Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Self-Assembled Monolayers in Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition and Their Challenges
- Si Eun Jung, Ji Woong Shin, Ye Jin Han, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(3):179-190. Published online June 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2025.00094

- 4,763 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Area-selective atomic layer deposition (AS-ALD) is a bottom-up process that selectively deposits thin films onto specific areas of a wafer surface. The surface reactions of AS-ALD are controlled by blocking the adsorption of precursors using inhibitors such as self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) or small molecule inhibitors. To increase selectivity during the AS-ALD process, the design of both the inhibitor and the precursor is crucial. Both inhibitors and precursors vary in reactivity and size, and surface reactions are blocked through interactions between precursor molecules and surface functional groups. However, challenges in the conventional SAM-based AS-ALD method include thermal instability and potential damage to substrates during the removal of residual SAMs after the process. To address these issues, recent studies have proposed alternative inhibitors and process design strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Temperature-Dependent Surface Structural Change in Self-Assembled Monolayers Studied with Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation and QM/MD Simulation
Hojeong Yoon, Saima Sadiq, Junhyeok Park, Kyungwon Kwak, Minhaeng Cho
The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.2026; 17(4): 1119. CrossRef
- Temperature-Dependent Surface Structural Change in Self-Assembled Monolayers Studied with Vibrational Sum-Frequency Generation and QM/MD Simulation
- [English]
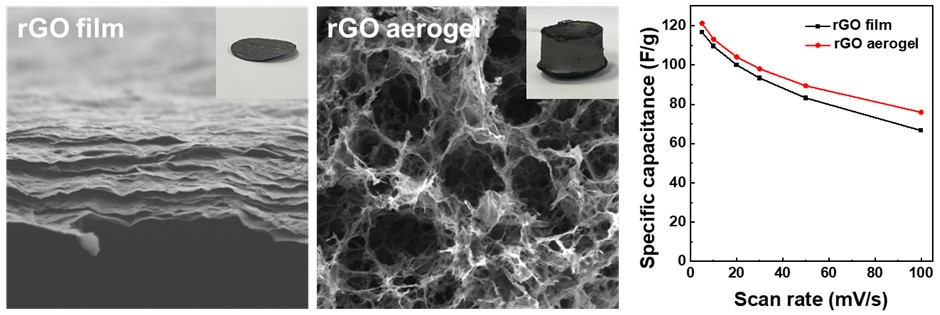
- Comparative Study of Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogels and Films for Supercapacitor Electrodes
- Sunghee Choi, Seulgi Kim, Seojin Woo, Dongju Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):23-29. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00472
- 1,784 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Supercapacitors, renowned for their high power density and rapid charge-discharge rates, are limited by their low energy density. This limitation has prompted the need for advanced electrode materials. The present study investigated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in two distinct structures, as a film and as an aerogel, for use as supercapacitor electrodes. The rGO film, prepared by vacuum filtration and thermal reduction, exhibited a compact, lamellar structure, while the aerogel, synthesized through hydrothermal treatment, was a highly porous three-dimensional network. Electrochemical analyses demonstrated the aerogel’s superior performance, as shown by a specific capacitance of 121.2 F/g at 5 mV/s, with 94% capacitance retention after 10,000 cycles. These findings emphasize the importance of structural design in optimizing ion accessibility and charge transfer. They also demonstrate the potential of rGO aerogels for increasing the energy storage efficiency of advanced supercapacitor systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
