Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Effect of Calcium Addition on the High-Temperature Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Scrap Using Mg-Based Extractants
- Hyoseop Kim
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):493-499. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00283
- 1,138 View
- 15 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
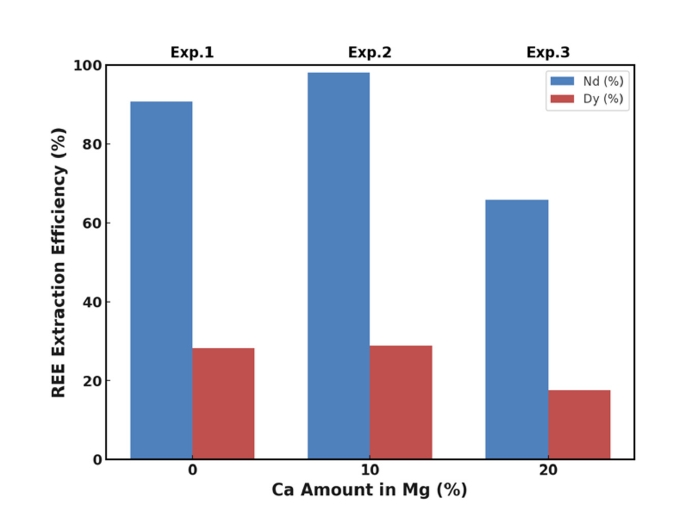
PDF - This study investigated whether calcium (Ca) addition improved the recovery of neodymium (Nd) and dysprosium (Dy) from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap using magnesium (Mg)-based liquid metal extraction (LME). Traditional LME processes are limited to temperatures up to 850 °C due to oxidation issues, reducing the efficiency of rare earth element (REE) recovery, especially for Dy. By adding 10 wt.% Ca to Mg and increasing the processing temperature to 1,000 °C, we achieved nearly 100% Nd and approximately 38% Dy recovery, compared to 91% and 28%, respectively, with pure Mg at 850 °C. However, excessive Ca addition (20 wt.%) decreased the recovery efficiency due to the formation of stable intermetallic compounds. These results highlight the critical role of Ca in optimizing REE recycling from Nd-Fe-B magnet scrap.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Acid Leaching Conditions on the Properties of Cr Powder Produced by Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis
- YongKwan Lee, YeongWoo Cho, ShinYoung Choi, SungGue Heo, Ju Won, KyoungTae Park, MiHye Lee, JaeJin Sim
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(3):233-241. Published online June 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.3.233
- 624 View
- 3 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
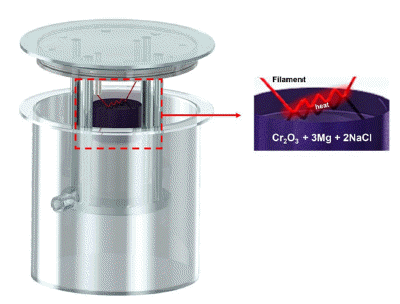
PDF In this study, we evaluated the effects of acid leaching on the properties of Cr powder synthesized using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS). Cr powder was synthesized from a mixture of Cr2O3 and magnesium (Mg) powders using the SHS Process, and the byproducts after the reaction were removed using acid leaching. The properties of the recovered Cr powder were analyzed via X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), particle size analysis (PSA), and oxygen content analysis. The results show that perfect selective leaching of Cr is challenging because of various factors such as incomplete reaction, reaction kinetics, the presence of impurities, and incompatibility between the acid and metal mixture. Therefore, this study provides essential information on the properties under acidic conditions during the production of high-quality Cr powder using a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method.
- [Korean]
- Recycling of Hardmetal Tool through Alkali Leaching Process and Fabrication Process of Nano-sized Tungsten Carbide Powder using Self-propagation High-temperature Synthesis
- Hee-Nam Kang, Dong Il Jeong, Young Il Kim, In Yeong Kim, Sang Cheol Park, Cheol Woo Nam, Seok-Jun Seo, Jin Yeong Lee, Bin Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(1):47-55. Published online February 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.1.47

