Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Effect of Single and Dual Doping of Rare Earth Metal Ce and Nd Elements on Electrochemical Properties of LiNi0.83 Co0.11Mn0.06O2 Cathode Lithium-ion Battery Material
- Yoo-Young Kim, Jong-Keun Ha, Kwon-Koo Cho
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):49-57. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.49
- 1,993 View
- 21 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
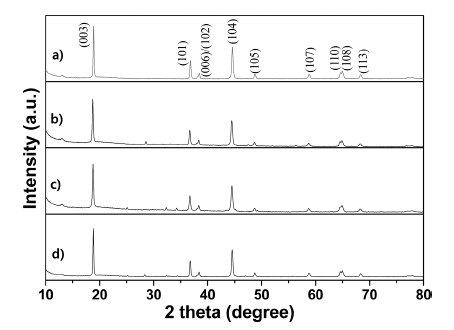
PDF Layered LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode materials single- and dual-doped by the rare-earth elements Ce and Nd are successfully fabricated by using a coprecipitation-assisted solid-phase method. For comparison purposes, nondoping pristine LiNi0.83Co0.11Mn0.06O2 cathode material is also prepared using the same method. The crystal structure, morphology, and electrochemical performances are characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) mapping, and electrochemical techniques. The XRD data demonstrates that all prepared samples maintain a typical α-NaFeO2-layered structure with the
R-3m -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
Heewon Choi, Nam-gyu Lim, Seong Jun Lee, Jungsoo Park
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology.2021; 35(6): 2697. CrossRef - Synthesis of CeVO4-V2O5 nanowires by cation-exchange method for high-performance lithium-ion battery electrode
Xueliu Xu, Shiying Chang, Taofang Zeng, Yidan Luo, Dong Fang, Ming Xie, Jianhong Yi
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2021; 887: 161237. CrossRef
- Numerical approach for lithium-ion battery performance considering various cathode active material composition for electric vehicles using 1D simulation
- [Korean]
- Effects of Porous Microstructure on the Electrochemical Properties of Si-Ge-Al Base Anode Materials for Li-ion Rechargeable Batteries
- Chung Rae Cho, Myeong Geun Kim, Keun Yong Sohn, Won-Wook Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(1):24-28. Published online February 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.1.24
- 645 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
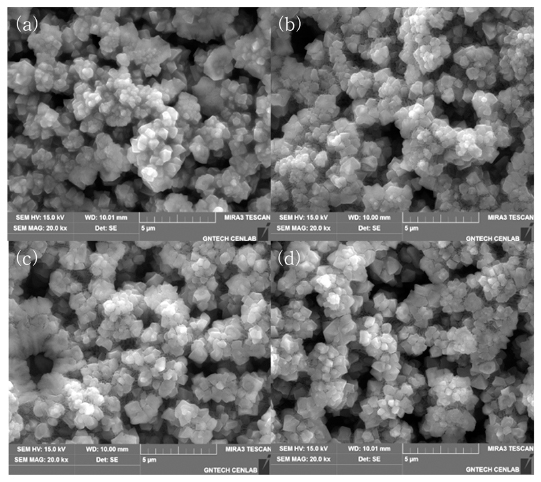
PDF Silicon alloys are considered promising anode active materials to replace Li-ion batteries by graphite powder, because they have a relatively high capacity of up to 4200 mAh/g, and are environmentally friendly and inexpensive ECO-materials. However, its poor charge/discharge properties, induced by cracking during cycles, constitute their most serious problem as anode electrode. In order to solve these problems, Si-Ge-Al alloys with porous structure are designed as anode alloy powders, to improve cycling stability. The alloys are melt-spun to obtain the rapidly solidified ribbons, and then ball-milled to make fine powders. The powders are etched using 1 M HCl solution, which gives the powders a porous structure by removing the element Al. Subsequently, in this study, the microstructures and the characteristics of the etched powders are evaluated for application as anode materials. As a result, the etched porous powder shows better electrochemical properties than as-milled Si-Ge-Al powder.
- [English]
- Using Carboxylmethylated Cellulose as Water-Borne Binder to Enhance the Electrochemical Properties of Li4Ti5O12-Based Anodes
- Lili Liu, Chongling Cheng, Hongjiang Liu, Liyi Shi, Dayang Wang
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(5):315-320. Published online October 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.5.315
- 1,242 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
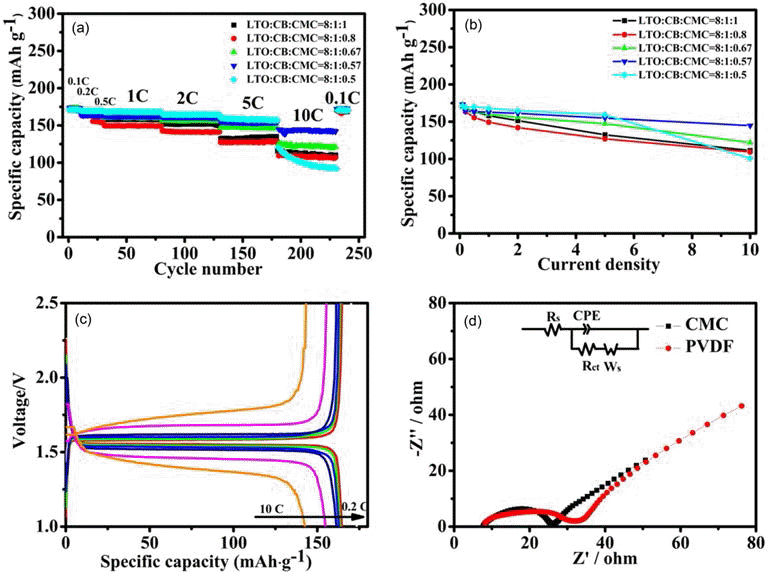
PDF The present work reports a systematic study of using carboxymethylated cellulose (CMC) as water-borne binder to produce Li4Ti5O12-based anodes for manufacture of high rate performance lithium ion batteries. When the LTO-to-CB-to-CMC mass ratio is carefully optimized to be 8:1:0.57, the special capacity of the resulting electrodes is 144 mAh·g−1 at 10 C and their capacity retention was 97.7% after 1000 cycles at 1 C and 98.5% after 500 cycles at 5 C, respectively. This rate performance is comparable or even better than that of the electrolytes produced using conventional, organic, polyvinylidene fluoride binder.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


