Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Manufacturing of Fe-Mn-Al-C Based Low Mn Lightweight Steel Via Direct Energy Deposition
- Kwang Kyu Ko, Han Sol Son, Cha Hee Jung, Hyo Ju Bae, Eun Hye Park, Jung Gi Kim, Hyunjoo Choi, Jae Bok Seol
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(4):320-324. Published online August 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.4.320
- 885 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
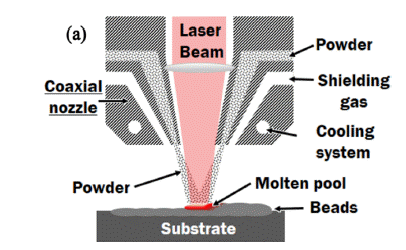
PDF Lightweight steel is a crucial material that is being actively studied because of increased carbon emissions, tightening regulations regarding fuel efficiency, and the emergence of UAM, all of which have been recently labeled as global issues. Hence, new strategies concerning the thickness and size reduction of steel are required. In this study, we manufacture lightweight steel of the Fe-Mn-Al-C system, which has been recently studied using the DED process. By using 2.8 wt.% low-Mn lightweight steel, we attempt to solve the challenge of joining steel parts with a large amount of Mn. Among the various process variables, the laser scan power is set at 600 and 800W, and the laser scan speed is fixed at 16.67 mm/s before the experiments. Several pores and cracks are observed under both conditions, and negligibly small pores of approximately 0.5 μm are observed.
- [Korean]
- Measurement Method of Prior Austenite Grain Size of Nb-added Fe-based Alloys
- Kwang Kyu Ko, Hyo Ju Bae, Sin Woo Jung, Hyo Kyung Sung, Jung Gi Kim, Jae Bok Seol
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):317-324. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.317

- 715 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels show excellent toughness when trace amounts of transition elements are added. In steels, prior austenite grain size (PAGS), which is often determined by the number of added elements, is a critical factor in determining the mechanical properties of the material. In this study, we used two etching methods to measure and compare the PAGS of specimens with bainitic HSLA steels having different Nb contents These two methods were nital etching and picric acid etching. Both methods confirmed that the sample with high Nb content exhibited smaller PAGS than its low Nb counterpart because of Nb’s ability to hinder austenite recrystallization at high temperatures. Although both etching approaches are beneficial to PAGS estimation, the picric acid etching method has the advantage of enabling observation of the interface containing Nb precipitate. By contrast, the nital etching method has the advantage of a very short etching time (5 s) in determining the PAGS, with the picric acid etching method being considerably longer (5 h).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Austempering vs. Q&P: Comparative effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of complex-alloyed TRIP-assisted steel
V.G. Efremenko, Yu.G. Chabak, I. Petryshynets, I. Sili, T.M. Kovbasiuk, A.V. Efremenko, M.N. Brykov, M. Dabalá, M. Franceschi, H. Halfa, A.G. Lekatou
Materials Today Communications.2025; 47: 113179. CrossRef
- Austempering vs. Q&P: Comparative effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of complex-alloyed TRIP-assisted steel
TOP
 kpmi
kpmi


 First
First Prev
Prev


