Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- A Parametric Study on the L-PBF Process of an AlSi10Mg Alloy for High-Speed Productivity of Automotive Prototype Parts
- Yeonha Chang, Hyomoon Joo, Wanghyun Yong, Yeongcheol Jo, Seongjin Kim, Hanjae Kim, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(5):390-398. Published online October 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00325
- 2,084 View
- 61 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The AlSi10Mg alloy has garnered significant attention for its application in laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF), due to its lightweight properties and good printability using L-PBF. However, the low production speed of the L-PBF process is the main bottleneck in the industrial commercialization of L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy parts. Furthermore, while L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy exhibits excellent mechanical properties, the properties are often over-specified compared to the target properties of parts traditionally fabricated by casting. To accelerate production speed in L-PBF, this study investigated the effects of process parameters on the build rate and mechanical properties of the AlSi10Mg alloy. Guidelines are proposed for high-speed additive manufacturing of the AlSi10Mg alloy for use in automotive parts. The results show a significant increase in the build rate, exceeding the conventional build rate by a factor of 3.6 times or more, while the L-PBF AlSi10Mg alloy met the specifications for automotive prototype parts. This strategy can be expected to offer significant cost advantages while maintaining acceptable mechanical properties of topology-optimized parts used in the automobile industry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
Jaemin Wang, Seungyeon Lee, Yeon Woo Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Jeong Min Park, Dierk Raabe
Acta Materialia.2026; 304: 121751. CrossRef - Lightweight Design of a Connecting Rod Using Lattice-Structure Parameter Optimisation: A Test Case for L-PBF
Michele Amicarelli, Michele Trovato, Paolo Cicconi
Machines.2025; 13(3): 171. CrossRef - Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Data-Driven analysis relates mechanical properties to pore morphology in laser powder bed fusion
- [Korean]
- Application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Predicting Hardness of AlSi10Mg Alloy Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Junhyub Jeon, Namhyuk Seo, Min-Su Kim, Seung Bae Son, Jae-Gil Jung, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):210-216. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.210
- 1,240 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
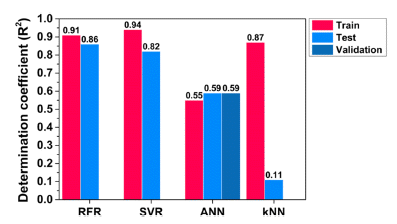
PDF In this study, machine learning models are proposed to predict the Vickers hardness of AlSi10Mg alloys fabricated by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). A total of 113 utilizable datasets were collected from the literature. The hyperparameters of the machine-learning models were adjusted to select an accurate predictive model. The random forest regression (RFR) model showed the best performance compared to support vector regression, artificial neural networks, and k-nearest neighbors. The variable importance and prediction mechanisms of the RFR were discussed by Shapley additive explanation (SHAP). Aging time had the greatest influence on the Vickers hardness, followed by solution time, solution temperature, layer thickness, scan speed, power, aging temperature, average particle size, and hatching distance. Detailed prediction mechanisms for RFR are analyzed using SHAP dependence plots.
- [Korean]
- Improving Flow Property of AlSi10Mg Powder for Additive Manufacturing via Surface Treatment using Methyltrichlorosilane
- Sang Cheol Park, In Yeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee, Soong Ju Oh, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):363-369. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.363
- 898 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
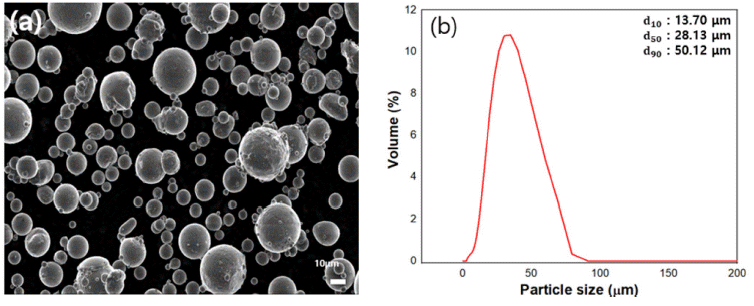
