Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Laser Processing of an Al0.1CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy + Cu Composite Powders via Laser Powder Bed Fusion
- Kwangtae Son, Ji-Woon Lee, Soon-Jik Hong, Somayeh Pasebani
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(4):277-287. Published online August 29, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00101

- 1,103 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study examined process–structure relationships in laser powder bed fusion of Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi + Cu composites, focusing on densification, elemental distribution, and solidification cracking. Mechanically mixed Al₀.₁CoCrFeNi and Cu powders were processed across a range of laser powers (100–250 W) and scan speeds (200–800 mm/s). Increased volumetric energy density (VED) improved densification, with a plateau near 200 J/mm³ yielding ~96% relative density; however, this value was still below application-grade thresholds. At low VED, insufficient thermal input and short melt pool residence times promoted Cu segregation, while higher VED facilitated improved elemental mixing. Elemental mapping showed partial co-segregation of Ni with Cu at low energies. Solidification cracks were observed across all processing conditions. In high VED regimes, cracking exhibited a minimal correlation with segregation behavior and was primarily attributed to steep thermal gradients, solidification shrinkage, and residual stress accumulation. In contrast, at low VED, pronounced Cu segregation appeared to exacerbate cracking through localized thermal and mechanical mismatch.
- [English]
- Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
- Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang Oanh, , Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):191-201. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00143

- 2,384 View
- 76 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) exhibit complex phase formation behavior, challenging conventional predictive methods. This study presents a machine learning (ML) framework for phase prediction in HEAs, using a curated dataset of 648 experimentally characterized compositions and features derived from thermodynamic and electronic descriptors. Three classifiers—random forest, gradient boosting, and CatBoost—were trained and validated through cross-validation and testing. Gradient boosting achieved the highest accuracy, and valence electron concentration (VEC), atomic size mismatch (δ), and enthalpy of mixing (ΔHmix) were identified as the most influential features. The model predictions were experimentally verified using a non-equiatomic Al₃₀Cu₁₇.₅Fe₁₇.₅Cr₁₇.₅Mn₁₇.₅ alloy and the equiatomic Cantor alloy (CoCrFeMnNi), both of which showed strong agreement with predicted phase structures. The results demonstrate that combining physically informed feature engineering with ML enables accurate and generalizable phase prediction, supporting accelerated HEA design.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef - Preparation and Arc Erosion Behavior of Cu-Based Contact Materials Reinforced with High Entropy Particles CuCrNiCoFe
Jiacheng Tong, Jun Wang, Huimin Zhang, Haoran Liu, Youchang Sun, Zhiguo Li, Wenyi Zhang, Zhe Wang, Yanli Chang, Zhao Yuan, Henry Hu
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B.2025; 56(5): 5948. CrossRef - Recent progresses on high entropy alloy development using machine learning: A review
