Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Austenite Stability of Nanocrystalline FeMnNiC Alloy
- Seung-Jin Oh, Junhyub Jeon, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):389-394. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.389
- 905 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
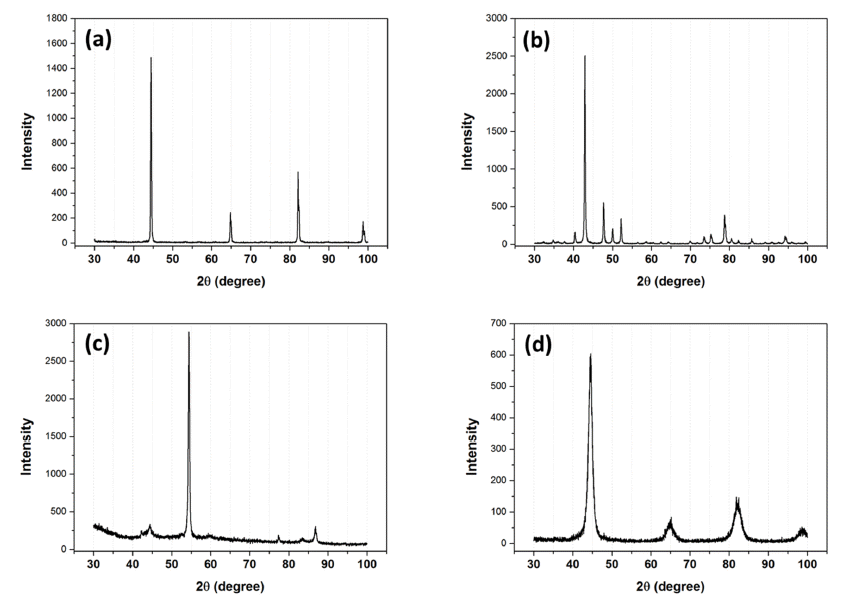
PDF In the present study, we have investigated the effect of sintering process conditions on the stability of the austenite phase in the nanocrystalline Fe-5wt.%Mn-0.2wt.%C alloy. The stability and volume fraction of the austenite phase are the key factors that determine the mechanical properties of FeMnC alloys, because strain-induced austenitemartensite transformation occurs under the application of an external stress at room temperature. Nanocrystalline Fe-5wt.%Mn-0.2wt.%C samples are fabricated using the spark plasma sintering method. The stability of the austenite phase in the sintered samples is evaluated by X-ray diffraction analysis and hardness test. The volume fraction of austenite at room temperature increases as the sample is held for 10 min at the sintering temperature, because of carbon diffusion in austenite. Moreover, water quenching effectively prevents the formation of cementite during cooling, resulting in a higher volume fraction of austenite. Furthermore, it is found that the hardness is influenced by both the austenite carbon content and volume fraction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Cobalt Content on Austenite Stability and Strain-Induced Martensite Transformation of Nanocrystalline Fe-7Mn Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
Sungjin Kim, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2025; 66(7): 811. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 414. CrossRef
- Influence of Cobalt Content on Austenite Stability and Strain-Induced Martensite Transformation of Nanocrystalline Fe-7Mn Alloy Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering
- [Korean]
- Effect of Milling Time and Addition of PCA on Austenite Stability of Fe-7%Mn Alloy