PDF AlSi10Mg alloys are being actively studied through additive manufacturing for application in the automobile and aerospace industries because of their excellent mechanical properties. To obtain a consistently high quality product through additive manufacturing, studying the flowability and spreadability of the metal powder is necessary. AlSi10Mg powder easily forms an oxide film on the powder surface and has hydrophilic properties, making it vulnerable to moisture. Therefore, in this study, AlSi10Mg powder was hydrophobically modified through silane surface treatment to improve the flowability and spreadability by reducing the effects of moisture. The improved flowability according to the number of silane surface treatments was confirmed using a Carney flowmeter. In addition, to confirm the effects of improved spreadability, the powder prior to surface treatment and that subjected to surface treatment four times were measured and compared using s self-designed recoating tester. The results of this study confirmed the improved flowability and spreadability based on the modified metal powder from hydrophilic to hydrophobic for obtaining a highquality additive manufacturing product.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
SangCheol Park, InYeong Kim, Young Il Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Soong Ju Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee, Bin Lee
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(7): 534. CrossRef
- Residual Stress Analysis of Additive Manufactured A356.2 Aluminum Alloys using X-Ray Diffraction Methods
- [Korean]
- Influence of Si-rich Phase Morphologies on Mechanical Properties of AlSi10Mg Alloys p rocessed by S elective L aser M elting a nd P ost-Heat Treatment
- Jung-woo Nam, Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Injoon Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):134-142. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.134
- 722 View
- 0 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, AlSi10Mg powders with average diameters of 44 μm are additively manufactured into bulk samples using a selective laser melting (SLM) process. Post-heat treatment to reduce residual stress in the as-synthesized sample is performed at different temperatures. From the results of a tensile test, as the heat-treatment temperature increases from 270 to 320°C, strength decreases while elongation significantly increases up to 13% at 320°C. The microstructures and tensile properties of the two heat-treated samples at 290 and 320°C, respectively, are characterized and compared to those of the as-synthesized samples. Interestingly, the Si-rich phases that network in the as-synthesized state are discontinuously separated, and the size of the particle-shaped Si phases becomes large and spherical as the heat-treatment temperature increases. Due to these morphological changes of Si-rich phases, the reduction in tensile strengths and increase in elongations, respectively, can be obtained by the post-heat treatment process. These results provide fundamental information for the practical applications of AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by SLM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Wear behavior of aluminum-matrix particle (TiH2 and ZrH2)-reinforced composite foam additively manufactured using directed energy deposition
Hwa-Jeong Kim, Gwang-Yong Shin, Ki-Yong Lee, Do-Sik Shim
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 25: 222. CrossRef - Effect of Microstructural Evolution on Mechanical Properties and Fracture Modes of AlSi10Mg Blocks Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting after Stress Relief Annealing
Jianzhu Li, Yujie Li, Zhe Wang, Changguang Li, Hai Yuan, Yun Hao
Advanced Engineering Materials.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Wear behavior of aluminum-matrix particle (TiH2 and ZrH2)-reinforced composite foam additively manufactured using directed energy deposition
- [Korean]
- Manufacture of AlSi10Mg Alloy Powder for Powder Bed Fusion(PBF) Process using Gas Atomization Method
- Weon Bin Im, Seung Joon Park, Yeo Chun Yun, Byeong Cheol Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(2):120-126. Published online April 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.2.120

- 1,468 View
- 13 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
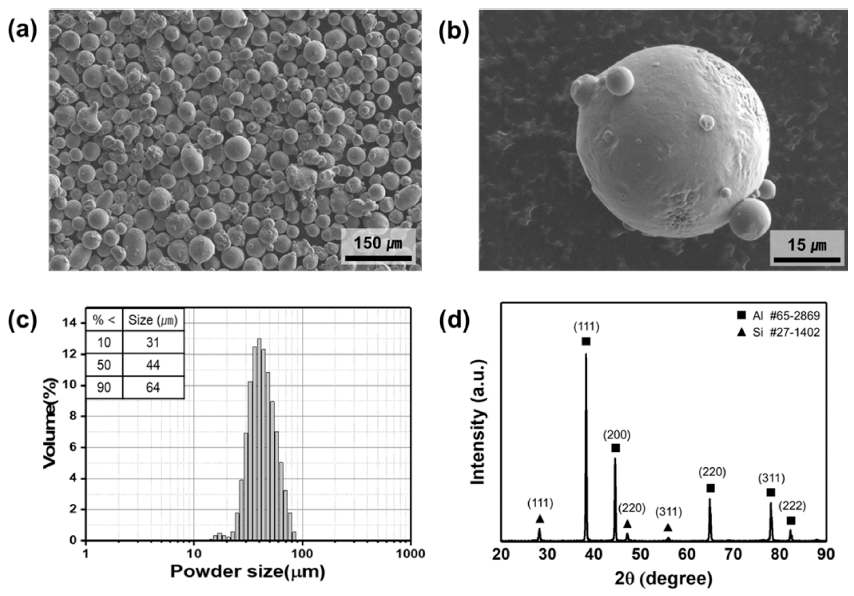