Min Gi An, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 492. CrossRef
- Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrodes for Flexible Heater
- [English]
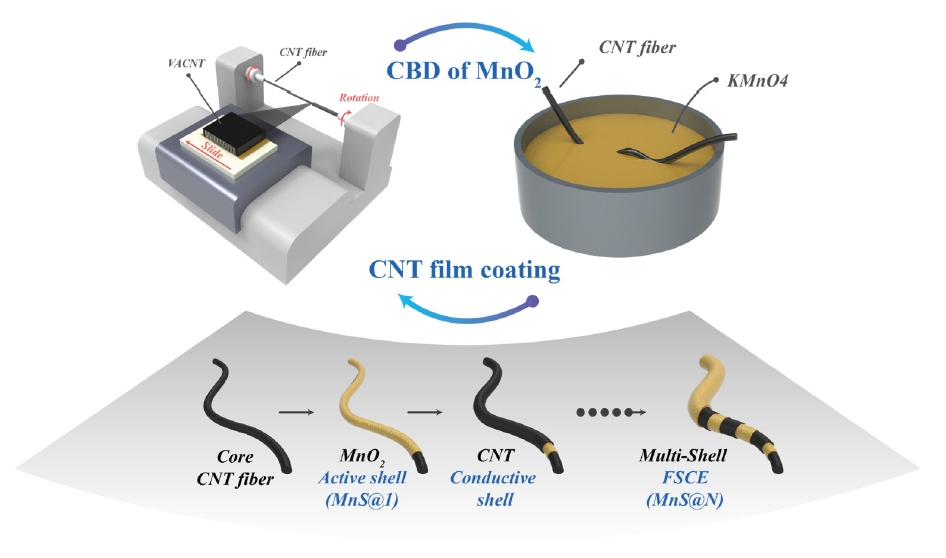
- The Effect of a CNT/MnO2 Nanoparticle Composite–Based Multi-Shell Typed Electrode for a Fiber Supercapacitor (FSC)
- Yeonggwon Kim, Hyung Woo Lee
- J Powder Mater. 2025;32(1):30-36. Published online February 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00416
- 1,140 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fiber supercapacitors have attracted significant interest as potential textile energy storage devices due to their remarkable flexibility and rapid charge/discharge capabilities. This study describes the fabrication of a composite fiber supercapacitor (FSC) electrode through a multi-shell architecture, featuring layers of carbon nanotube (CNT) conductive shells and MnO₂ nanoparticle active shells. The number of layers was adjusted to assess their impact on FSC energy storage performance. Increasing the number of shells reduced electrode resistance and enhanced pseudocapacitive characteristics. Compared to the MnS@1 electrode, the MnS@5 electrode exhibited a high areal capacitance of 301.2 mF/cm², a 411% increase, but showed a higher charge transfer resistance (RCT) of 701.6 Ω. This is attributed to reduced ion diffusion and charge transfer ability resulting from the thicker multi-shell configuration. These results indicate that fine-tuning the quantity of shells is crucial for achieving an optimal balance between energy storage efficiency and stability.
- [Korean]
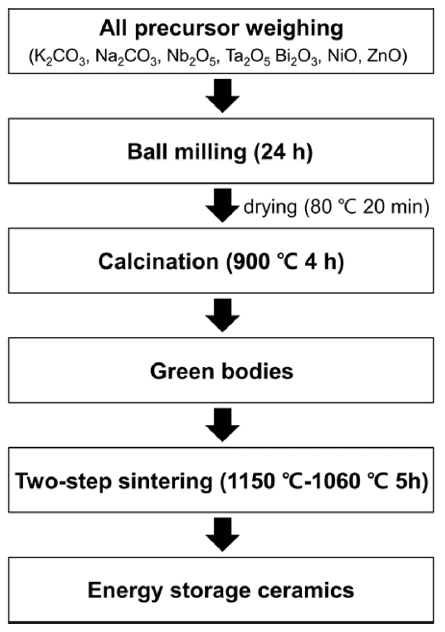
- Modulation of Microstructure and Energy Storage Performance in (K,Na)NbO3-Bi(Ni,Ta)O3 Ceramics through Zn Doping
- Jueun Kim, Seonhwa Park, Yuho Min
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(6):509-515. Published online December 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.6.509
- 904 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Lead-free perovskite ceramics, which have excellent energy storage capabilities, are attracting attention owing to their high power density and rapid charge-discharge speed. Given that the energy-storage properties of perovskite ceramic capacitors are significantly improved by doping with various elements, modifying their chemical compositions is a fundamental strategy. This study investigated the effect of Zn doping on the microstructure and energy storage performance of potassium sodium niobate (KNN)-based ceramics. Two types of powders and their corresponding ceramics with compositions of (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni2/3Ta1/3)O3 (KNN-BNT) and (1-x)(K,Na)NbO3-xBi(Ni1/3Zn1/3Ta1/3) O3 (KNN-BNZT) were prepared via solid-state reactions. The results indicate that Zn doping retards grain growth, resulting in smaller grain sizes in Zn-doped KNN-BNZT than in KNN-BNT ceramics. Moreover, the Zn-doped KNNBNZT ceramics exhibited superior energy storage density and efficiency across all x values. Notably, 0.9KNN-0.1BNZT ceramics demonstrate an energy storage density and efficiency of 0.24 J/cm3 and 96%, respectively. These ceramics also exhibited excellent temperature and frequency stability. This study provides valuable insights into the design of KNNbased ceramic capacitors with enhanced energy storage capabilities through doping strategies.