Abhishek Kumar, Nilay Krishna Mukhopadhyay, Thakur Prasad Yadav
Computational Materials Today.2025; 8: 100038. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Alloying Behavior of Ultra-Lightweight AlTiCrVMg High-Entropy Alloy via Al-Mg Mutual Solubility and Sintering Control
- Eunhyo Song, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):254-261. Published online June 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00059

- 652 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) incorporating low-melting-point elements (Mg and Al) and high-melting-point elements (Ti, Cr, and V) were fabricated via mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Sintering temperatures were varied to investigate phase behavior and microstructural evolution. X-ray diffraction was used to identify phase structures, scanning electron microscopy to analyze microstructures, X-ray fluorescence to determine elemental composition, and a gas pycnometer to measure density. Micro-Vickers hardness testing was conducted to evaluate mechanical properties. Mechanical-alloyed HEAs exhibited a body-centered cubic (BCC) phase and lamellar structures with element-enriched regions. Sintering introduced additional BCC and Laves phases, while higher temperatures promoted Mg liquid-phase sintering, increasing density and hardness. This study highlights the effects of sintering on HEAs containing elements with differing melting points to optimize their properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
Wooyoung Lee, Munsu Choi, Sungwook Kim, Dae-Kyeom Kim, Myungsuk Song, Taek-Soo Kim, Jungwan Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Materials Science and Engineering: A.2026; 954: 149811. CrossRef
- Effect of annealing temperature on thermal expansion and cryogenic mechanical properties of low-thermal-expansion Co22.2Cr6.2Fe48.8Ni17.8Cu5.0 medium-entropy alloy
- [English]
- Characterization of the Manufacturing Process and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys via Metal Injection Molding and Hot Isostatic Pressing
- Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Do Won Lee, Hyojeong Ha, Jungho Choe, Jaemin Wang, Seong Jin Park, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(3):243-254. Published online June 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00059
- 2,221 View
- 56 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
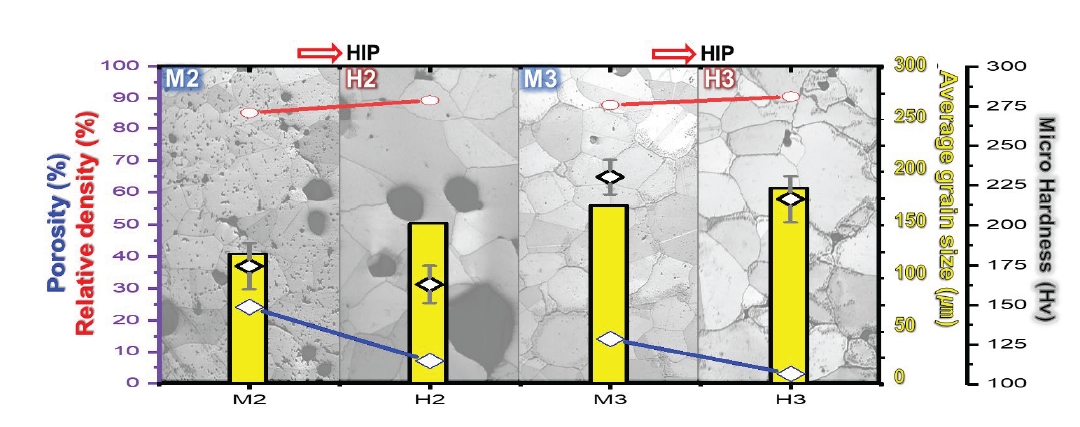
PDF - High-entropy alloys (HEAs) have been reported to have better properties than conventional materials; however, they are more expensive due to the high cost of their main components. Therefore, research is needed to reduce manufacturing costs. In this study, CoCrFeMnNi HEAs were prepared using metal injection molding (MIM), which is a powder metallurgy process that involves less material waste than machining process. Although the MIM-processed samples were in the face-centered cubic (FCC) phase, porosity remained after sintering at 1200°C, 1250°C, and 1275°C. In this study, the hot isostatic pressing (HIP) process, which considers both temperature (1150°C) and pressure (150 MPa), was adopted to improve the quality of the MIM samples. Although the hardness of the HIP-treated samples decreased slightly and the Mn composition was significantly reduced, the process effectively eliminated many pores that remained after the 1275°C MIM process. The HIP process can improve the quality of the alloy.
