Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Property Evaluation of Tungsten-Carbide Hard Materials as a Function of Binder
- Ju-Hun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Jeong-Han Lee, Sung-Kil Hong, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):132-137. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.132
- 1,061 View
- 8 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Tungsten carbide (WC) hard materials are used in various industries and possess a superior hardness compared to other hard materials. They have particularly high melting points, high strength, and abrasion resistance. Accordingly, tungsten carbide hard materials are used for wear-resistant tools, cutting tools, machining tools, and other tooling materials. In this study, the WC-5wt.%Co, Fe, Ni hard materials are densified using the horizontal ball milled WC-Co, WC-Fe, and WC-Ni powders by a spark plasma sintering process. The WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, and WC-5Ni hard materials are almost completely densified with a relative density of up to 99.6% after simultaneous application of a pressure of 60 MPa and an electric current for about 15 min without any significant change in the grain size. The average grain size of WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, and WC-5Ni that was produced through SPS was about 0.421, 0.779, and 0.429 μm, respectively. The hardness and fracture toughness of the dense WC-5Co, WC-5Fe, WC-5Ni hard materials were also investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
Jong Min Gwak, Min Soo Park, Gook Hyun Ha, Nam Hyun Kang
Metals and Materials International.2025; 31(12): 3733. CrossRef - Synthesis of W2C by Spark Plasma Sintering of W-WC Powder Mixture and Its Etching Property
Gyu-Sang Oh, Sung-Min Lee, Sung-Soo Ryu
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(4): 293. CrossRef - Fabrication and Properties of Densified Tungsten by Magnetic Pulse Compaction and Spark Plasma Sintering
Eui Seon Lee, Jongmin Byun, Young-Keun Jeong, Sung-Tag Oh
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2020; 30(6): 321. CrossRef
- Enhancing Mechanical Properties via Grain Growth Suppression and High Densification in WC Compacts
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
- Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(4):302-307. Published online August 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.4.302
- 1,094 View
- 6 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
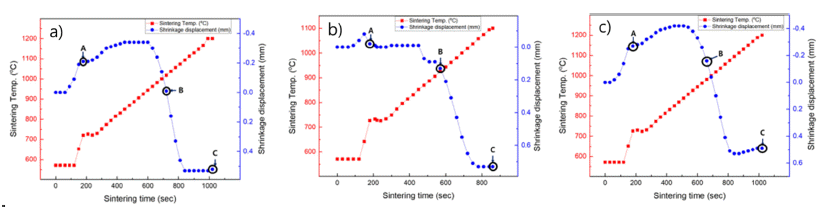
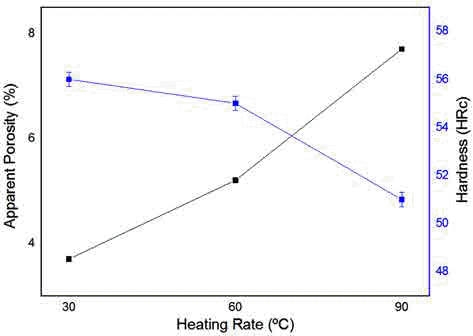
PDF In this study, Fe-Cu-C alloy is sintered by spark plasma sintering (SPS). The sintering conditions are 60 MPa pressure with heating rates of 30, 60 and 9°C/min to determine the influence of heating rate on the mechanical and microstructure properties of the sintered alloys. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the sintered Fe-Cu-C alloy is investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The temperature of shrinkage displacement is changed at 450°C with heating rates 30, 60, and 90°C/min. The temperature of the shrinkage displacement is finished at 650°C when heating rate 30°C/min, at 700°C when heating rate 60oC/min and at 800°C when heating rate 90oC/min. For the sintered alloy at heating rates of 30, 60, and 90oC/min, the apparent porosity is calculated to be 3.7%, 5.2%, and 7.7%, respectively. The hardness of the sintered alloys is investigated using Rockwell hardness measurements. The objective of this study is to investigate the densification behavior, porosity, and mechanical properties of the sintered Fe-Cu-C alloys depending on the heating rate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2018; 25(2): 126. CrossRef
- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Property Evaluation of Cu-Mn Compacts for Sputtering Target Application by a Pulsed Current Activated Sintering Method
- Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Jae-Won Lim, Hyun-Kuk Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(1):1-7. Published online February 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.1.1
- 1,141 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
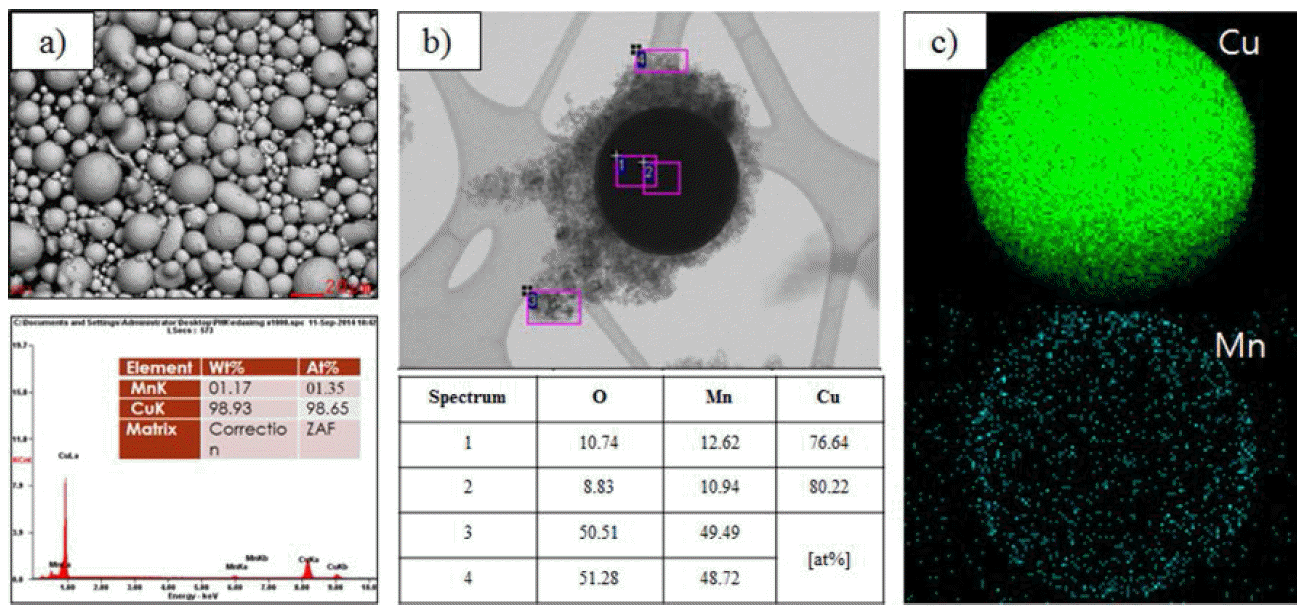
PDF Cu-Mn compacts are fabricated by the pulsed current activated sintering method (PCAS) for sputtering target application. For fabricating the compacts, optimized sintering conditions such as the temperature, pulse ratio, pressure, and heating rate are controlled during the sintering process. The final sintering temperature and heating rate required to fabricate the target materials having high density are 700°C and 80°C/min, respectively. The heating directly progresses up to 700°C with a 3 min holding time. The sputtering target materials having high relative density of 100% are fabricated by employing a uniaxial pressure of 60 MPa and a sintering temperature of 700°C without any significant change in the grain size. Also, the shrinkage displacement of the Cu-Mn target materials considerably increases with an increase in the pressure at sintering temperatures up to 700°C.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
Jung-Han Ryu, Soo-Sik Shin, Byung-Rok Ryu, Kyung-Sik Kim, Jun-Ho Jang, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kap-Tae Kim, Hyun-Kuk Park
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2017; 24(4): 302. CrossRef
- Fabrication and Mechanical Property of Fe-20Cu-1C Compacts by SPS process with Different Heating Rate
- [English]
- Manufacturing and Macroscopic Properties of Cold Sprayed Cu-Ga Coating Material for Sputtering Target
- Young-Min Jin, Min-Gwang Jeon, Dong-Yong Park, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(4):245-252.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.4.245

- 811 View