- [Korean]
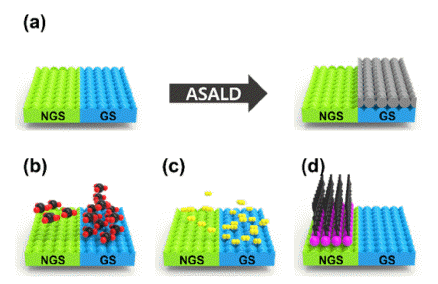
- Recent Studies on Area Selective Atomic Layer Deposition of Elemental Metals
- Min Gyoo Cho, Jae Hee Go, Byung Joon Choi
- J Powder Mater. 2023;30(2):156-168. Published online April 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2023.30.2.156
- 3,107 View
- 81 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The semiconductor industry faces physical limitations due to its top-down manufacturing processes. High cost of EUV equipment, time loss during tens or hundreds of photolithography steps, overlay, etch process errors, and contamination issues owing to photolithography still exist and may become more serious with the miniaturization of semiconductor devices. Therefore, a bottom-up approach is required to overcome these issues. The key technology that enables bottom-up semiconductor manufacturing is area-selective atomic layer deposition (ASALD). Here, various ASALD processes for elemental metals, such as Co, Cu, Ir, Ni, Pt, and Ru, are reviewed. Surface treatments using chemical species, such as self-assembled monolayers and small-molecule inhibitors, to control the hydrophilicity of the surface have been introduced. Finally, we discuss the future applications of metal ASALD processes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
Chan Hyeon Yang, Jaehak Lee, Jung Hwan Park
Journal of Powder Materials.2025; 32(6): 509. CrossRef - Selective Atomic Layer Deposition of Co Thin Films Using Co(EtCp)2 Precursor
Sujeong Kim, Yong Tae Kim, Jaeyeong Heo
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(3): 163. CrossRef
- Ultrafast Synthesis of Molybdenum Disulfide via Flashlamp Annealing
- [Korean]
- Preparation of CoFe2O4 Nanoparticle Decorated on Electrospun Carbon Nanofiber Composite Electrodes for Supercapacitors
- Hyewon Hwang, Seoyeon Yuk, Minsik Jung, Dongju Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(6):470-477. Published online December 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.6.470
- 749 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
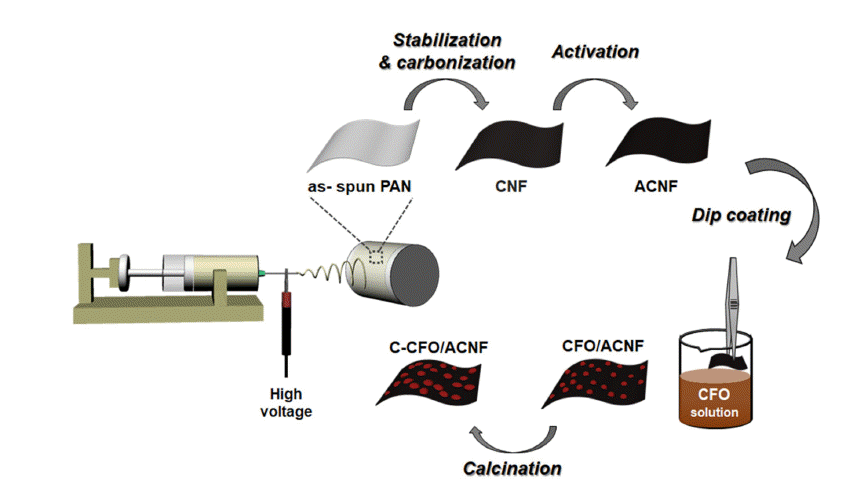
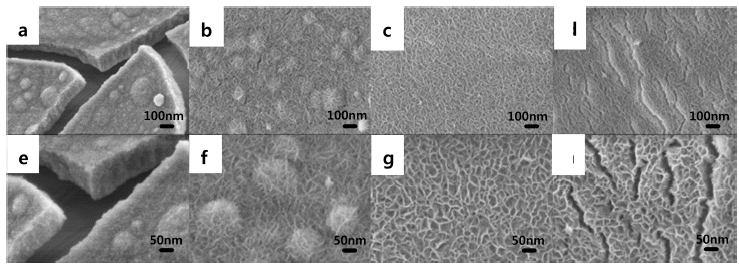