- [English]
- Fabrication of Equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy by Metal Injection Molding Process Using Coarse-Sized Powders
- Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Ji Sun Lee, Jungho Choe, Soung Yeoul Ahn, Sang Guk Jeong, Do Won Lee, Seong Jin Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(1):1-6. Published online February 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.1.1
- 1,770 View
- 33 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
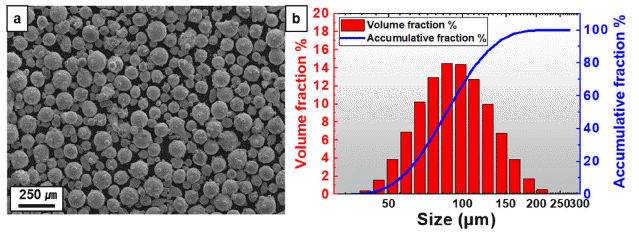
PDF High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are attracting attention because of their excellent properties and functions; however, they are relatively expensive compared with commercial alloys. Therefore, various efforts have been made to reduce the cost of raw materials. In this study, MIM is attempted using coarse equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi HEA powders. The mixing ratio (powder:binder) for HEA feedstock preparation is explored using torque rheometer. The block-shaped green parts are fabricated through a metal injection molding process using feedstock. The thermal debinding conditions are explored by thermogravimetric analysis, and solvent and thermal debinding are performed. It is densified under various sintering conditions considering the melting point of the HEA. The final product, which contains a small amount of non-FCC phase, is manufactured at a sintering temperature of 1250°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of 3D interconnected nanoporous TiZrHfNbTaNi high-entropy alloy via liquid metal dealloying and subsequent synthesis of (TiZrHfNbTaNi)O high-entropy oxide
Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Vin Ha, Jihye Seong, Akira Takeuchi, Ruirui Song, Hidemi Kato, Soo-Hyun Joo
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 35: 5204. CrossRef - Development of 3D interconnected heterogeneous high-entropy alloy composites with enhanced multifunctionality via liquid metal dealloying
Munsu Choi, Gang Hee Gu, Jongun Moon, Jae Wung Bae, Hidemi Kato, Seung Zeon Han, Hyoung Seop Kim, Yongseok Choi, Soo-Hyun Joo
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 37: 5672. CrossRef - Characterization of the Manufacturing Process and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys via Metal Injection Molding and Hot Isostatic Pressing
Eun Seong Kim, Jae Man Park, Do Won Lee, Hyojeong Ha, Jungho Choe, Jaemin Wang, Seong Jin Park, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(3): 243. CrossRef
- Development of 3D interconnected nanoporous TiZrHfNbTaNi high-entropy alloy via liquid metal dealloying and subsequent synthesis of (TiZrHfNbTaNi)O high-entropy oxide
- [Korean]
- Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeMnNi-type High-entropy Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting: A Review
- Jeong Min Park
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(2):132-151. Published online April 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.2.132
- 2,588 View
- 37 Download
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
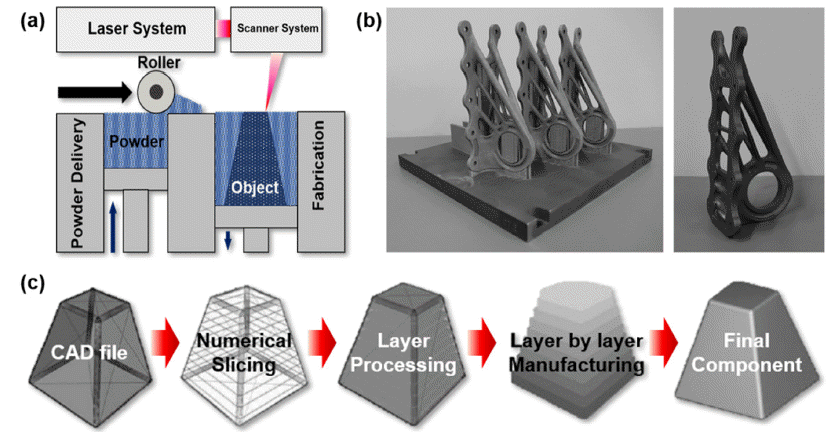
PDF The CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy (HEA), which is the most widely known HEA with a single facecentered cubic structure, has attracted significant academic attention over the past decade owing to its outstanding multifunctional performance. Recent studies have suggested that CoCrFeMnNi-type HEAs exhibit excellent printability for selective laser melting (SLM) under a wide range of process conditions. Moreover, it has been suggested that SLM can not only provide great topological freedom of design but also exhibit excellent mechanical properties by overcoming the strength–ductility trade-off via producing a hierarchical heterogeneous microstructure. In this regard, the SLM-processed CoCrFeMnNi HEA has been extensively studied to comprehensively understand the mechanisms of microstructural evolution and resulting changes in mechanical properties. In this review, recent studies on CoCrFeMnNi-type HEAs produced using SLM are discussed with respect to process-induced microstructural evolution and the relationship between hierarchical heterogeneous microstructure and mechanical properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
