synthesized a NiCo2O4/NF electrode for an oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline water splitting using a hydrothermal method, which was followed by post-heat treatment. The effects of heat treatment on the electrochemical performance of the electrodes were evaluated under different heat-treatment conditions. The optimized NCO/NF-300 electrode showed an overpotential of 416 mV at a high current density of 50 mA/cm2 and a low Tafel slope (49.06 mV dec-1). It also showed excellent stability (due to the large surface area) and the lowest charge transfer resistance (12.59 Ω). The results suggested that our noble-metal free electrodes have great potential for use in developing alkaline electrolysis systems.
- [English]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Thermal Battery using Porous MgO Separator Infiltrated with Li based Molten Salts
-
Kyungho Kim, Sungmin Lee, Chae-Nam Im, Seung-Ho Kang, Hae-Won Cheong, Yoonsoo Han
-
J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(5):364-369. Published online October 1, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.5.364
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
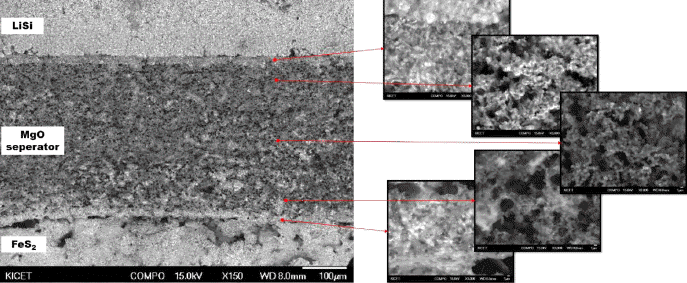
Ceramic powder, such as MgO, is added as a binder to prepare the green compacts of molten salts of an electrolyte for a thermal battery. Despite the addition of a binder, when the thickness of the electrolyte decreases to improve the battery performance, the problem with the unintentional short circuit between the anode and cathode still remains. To improve the current powder molding method, a new type of electrolyte separator with porous MgO preforms is prepared and characteristics of the thermal battery are evaluated. A Spherical PMMA polymer powder is added as a pore-forming agent in the MgO powder, and an organic binder is used to prepare slurry appropriate for tape casting. A porous MgO preform with 300 μm thickness is prepared through a binder burnout and sintering process. The particle size of the starting MgO powder has an effect, not on the porosity of the porous MgO preform, but on the battery characteristics. The porosity of the porous MgO preforms is controlled from 60 to 75% using a pore-forming agent. The batteries prepared using various porosities of preforms show a performance equal to or higher than that of the pellet-shaped battery prepared by the conventional powder molding method.
|