Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Trends and Implications of International Standardization for Rare Earths
- Sardar Farhat Abbas, Sang-Hyun lee, Bin Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):165-169. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.165
- 998 View
- 7 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth elements (REEs) are considered to be vital to modern industry due to their important roles in applications such as permanent magnets, automobile production, displays, and many more. The imbalance between demand and supply of REEs can be solved by recycling processes. Regarding the needs of industry and society, the International Organization for Standardization, Technical Committee 298 (ISO/TC298) Rare Earths has been recently launched for developing international standards on rare earth elements. In accordance with the suggestion of its constituents, it is tentatively working to develop the appropriate standards under five working groups (WG) on terms and definitions (WG1), element recycling (WG2), environmental stewardship (WG3), packaging, labelling, marking, transport, and storage (WG4), and testing analysis (WG5). The scope and structure of ISO/TC298 on the topic of rare earths is discussed in this document.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sm2Co17 particles using salt-assisted spray pyrolysis and a reduction-diffusion process
Tae-Yeon Hwang, Jimin Lee, Min Kyu Kang, Gyutae Lee, Jongryoul Kim, Yong-Ho Choa
Applied Surface Science.2019; 475: 986. CrossRef - Worker Safety in the Rare Earth Elements Recycling Process From the Review of Toxicity and Issues
Seo-Ho Shin, Hyun-Ock Kim, Kyung-Taek Rim
Safety and Health at Work.2019; 10(4): 409. CrossRef
- Synthesis and magnetic properties of Sm2Co17 particles using salt-assisted spray pyrolysis and a reduction-diffusion process
- [Korean]
- Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
- Doyeon Kim, Hyun-Su Park, Hye Mi Cho, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(6):489-493. Published online December 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.6.489
- 1,596 View
- 12 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
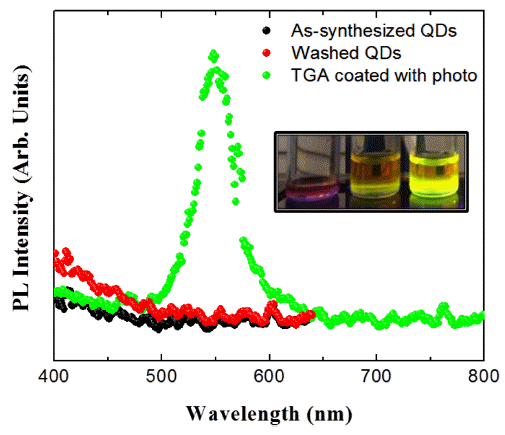
PDF In this study, the surface passivation process for InP-based quantum dots (QDs) is investigated. Surface coating is performed with poly(methylmethacrylate) (PMMA) and thioglycolic acid. The quantum yield (QY) of a PMMA-coated sample slightly increases by approximately 1.3% relative to that of the as-synthesized InP/ZnS QDs. The QYs of the uncoated and PMMA-coated samples drastically decrease after 16 days because of the high defect state density of the InP-based QDs. PMMA does not have a significant effect on the defect passivation. Thioglycolic acid is investigated in this study for the effective surface passivation of InP-based QDs. Surface passivation with thioglycolic acid is more effective than that with the PMMA coating, and the QY increases from 1.7% to 11.3%. ZnS formed on the surface of the InP QDs and S in thioglycolic acid show strong bonding property. Additionally, the QY is further increased up to 21.0% by the photochemical reaction. Electron–hole pairs are formed by light irradiation and lead to strong bonding between the inorganic and thioglycolic acid sulfur. The surface of the InP core QDs, which does not emit light, is passivated by the irradiated light and emits green light after the photochemical reaction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef
- Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
- [Korean]
- Surface Treatment Method for Long-term Stability of CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots
- Hyun-Su Park, Da-Woon Jeong, Bum-Sung Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan-Gi Lee, Woo-Byoung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):1-5. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.1
- 1,530 View
- 5 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
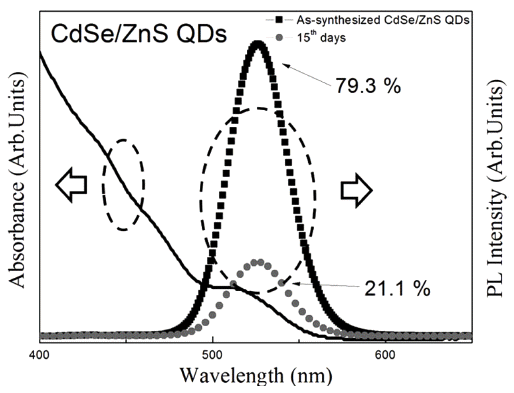
PDF We have investigated the washing method of as-synthesized CdSe/ZnS core/shell structure quantum dots (QDs) and the effective surface passivation method of the washed QDs using PMMA. The quantum yield (QY%) of assynthesized QDs decreases with time, from 79.3% to 21.1%, owing to surface reaction with residual organics. The decreased QY% is restored to the QY% of as-synthesized QDs by washing. However, the QY% of washed QDs also decreases with time, owing to the absence of surface passivation layer. On the other hand, the PMMA-treated QDs maintained a relatively higher QY% after washing than that of the washed QDs that were kept in toluene solution for 30 days. Formation of the PMMA coating layer on CdSe/ZnS QD surface is confirmed by HR-TEM and FT-IR. It is found that the PMMA surface coating, when combined with washing, is useful to be applied in the storage of QDs, owing to its long-term stability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improvement of Short-Circuit Current of Quantum Dot Sensitive Solar Cell Through Various Size of Quantum Dots
Seung Hwan Ji, Hye Won Yun, Jin Ho Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2021; 31(1): 16. CrossRef - Poly(methylmethacrylate) coating on quantum dot surfaces via photo-chemical reaction for defect passivation
Doyeon Kim, So-Yeong Joo, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2019; 376: 206. CrossRef - Study on Surface-defect Passivation of InP System Quantum Dots by Photochemical Method
Doyeon Kim, Hyun-Su Park, Hye Mi Cho, Bum-Sung Kim, Woo-Byoung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(6): 489. CrossRef
- Improvement of Short-Circuit Current of Quantum Dot Sensitive Solar Cell Through Various Size of Quantum Dots
- [Korean]
- Synthesis and analysis CdSe Quantum dot with a Microfluidic Reactor Using a Combinatorial Synthesis System
- Myung Hwan Hong, Duk-Hee Lee, Lee-Seung Kang, Chan Gi Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Nam-Hoon Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(2):143-148. Published online April 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.2.143
- 871 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
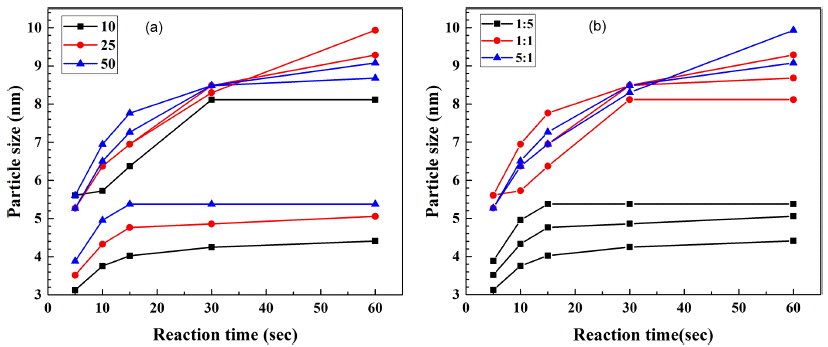
PDF A microfluidic reactor with computer-controlled programmable isocratic pumps and online detectors is employed as a combinatorial synthesis system to synthesize and analyze materials for fabricating CdSe quantum dots for various applications. Four reaction condition parameters, namely, the reaction temperature, reaction time, Cd/Se compositional ratio, and precursor concentration, are combined in synthesis condition sets, and the size of the synthesized CdSe quantum dots is determined for each condition. The average time corresponding to each reaction condition for obtaining the ultraviolet–visible absorbance and photoluminescence spectra is approximately 10 min. Using the data from the combinatorial synthesis system, the effects of the reaction conditions on the synthesized CdSe quantum dots are determined. Further, the data is used to determine the relationships between the reaction conditions and the CdSe particle size. This method should aid in determining and selecting the optimal conditions for synthesizing nanoparticles for diverse applications.