- 1 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study attempted to manufacture a Cu-Ga coating layer via the cold spray process and to investigate the applicability of the layer as a sputtering target material. In addition, changes made to the microstructure and properties of the layer due to annealing heat treatment were evaluated, compared, and analyzed. The results showed that coating layers with a thickness of 520 mm could be manufactured via the cold spray process under optimal conditions. With the Cu-Ga coating layer, the alpha-Cu and Cu_3Ga were found to exist inside the layer regardless of annealing heat treatment. The microstructure that was minute and inhomogeneous prior to thermal treatment changed to homogeneous and dense with a more clear division of phases. A sputtering test was actually conducted using the sputtering target Cu-Ga coating layer (~2 mm thickness) that was additionally manufactured via the cold-spray coating process. Consequently, this test result confirmed that the cold sprayed Cu-Ga coating layer may be applied as a sputtering target material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Microscopic Examination of Cold Spray Cermet Sn+In2O3Coatings for Sputtering Target Materials
M. Winnicki, A. Baszczuk, M. Rutkowska-Gorczyca, M. Jasiorski, A. Małachowska, W. Posadowski, Z. Znamirowski, A. Ambroziak
Scanning.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Effect of powder alloy composition on the microstructure and properties of kinetic sprayed Cu-Ga based coating materials
Byung-Chul Choi, Dong-Yong Park, Kee-Ahn Lee
Metals and Materials International.2016; 22(4): 649. CrossRef - Manufacturing and Properties of CGI-based Composite Coating Layer Utilizing a Warm Spray Process and Cu-Ga and Cu-In Mixed Powders
Min-Gwang Jeon, Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyeong-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(3): 229. CrossRef - Manufacturing of Cu Repair Coating Material Using the Kinetic Spray Process and Changes in the Microstructures and Properties by Heat Treatment
Min-Gwang Jeon, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(5): 349. CrossRef
- Microscopic Examination of Cold Spray Cermet Sn+In2O3Coatings for Sputtering Target Materials
- [Korean]
- Effect of Carrier Gases on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti Coating Layers Manufactured by Cold Spraying
- Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(1):24-32.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.1.024

- 407 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The effect of carrier gases (He, N_2) on the properties of Ti coating layers were investigated to manufacture high-density Ti coating layers. Cold spray coating layers manufactured using He gas had denser and more homogenous structures than those using N_2 gas. The He gas coating layers showed porosity value of 0.02% and hardness value of Hv 229.1, indicating more excellent properties than the porosity and hardness of N_2 gas coating layers. Bond strengths were examined, and coating layers manufactured using He recorded a value of 74.3 MPa; those manufactured using N_2 gas had a value of 64.6 MPa. The aforementioned results were associated with the fact that, when coating layers were manufactured using He gas, the powder could be easily deposited because of its high particle impact velocity. When Ti coating layers were manufactured by the cold spray process, He carrier gas was more suitable than N_2 gas for manufacturing excellent coating layers.