PDF Energy storage systems should address issues such as power fluctuations and rapid charge-discharge; to meet this requirement, CoFe2O4 (CFO) spinel nanoparticles with a suitable electrical conductivity and various redox states are synthesized and used as electrode materials for supercapacitors. In particular, CFO electrodes combined with carbon nanofibers (CNFs) can provide long-term cycling stability by fabricating binder-free three-dimensional electrodes. In this study, CFO-decorated CNFs are prepared by electrospinning and a low-cost hydrothermal method. The effects of heat treatment, such as the activation of CNFs (ACNFs) and calcination of CFO-decorated CNFs (C-CFO/ACNFs), are investigated. The C-CFO/ACNF electrode exhibits a high specific capacitance of 142.9 F/g at a scan rate of 5 mV/s and superior rate capability of 77.6% capacitance retention at a high scan rate of 500 mV/s. This electrode also achieves the lowest charge transfer resistance of 0.0063 Ω and excellent cycling stability (93.5% retention after 5,000 cycles) because of the improved ion conductivity by pathway formation and structural stability. The results of our work are expected to open a new route for manufacturing hybrid capacitor electrodes containing the C-CFO/ACNF electrode that can be easily prepared with a low-cost and simple process with enhanced electrochemical performance.
- [Korean]
- The Effects of Hexamethylenetetramine Concentration on the Structural and Electrochemical Performances of Ni(OH)2 Powder for Pseudocapacitor Applications
- Dong Yeon Kim, Young-Min Jeong, Seong-Ho Baek, Injoon Son
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(3):231-236. Published online June 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.3.231
- 1,178 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Ni hydroxides (Ni(OH)2) are synthesized on Ni foam by varying the hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) concentration using an electrodeposition process for pseudocapacitor (PC) applications. In addition, the effects of HMT concentration on the Ni(OH)2 structure and the electrochemical properties of the PCs are investigated. HMT is the source of amine-based OH− in the solution; thus, the growth rate and morphological structure of Ni(OH)2 are influenced by HMT concentration. When Ni(OH)2 is electrodeposited at a constant voltage mode of -0.85 V vs. Ag/AgCl, the cathodic current and the number of nucleations are significantly reduced with increasing concentration of HMT from 0 to 10 mM. Therefore, Ni(OH)2 is sparsely formed on the Ni foam with increasing HMT concentration, showing a layered double-hydroxide structure. However, loosely packed Ni(OH)2 grains that are spread on Ni foam maintain a much greater surface area for reaction and result in the effective utilization of the electrode material due to the steric hindrance effect. It is suggested that the Ni(OH)2 electrodes with HMT concentration of 7.5 mM have the maximum specific capacitance (1023 F/g), which is attributed to the facile electrolyte penetration and fast proton exchange via optimized surface areas.