- [Korean]
- Supply and Demand Strategy of Rare Metal in Korea − Focusing on the Stocking pile −
- Taek-Soo Kim, Bum-Sung Kim, Min-Ha Lee, Kyoung-Tae Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):313-317. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.313

- 964 View
- 4 Download
- [English]
- Production of Porous Metallic Glass Granule by Optimizing Chemical Processing
- Song-Yi Kim, Bo-Kyung Guem, Min-Ha Lee, Taek-Soo Kim, Jurgen Eckert, Bum-Sung Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(4):251-255. Published online August 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.4.251
- 1,107 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
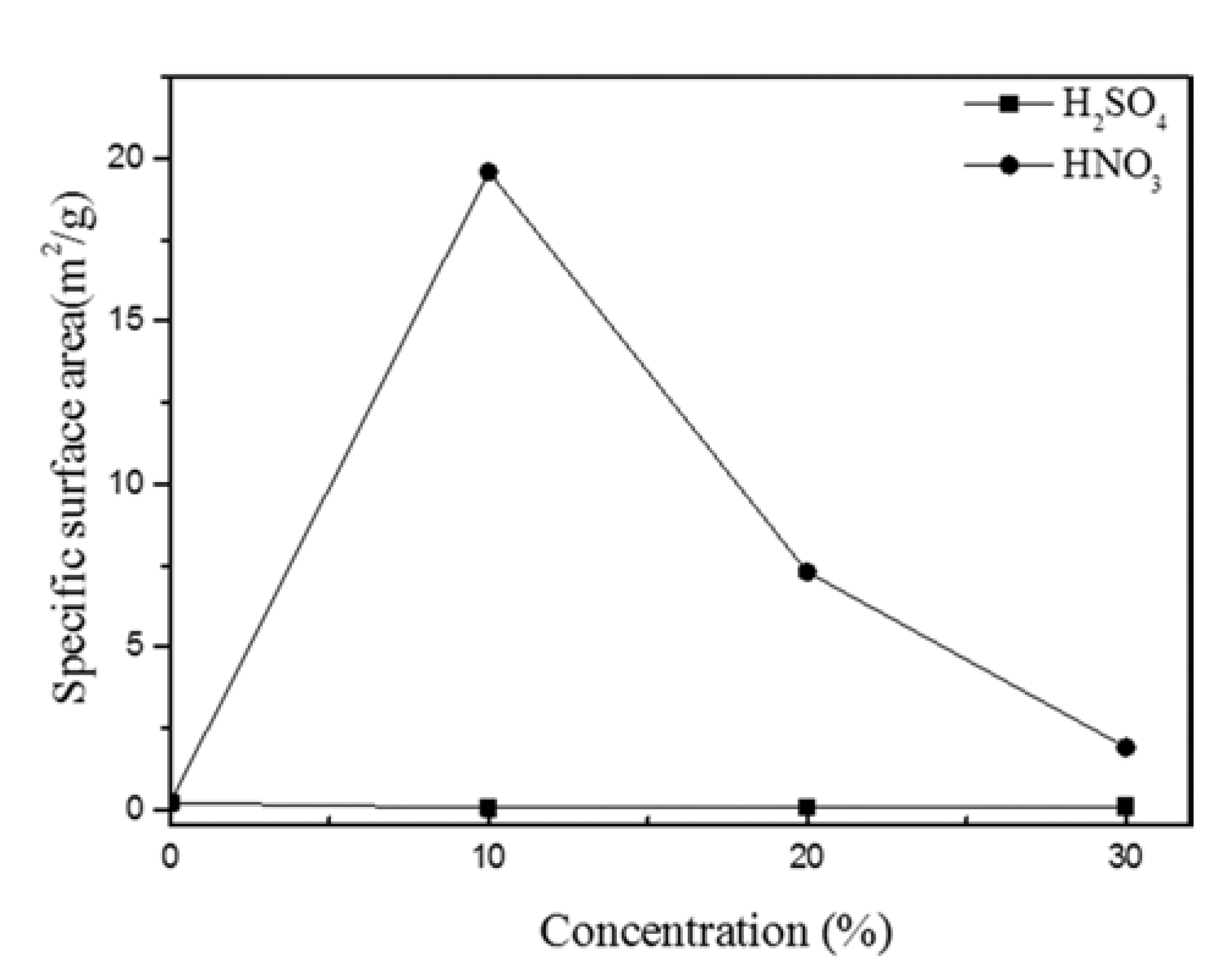
PDF In this study, we optimized dissolution the dissolution conditions of porous amorphous powder to have high specific surface area. Porous metallic glass(MG) granules were fabricated by selective phase dissolution, in which brass is removed from a composite powder consisting of MG and 40 vol.% brass. Dissolution was achieved through various concentrations of H2SO4 and HNO3, with HNO3 proving to have the faster reaction kinetics. Porous powders were analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry to observe crystallization behavior. The Microstructure of milled powder and dissolved powder was analyzed by scanning electron microscope. To check for residual in the dissolved powder after dissolution, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscory and elemental mapping was conducted. It was confirmed that the MG/brass composite powder dissolved in 10% HNO3 produced a porous MG granule with a relatively high specific surface area of 19.60 m2/g. This proved to be the optimum dissolution condition in which both a porous internal granule structure and amorphous phase were maintained. Consequently, porous MG granules were effectively fabricated and applications of such structures can be expanded.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
Soo-Hyun Joo, Dong-Hai Pi, Jing Guo, Hidemi Kato, Sunghak Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(3): 383. CrossRef
- Enhanced wear resistivity of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass processed by high-pressure torsion under reciprocating dry conditions
- [Korean]
- Patent Analysis for the Preparation of Rare Metals
- Kee-Ahn Lee, Jae-Sung Oh, Jae-Yeon Kim, Bum-Sung Kim, Taek-Soo Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(2):147-154. Published online April 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.2.147

- 806 View
- 2 Download
- [Korean]
- Development of Heat Shielding Part for RFID Tag using Porous Aluminum Alloy