- [Korean]
- Effects of Powder Morphology and Powder Preheating on the Properties and Deposition Behavior of Titanium Coating Layer Manufactured by Cold Spraying
- Jae-Nam Hwang, Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(5):348-355.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.5.348

- 845 View
- 7 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cold spray deposition using Titanium powder was carried out to investigate the effects of powder morphology and powder preheating on the coating properties such as porosity and hardness. The in-flight particle velocity of Ti powder in cold spray process was directly measured using the PIV (particle image velocimetry) equipment. Two types of powders (spherical and irregular ones) were used to manufacture cold sprayed coating layer. The results showed that the irregular morphology particle appeared higher in-flight particle velocity than that of the spherical one under the same process condition. The coating layer using irregular morphology powder represented lower porosity level and higher hardness. Two different preheating conditions (no preheating and preheating at 500°C) were used in the process of cold spraying. The porosity decreased and the hardness increased by conducting preheating at 500°C. It was found that the coating properties using different preheating conditions were dependent not on the particle velocity but on the deformation temperature of particle. The deposition mechanism of particles in cold spray process was also discussed based on the experimental results of in flight-particle velocity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Solid-state cold spray additive manufacturing of pure tantalum with extraordinary high-temperature mechanical properties
Young-Kyun Kim, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2023; 23: 5698. CrossRef - Effect of Fe Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti-Al-Mo-V-Cr-Fe Alloys
K.C. Bae, J.J. Oak, Y.H. Kim, Y.H. Park
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2017; 62(2): 1105. CrossRef - Effects Of Process Parameters On Cu Powder Synthesis Yield And Particle Size In A Wet-Chemical Process
Y.M. Shin, J.-H. Lee
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2015; 60(2): 1247. CrossRef - Property Evaluation of Kinetic Sprayed Al-Ni Composite Coatings
GyeongJun Byun, JaeIck Kim, Changhee Lee, SeeJo Kim, Seong Lee
Journal of Welding and Joining.2014; 32(5): 72. CrossRef - Manufacturing and Properties of CGI-based Composite Coating Layer Utilizing a Warm Spray Process and Cu-Ga and Cu-In Mixed Powders
Min-Gwang Jeon, Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyeong-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(3): 229. CrossRef - Effect of Carrier Gases on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti Coating Layers Manufactured by Cold Spraying
Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(1): 24. CrossRef
- Solid-state cold spray additive manufacturing of pure tantalum with extraordinary high-temperature mechanical properties
- [Korean]
- Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Densification of Cold Sprayed Ti Coating Layer
- Ji-Sang Yu, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(2):110-116.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.2.110

- 763 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study investigated the effects of annealing environment for the densification and purification properties of pure titanium coating layer manufactured by cold spraying. The annealing was conducted at 600°C/1 h and three kinds of environments of vacuum, Ar gas, and 5%H_2+Ar mixture gas were controlled. Cold sprayed Ti coating layer (as sprayed) represented 6.7% of porosity and 228 HV of hardness, showing elongated particle shapes (severe plastic deformation) perpendicular to injection direction. Regardless of gas environments, all thermally heat treated coating layers consisted of pure alpha-Ti and minimal oxide. Vacuum environment during heat treatment represented superior densification properties (3.8% porosity, 156.7 HV) to those of Ar gas (5.3%, 144.5 HV) and 5%H_2+Ar mixture gas (5.5%, 153.1 HV). From the results of phase analysis (XRD, EPMA, SEM, EDS), it was found that the vacuum environment during heat treatment could be effective for reducing oxide contents (purification) in the Ti coating layer. The characteristic of microstructural evolution with heat treatment was found to be different at three different gas environments. The controlling method for improving densification and purification in the cold sprayed Ti coating material was also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Microstructure and Propertiesof Kinetic Sprayed Nb Coating Material
Ji-Hye Lee, Sangsun Yang, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 15. CrossRef - Fabrication and Microstructure/Properties of Bulk-typeTantalum Material by a Kinetic Spray Process
Ji-Hye Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 8. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Microstructure and Properties of Kinetic Sprayed Tantalum Coating Layer
Ji-Hye Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(1): 32. CrossRef - Effect of Powder Preheating Temperature on the Properties of Titanium Coating Layers Manufactured by Kinetic Spraying
Kee-Ahn Lee, Myeong-Ju Lee, Ji-Sang Yu, Hyung-Jun Kim