PDF In this study, AlSi10Mg alloy powders are synthesized using gas atomization and sieving processes for powder bed fusion (PBF) additive manufacturing. The effect of nozzle diameter (ø = 4.0, 4.5, 5.0 and 8.0 mm) on the gas atomization and sieving size on the properties of the prepared powder are investigated. As the nozzle diameter decreases, the size of the manufactured powder decreases, and the uniformity of the particle size distribution improves. Therefore, the ø 4.0 mm nozzle diameter yields powder with superior properties. Spherically shaped powders can be prepared at a scale suitable for the PBF process with a particle size distribution of 10–45 μm. The Hausner ratio value of the powder is measured to be 1.24. In addition, the yield fraction of the powder prepared in this study is 26.6%, which is higher than the previously reported value of 10–15%. These results indicate that the nozzle diameter and the post-sieve process simultaneously influence the shape of the prepared powder as well as the satellite powder on its surface.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
Jongik Lee, Taehoo Kang, Ukju Gim, Sehun Kim, Sanghee Jung, Jimin Han, Bin Lee
Powder Metallurgy.2025; 68(4): 333. CrossRef - Effect of thermal debinding conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of a biomedical Ti-15Nb-5Sn alloy prepared by material extrusion additive manufacturing (MEAM) process
Jin-hwan Lim, Soo-yeong Kim, Tae-gyun Gu, Shuanglei Li, Tae-hyun Nam
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2025; 1044: 184366. CrossRef - Effect of Phase Composition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Biomedical Ti-15Nb-5Sn Alloy Prepared by Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing
Jin-hwan Lim, Gyeong-ho Kang, Shuanglei Li, Tae-hyun Nam
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of a Laboratory-Scale Gas-Atomized AlSi10Mg Powder and a Commercial-Grade Counterpart for Laser Powder Bed Fusion Processing
Fabrizio Marinucci, Alberta Aversa, Diego Manfredi, Mariangela Lombardi, Paolo Fino
Materials.2022; 15(21): 7565. CrossRef
-
SiO
2
nanoparticle-coated Ti-6Al-4V spherical powder for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process
- [Korean]
- Influence of Powder Size on Properties of Selectively Laser-Melted- AlSi10Mg Alloys
- Yeong Seong Eom, Dong Won Kim, Kyung Tae Kim, Sang Sun Yang, Jungho Choe, Injoon Son, Ji Hun Yu
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2020;27(2):103-110. Published online April 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2020.27.2.103

- 1,093 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Aluminum (Al) - based powders have attracted attention as key materials for 3D printing because of their excellent specific mechanical strength, formability, and durability. Although many studies on the fabrication of 3Dprinted Al-based alloys have been reported, the influence of the size of raw powder materials on the bulk samples processed by selective laser melting (SLM) has not been fully investigated. In this study, AlSi10Mg powders of 65 μm in average particle size, prepared by a gas atomizing process, are additively manufactured by using an SLM process. AlSi10Mg powders of 45 μm average size are also fabricated into bulk samples in order to compare their properties. The processing parameters of laser power and scan speed are optimized to achieve densified AlSi10Mg alloys. The Vickers hardness value of the bulk sample prepared from 45 μm-sized powders is somewhat higher than that of the 65 μm-sized powder. Such differences in hardness are analyzed because the reduction in melt pool size stems from the rapid melting and solidification of small powders, compared to those of coarse powders, during the SLM process. These results show that the size of the powder should be considered in order to achieve optimization of the SLM process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser Soldering Process Optimization of MEMS Probe of Probe Card for Semiconductor Wafer Test
Myeongin Kim, Won Sik Hong, Mi-Song Kim
Journal of Welding and Joining.2022; 40(3): 271. CrossRef - Investigation on Interfacial Microstructures of Stainless Steel/Inconel Bonded by Directed Energy Deposition of alloy Powders
Yeong Seong Eom, Kyung Tae Kim, Soo-Ho Jung, Jihun Yu, Dong Yeol Yang, Jungho Choe, Chul Yong Sim, Seung Jun An
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 219. CrossRef
- Laser Soldering Process Optimization of MEMS Probe of Probe Card for Semiconductor Wafer Test
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