Nguyen Lam Khoa, Nguyen Duy Khanh, Hoang Thi Ngoc Quyen, Nguyen Thi Hoang, Oanh, Le Hong Thang, Nguyen Hoa Khiem, Nguyen Hoang Viet
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(3): 191. CrossRef - Investigation of effects of process parameters on microstructure and fracture toughness of SLM CoCrFeMnNi
Joseph Agyapong, Diego Mateos, Aleksander Czekanski, Solomon Boakye-Yiadom
Journal of Alloys and Compounds.2024; 987: 173998. CrossRef - Cryogenic Tensile Behavior of Ferrous Medium-entropy Alloy Additively Manufactured by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Seungyeon Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jae Wung Bae, Jeong Min Park
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(1): 8. CrossRef - Data-driven Approach to Explore the Contribution of Process Parameters for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Jeong Min Park, Jaimyun Jung, Seungyeon Lee, Haeum Park, Yeon Woo Kim, Ji-Hun Yu
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2024; 31(2): 137. CrossRef - Cryogenic tensile behavior of carbon-doped CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloys additively manufactured by laser powder bed fusion
Haeum Park, Hyeonseok Kwon, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-Hun Yu, Jungho Choe, Hyokyung Sung, Hyoung Seop Kim, Jung Gi Kim, Jeong Min Park
Additive Manufacturing.2024; 86: 104223. CrossRef - Microstructural evolution and high strain rate deformation response of SLM-printed CoCrFeMnNi after annealing and deep-cryogenic treatment
Joseph Agyapong, Aleksander Czekanski, Solomon Boakye Yiadom
Materials Characterization.2024; 218: 114506. CrossRef - High-speed manufacturing-driven strength-ductility improvement of H13 tool steel fabricated by selective laser melting
Yeon Woo Kim, Haeum Park, Young Seong Eom, Dong Gill Ahn, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji-hun Yu, Yoon Suk Choi, Jeong Min Park
Powder Metallurgy.2023; 66(5): 582. CrossRef
- Thermodynamic and Electronic Descriptor-Driven Machine Learning for Phase Prediction in High-Entropy Alloys: Experimental Validation
- [Korean]
- New Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 high-entropy alloy Fabricated by Powder Metallurgy
- Dami Yim, Hyung Keun Park, Antonio Joao Seco Ferreira Tapia, Byeong-Joo Lee, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(3):208-212. Published online June 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.3.208

- 1,024 View
- 5 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this paper, a new Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 high entropy alloy (HEA) is identified as a strong candidate for the single face-centered cubic (FCC) structure screened using the upgraded TCFE2000 thermodynamic CALPHAD database. The Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA is fabricated using the mechanical (MA) procedure and pressure-less sintering method. The Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA, which consists of elements with a large difference in melting point and atomic size, is successfully fabricated using powder metallurgy techniques. The MA behavior, microstructure, and mechanical properties of the Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA are systematically studied to understand the MA behavior and develop advanced techniques for fabricating HEA products. After MA, a single FCC phase is found. After sintering at 900°C, the microstructure has an FCC single phase with an average grain size of 18 μm. Finally, the Co10Fe10Mn35Ni35Zn10 HEA has a compressive yield strength of 302 MPa.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Composites of equiatomic Y, La, Ce, Nd, and Gd rare earth oxides: Chemical-shift effects and valence spectra
Jungsu Bin, Hyunbae Gee, Taesung Park, UiJun Go, Jeoung Han Kim, Youn-Seoung Lee
Current Applied Physics.2024; 59: 85. CrossRef - Fabrication, microstructure and mechanical property of a novel Nb-rich refractory high-entropy alloy strengthened by in-situ formation of dispersoids
Byungchul Kang, Taeyeong Kong, Ahmad Raza, Ho Jin Ryu, Soon Hyung Hong
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 81: 15. CrossRef
- Composites of equiatomic Y, La, Ce, Nd, and Gd rare earth oxides: Chemical-shift effects and valence spectra
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


