Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Hot-Cracking Behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 Medium-Entropy Alloys Manufactured via Powder Bed Fusion
- Seungjin Nam, Heechan Jung, Haeum Park, Chahee Jung, Jeong Min Park, Hyoung Seop Kim, Seok Su Sohn
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):537-545. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00262
- 959 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
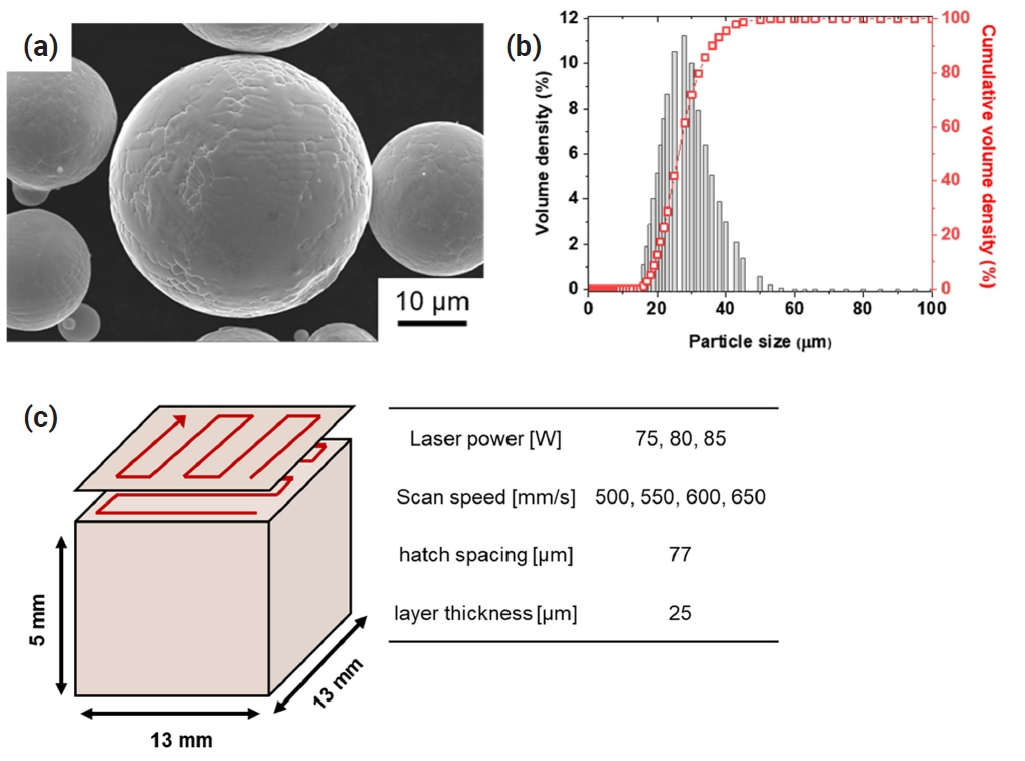
PDF - Additive manufacturing makes it possible to improve the mechanical properties of alloys through segregation engineering of specific alloying elements into the dislocation cell structure. In this study, we investigated the mechanical and microstructural characteristics of CoNi-based medium-entropy alloys (MEAs), including the refractory alloying element Mo with a large atomic radius, manufactured via laser-powder bed fusion (L-PBF). In an analysis of the printability depending on the processing parameters, we achieved a high compressive yield strength up to 653 MPa in L-PBF for (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs. However, severe residual stress remained at high-angle grain boundaries, and a brittle µ phase was precipitated at Mo-segregated dislocation cells. These resulted in hot-cracking behaviors in (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs during L-PBF. These findings highlight the need for further research to adjust the Mo content and processing techniques to mitigate cracking behaviors in L-PBF-manufactured (CoNi)85Mo15 MEAs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Min Jae Baek, Dong Jun Lee, Jae Wung Bae, Ji-Hun Yu, Jeong Min Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 244. CrossRef
- Effect of Support Structure on Residual Stress Distribution in Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- [Korean]
- Analyses of Creep Properties of Ni-base Superalloy Powders as Cooling Rate after Solid Solution Heat Treatment
- Chan Jun, Youngseon Lee, Byeong Beom Bae, Hong-Kyu Kim, Seong Suk Hong, Donghoon Kim, Jondo Yun, Eun Yoo Yoon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):247-253. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.247
- 752 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
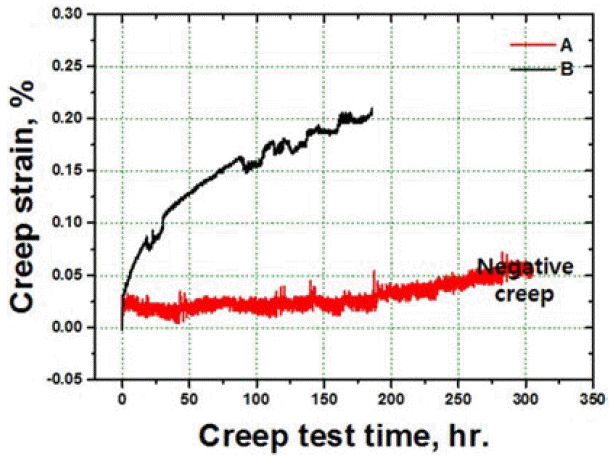
PDF In this study, solid solution heat treatment of consolidated nickel-based superalloy powders is carried out by hot isotactic pressing. The effects of the cooling rate of salt quenching, and air cooling on the microstructures and the mechanical properties of the specimens are analyzed . The specimen that is air cooled shows the formation of serrated grain boundaries due to their obstruction by the carbide particles. Moreover, the specimen that is salt quenched shows higher strength than the one that is air cooled due to the presence of fine and close-packed tertiary gamma prime phase. The tensile elongation at high temperatures improves due to the presence of grain boundary serrations in the specimen that is air cooled. On the contrary, the specimen that is salt quenched and consists of unserrated grain boundaries shows better creep properties than the air cooled specimen with the serrated grain boundaries, due to the negative creep phenomenon.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