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
Seon Yong Lee, YoungJae Kim, Young Jae Lee
Economic and Environmental Geology.2023; 56(1): 23. CrossRef
- Review of Domestic Research Trends on Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Materials: Based on Research Articles in Korean Citation Index (KCI)
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of WS2-W-WC Embedded Carbon Nanofiber Composites for Supercapacitors
- Yu-Jin Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(2):116-121. Published online April 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.2.116
- 848 View
- 2 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
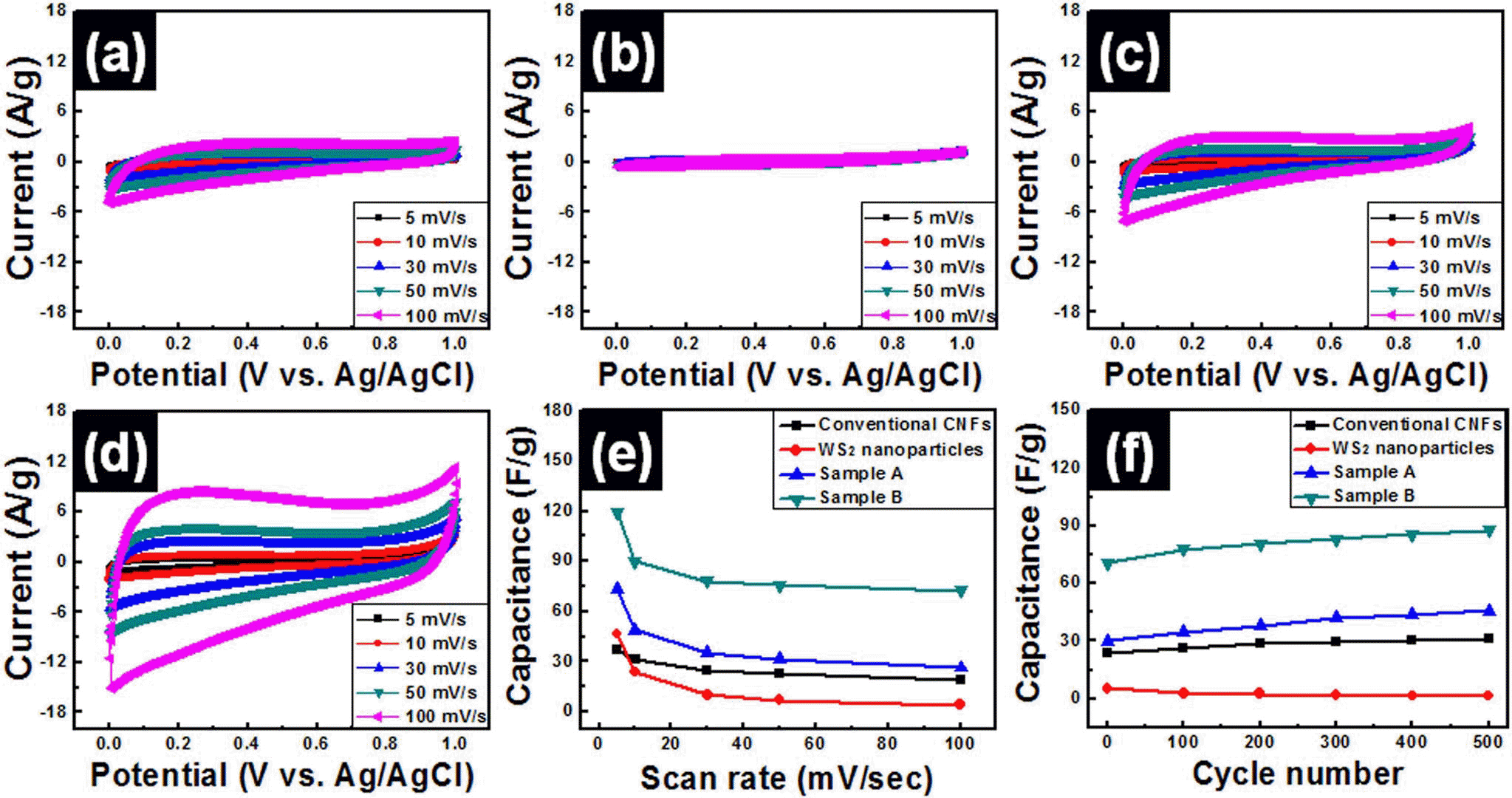
PDF WS2-W-WC embedded carbon nanofiber composites were fabricated by using electrospinning method for use in high-performance supercapacitors. In order to obtain optimum electrochemical properties for supercapacitors, WS2 nanoparticles were used as precursors and the amounts of WS2 precursors were controlled to 4 wt% (sample A) and 8 wt% (sample B). The morphological, structural, and chemical properties of all samples were investigated by means of field emission photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. These results demonstrated that the embedded phases of samples A and B were changed from WS2 to WS2-W-WC through carbothermal reaction during carbonization process. In particular, sample B presented high specific capacitance (~119.7 F/g at 5 mV/s), good high-rate capacitance (~60.5%), and superb cycleability. The enhanced electrochemical properties of sample B were explained by the synergistic effect of the using 1-D structure supports, increase of specific surface area, and improved conductivity from formation of W and WC phases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- WS2 Nanoparticles Embedded in Carbon Nanofibers for a Pseudocapacitor
Ki-Wook Sung, Jung Soo Lee, Tae-Kum Lee, Hyo-Jin Ahn
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2021; 31(8): 458. CrossRef
- WS2 Nanoparticles Embedded in Carbon Nanofibers for a Pseudocapacitor
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