- 1,174 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide is widely used in carbide tools. However, its production process generates a significant number of end-of-life products and by-products. Therefore, it is necessary to develop efficient recycling methods and investigate the remanufacturing of tungsten carbide using recycled materials. Herein, we have recovered 99.9% of the tungsten in cemented carbide hard scrap as tungsten oxide via an alkali leaching process. Subsequently, using the recovered tungsten oxide as a starting material, tungsten carbide has been produced by employing a self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) method. SHS is advantageous as it reduces the reaction time and is energy-efficient. Tungsten carbide with a carbon content of 6.18 wt % and a particle size of 116 nm has been successfully synthesized by optimizing the SHS process parameters, pulverization, and mixing. In this study, a series of processes for the highefficiency recycling and quality improvement of tungsten-based materials have been developed.
- [Korean]
- Research Trends of the Mo-Si-B Alloys as Next Generation Ultra-high-temperature Alloys
- Won June Choi, Chun Woong Park, Jung Hyo Park, Young Do Kim, Jong Min Byun
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):156-165. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.156

- 1,225 View
- 22 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Over the last decade, the next generation’s ultra-high-temperature materials as an alternative to Nickel-based superalloys have been highlighted. Ultra-high-temperature materials based on refractory metals are one of several potential candidates. In particular, molybdenum alloys with small amounts of silicon and boron (Mo-Si-B alloys) have superior properties at high temperature. However, research related to Mo-Si-B alloys were mainly conducted by several developed countries but garnered little interest in Korea. Therefore, in this review paper, we introduce the development history of Mo-Si-B alloys briefly and discuss the properties, particularly the mechanical and oxidation properties of Mo-Si-B alloys. We also introduce the latest research trends of Mo-Si-B alloys based on the research paper. Finally, for domestic research related to this field, we explain why Mo-Si-B alloys should be developed and suggest the potential directions for Mo-Si-B alloys research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
Minsu Kim, Hansung Lee, Byungmin Ahn
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(6): 478. CrossRef - Preparation and Structure of Chromium Coatings Doped with Diamond Nanoparticles Deposited Directly on a Monolithic Composite of Molybdenum and Aluminum
V. P. Petkov, M. K. Aleksandrova, R. V. Valov, V. P. Korzhov, V. M. Kiiko, I. S. Zheltyakova
Protection of Metals and Physical Chemistry of Surfaces.2023; 59(3): 396. CrossRef - A Review of Mo-Si Intermetallic Compounds as Ultrahigh-Temperature Materials
Liang Jiang, Bin Zheng, Changsong Wu, Pengxiang Li, Tong Xue, Jiandong Wu, Fenglan Han, Yuhong Chen
Processes.2022; 10(9): 1772. CrossRef - Heat-Resistant Molybdenum Borosilicate Alloys Hardened with Titanium Carbides: Mo–Si–B–TiC (Survey)
I. L. Svetlov, O. G. Ospennikova, M. I. Karpov, Yu. V. Artemenko
Inorganic Materials: Applied Research.2021; 12(4): 866. CrossRef
- Thermal Stability and Weight Reduction of Al0.75V2.82CrZr Refractory High Entropy Alloy Prepared Via Mechanical Alloying
- [English]
- Dispersion Behavior and Size Analysis of Thermally Purified High Pressure-high Temperature Synthesized Nanodiamond Particles
- Hansang Kwon, Jehong Park, Marc Leparoux
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):216-222. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.216

- 1,011 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Synthesized monocrystalline nanodiamond (nD) particles are heat-treated at various temperatures to produce highly structured diamond crystals. The heat-treated nDs show different weight loss ratios during thermogravimetric analysis. The crystallinities of the heat-treated nDs are analyzed using Raman spectroscopy. The average particle sizes of the heat-treated nDs are measured by a dynamic light scattering (DLS) system and direct imaging observation methods. Moreover, individual dispersion behaviors of the heat-treated nD particles are investigated based on ultrasonic dispersion methods. The average particle sizes of the dispersed nDs according to the two different measurement methods show very similar size distributions. Thus, it is possible to produce highly crystallized nD powder particles by a heattreatment process, and the nD particles are relatively easy to disperse individually without any dispersant. The heattreated nDs can lead to potential applications such as in nanocomposites, quantum dots, and biomedical materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Two extreme crystal size scales of diamonds, large single crystal and nanocrystal diamonds: Synthesis, properties and their mutual transformation
Yang Wang, Wei-hua Wang, Shi-lin Yang, Guo-yang Shu, Bing Dai, Jia-qi Zhu
New Carbon Materials.2021; 36(3): 512. CrossRef
- Two extreme crystal size scales of diamonds, large single crystal and nanocrystal diamonds: Synthesis, properties and their mutual transformation
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


