Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of Ti Porous body with Improved Specific Surface Area by Synthesis of CNTs
- Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):235-239. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.235
- 265 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
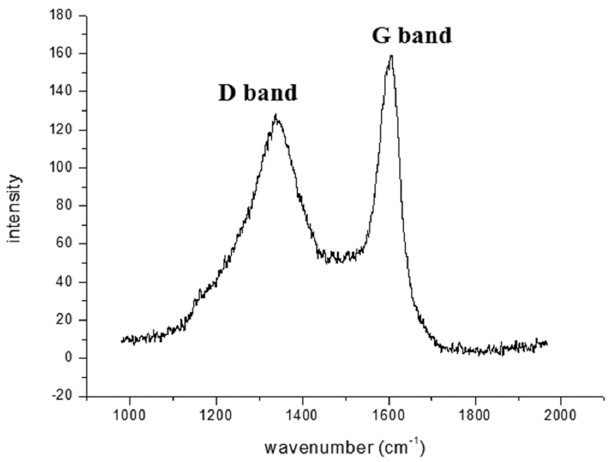
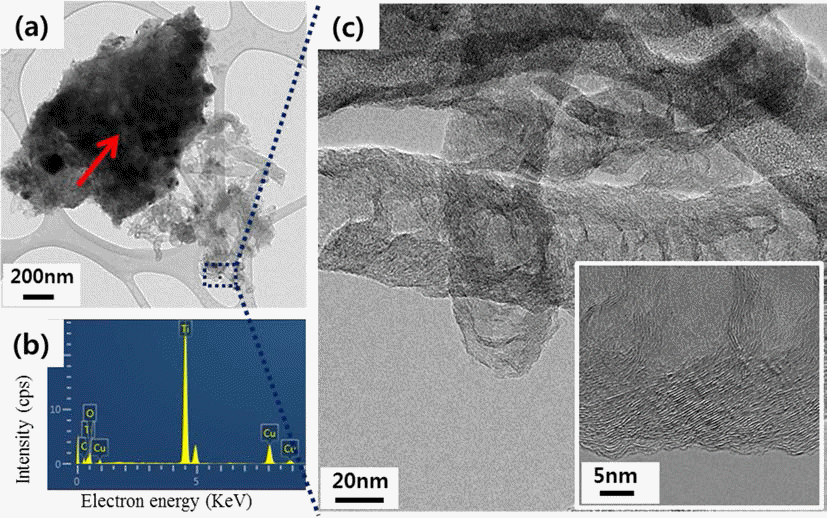
PDF This study is performed to fabricate a Ti porous body by freeze drying process using titanium hydride (TiH2) powder and camphene. Then, the Ti porous body is employed to synthesize carbon nanotubes (CNTs) using thermal catalytic chemical vapor deposition (CCVD) with Fe catalyst and methane (CH4) gas to increase the specific surface area. The synthesized Ti porous body has 100 μm-sized macropores and 10-30 μm-sized micropores. The synthesized CNTs have random directions and are entangled with adjacent CNTs. The CNTs have a bamboo-like structure, and their average diameter is about 50 nm. The Fe nano-particles observed at the tip of the CNTs indicate that the tip growth model is applicable. The specific surface area of the CNT-coated Ti porous body is about 20 times larger than that of the raw Ti porous body. These CNT-coated Ti porous bodies are expected to be used as filters or catalyst supports.
- [Korean]
- CNT Growth Behavior on Ti Substrate by Catalytic CVD Process with Temperature Gradient in Tube Furnace
- Ju Hyuk Park, Jong Min Byun, Hyung Soo Kim, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(5):371-376. Published online October 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.5.371
- 647 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, modified catalytic chemical vapor deposition (CCVD) method was applied to control the CNTs (carbon nanotubes) growth. Since titanium (Ti) substrate and iron (Fe) catalysts react one another and form a new phase (Fe2TiO5) above 700°C, the decrease of CNT yield above 800°C where methane gas decomposes is inevitable under common CCVD method. Therefore, we synthesized CNTs on the Ti substrate by dividing the tube furnace into two sections (left and right) and heating them to different temperatures each. The reactant gas flew through from the end of the right tube furnace while the Ti substrate was placed in the center of the left tube furnace. When the CNT growth temperature was set 700/950°C (left/right), CNTs with high yield were observed. Also, by examining the micro-structure of CNTs of 700/950°C, it was confirmed that CNTs show the bamboo-like structure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication of Ti Porous body with Improved Specific Surface Area by Synthesis of CNTs
Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(3): 235. CrossRef - Synthesis of CNT on a Camphene Impregnated Titanium Porous Body by Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition
Hogyu Kim, Hye Rim Choi, Jong Min Byun, Myung-Jin Suk, Sung-Tag Oh, Young Do Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(2): 122. CrossRef
- Fabrication of Ti Porous body with Improved Specific Surface Area by Synthesis of CNTs
TOP
 kpmi
kpmi


 First
First Prev
Prev