- Jae-Oh Bang, Hyo-Soo Lee, Taek-Kyun Jung, Min-Ha Lee, Bum-Sung Kim, Seung-Boo Jung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(2):135-140.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.2.135

- 847 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) is an automatic identification method, relying on storing and remotely retrieving data using devices called RFID tags or transponders. Some RFID tags have been used in severe environment of temperature ranged from 200°C to 250°C for a long time and may cause serious problems such as signal error, short life cycle and explosion. Conventionally, the RFID tags for high temperature applications consisted of Fe-alloy housing part, ceramic powder and RFID sensor. However, it has disadvantage of heavy weight, signal noise and heat shield capability. In this study, we newly applied the aluminum porous materials fabricated by polymer leaching process into RFID tags in order to improve heat shielding ability, and compared the properties of RFID tag inserted by aluminum porous with the conventional one.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Vacuum Thin-Film-Forming Mold using Porous Aluminum
Hyung-Sun Kang, Sunghyun Lee
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2020; 29(6): 435. CrossRef
- Development of Vacuum Thin-Film-Forming Mold using Porous Aluminum
- [Korean]
- Enhancement of the Light Harvesting of Dye-sensitized Solar Cell by Inserting Scattering Layer
- Jung-Gyu Nam, Bum-Sung Kim, Jai-Sung Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(5):305-309.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.5.305

- 491 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The effect of light scattering layers (400 nm, TiO_2 particle) of 4 mum thickness on the dye-sensitized solar cell has been investigated with a 12 mum thickness of photo-anode (20 nm, TiO_2 particle). Two different structures of scattering layers (separated and back) were applied to investigate the light transmitting behaviors and solar cell properties. The light transmittance and cell efficiency significantly improved with inserting scattering layers. The back scattering layer structure had more effective transmitting behavior, but separated scattering layer (center: 2 mum, back: 2 mum) structure (9.83% of efficiency) showing higher efficiency (0.6%), short circuit current density (0.26 mA/cm2) and fill factor (0.02). The inserting separating two scattering layers improved the light harvesting, and relatively thin back scattering layer (2 mum of thickness) minimized interruption of ion diffusion in liquid electrolyte.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