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2014; 55(3): 622. CrossRef - Effect of Carrier Gases on the Microstructure and Properties of Ti Coating Layers Manufactured by Cold Spraying
Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2013; 20(1): 24. CrossRef - Effects of Powder Morphology and Powder Preheating on the Properties and Deposition Behavior of Titanium Coating Layer Manufactured by Cold Spraying
Jae-Nam Hwang, Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(5): 348. CrossRef
- Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Microstructure and Propertiesof Kinetic Sprayed Nb Coating Material
- [Korean]
- Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Properties of Cold Sprayed Cu-15 at.%Ga Coating Material for Sputtering Target
- Byung-Chul Choi, Dong-Yong Park, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2011;18(6):552-561.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2011.18.6.552

- 798 View
- 0 Download
- 9 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - This study attempted to manufacture a Cu-15 at.%Ga coating layer via the cold spray process and investigated the effect of heat treatment environment on the properties of cold sprayed coating material. Three kinds of heat treatment environments, 5%H_2+argon, pure argon, and vacuum were used in this study. Annealing treatments were conducted at 200sim800°C/1 hr. With the cold sprayed coating layer, pure alpha-Cu and small amounts of Ga_2O_3 were detected in the XRD, EDS, EPMA analyses. Porosity significantly decreased and hardness also decreased with increasing annealing temperature. The inhomogeneous dendritic microstructure of cold sprayed coating material changed to the homogeneous and dense one (microstructural evolution) with annealing heat treatment. Oxides near the interface of particles could be reduced by heat treatment especially in vacuum and argon environments. Vacuum environment during heat treatment was suggested to be most effective one to improve the densification and purification properties of cold sprayed Cu-15 at.%Ga coating material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Manufacturing of Large-Scale Cold-Sprayed Ta Target Material and Its Sputtering Property
Gi-Su Ham, Dong-Yeol Wi, Jun-Mo Yang, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Thermal Spray Technology.2019; 28(8): 1974. CrossRef - Effect of Hot Isostatic Pressing on the Microstructure and Propertiesof Kinetic Sprayed Nb Coating Material
Ji-Hye Lee, Sangsun Yang, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 15. CrossRef - Fabrication and Microstructure/Properties of Bulk-typeTantalum Material by a Kinetic Spray Process
Ji-Hye Lee, Ji-Won Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2016; 23(1): 8. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Microstructure and Properties of Kinetic Sprayed Tantalum Coating Layer
Ji-Hye Lee, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2015; 22(1): 32. CrossRef - The Effect of Annealing Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties of Kinetic-Sprayed Ta Coating Layer
Myeong Ju Lee, Jae Sung Oh, Hyung Jun Kim, Ik Hyun Oh, Kee Ahn Lee
Advanced Materials Research.2014; 893: 64. CrossRef - Manufacturing of Cu Repair Coating Material Using the Kinetic Spray Process and Changes in the Microstructures and Properties by Heat Treatment
Min-Gwang Jeon, Hyung-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(5): 349. CrossRef - Manufacturing and Properties of CGI-based Composite Coating Layer Utilizing a Warm Spray Process and Cu-Ga and Cu-In Mixed Powders
Min-Gwang Jeon, Myeong-Ju Lee, Hyeong-Jun Kim, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(3): 229. CrossRef - Effect of Heat Treatment Environment on the Densification of Cold Sprayed Ti Coating Layer
Ji-Sang Yu, Hyung-Jun Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh, Kee-Ahn Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(2): 110. CrossRef - Sintering and Rolling Behavior of Cu-50In-13Ga Ternary Alloy Powder for Sputtering Target
Dae-Won Kim, Yong-Ho Kim, Jung-Han Kim, Dae-Guen Kim, Jong-Hyeon Lee, Kwang-Bo Choi, Hyeon-Taek Son
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2012; 19(4): 264. CrossRef
- Manufacturing of Large-Scale Cold-Sprayed Ta Target Material and Its Sputtering Property
- [Korean]
- Evaluation of Ni-YSZ Anode fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering for SOFC Application
- Se-Hun Chang, Jung-Chul Choi, Se-Weon Choi, Ho-Sung Kim, Ik-Hyun Oh
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(5):405-410.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.5.405

- 545 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - SOFC (Solid Oxide Fuel Cell) Ni-YSZ anode was fabricated by the spark plasma sintering (SPS) process and its microstructure and electrical properties were investigated in this study. The spark plasma sintering process was carried out at 800sim1000°C for holding time of 5 min under 40 MPa. To fabricate Ni-YSZ anode, the SPS processed specimens were reduced at 800°C under H_2 atmosphere. The reduced specimens showed relative density of 48.4sim64.8% according to sintering temperature. And also, the electrical conductivity of reduced specimens after sintering at 900 and 1000°C showed 480sim600 (S/cm) values at the measuring range of 600sim900°C.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