- Seung-Jin Oh, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):126-131. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.2.126
- 770 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
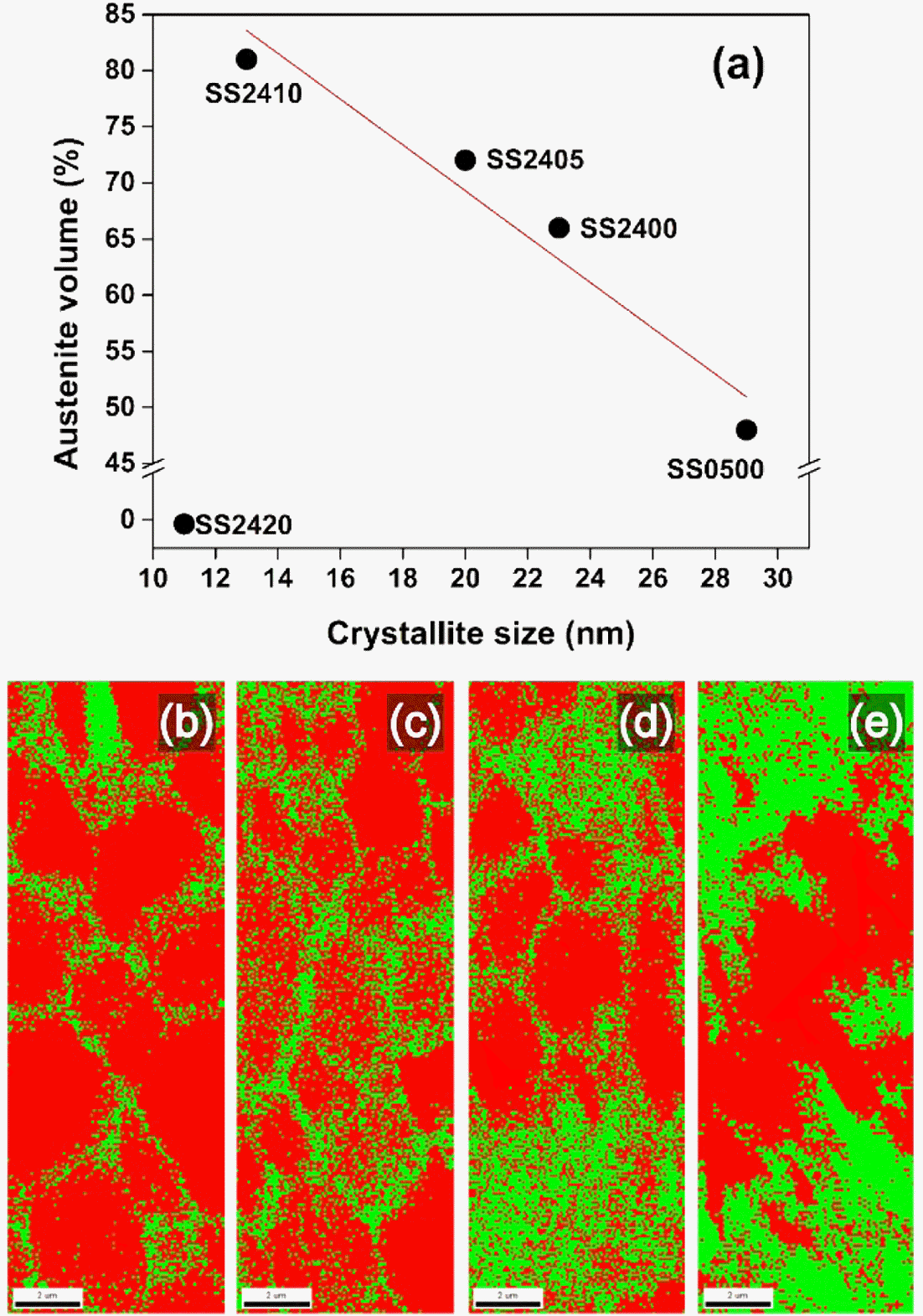
PDF In the present study, we investigate the effects of milling time and the addition of a process control agent (PCA) on the austenite stability of a nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloy by XRD analysis and micrograph observation. Nanocrystalline Fe-7%Mn alloys samples are successfully fabricated by spark plasma sintering. The crystallite size of ball-milled powder and the volume fraction of austenite in the sintered sample are calculated using XRD analysis. Changes in the shape and structure of alloyed powder according to milling conditions are observed through FE-SEM. It is found that the crystallite size is reduced with increasing milling time and amount of PCA addition due to the variation in the balance between the cold-welding and fracturing processes. As a result, the austenite stability increased, resulting in an exceptionally high volume fraction of austenite retained at room temperature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
Seonghyun Park, Sang-Hwa Lee, Eunjoo Shin, Seok-Jae Lee, Jae-Gil Jung
Journal of Materials Research and Technology.2025; 39: 4854. CrossRef - Effect of Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Hardness during Solution Treatment and Aging Process of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Aerospace Components
Seongji Seo, Hojoon Choi, Geeyoung Lee, Kee-Ahn Lee, Jeongho Han, Minsu Jung
Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance.2021; 30(5): 3406. CrossRef - Development of Fe-Mn-based Hybrid Materials Containing Nano-scale Oxides by a Powder Metallurgical Route
Jonggyu Jeon, Jungjoon Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(3): 203. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Sintered Fe-based Alloy
Seunggyu Choi, Namhyuk Seo, Junhyub Jun, Seung Bae Son, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2020; 27(5): 414. CrossRef - Austenite Stability of Nanocrystalline FeMnNiC Alloy
Seung-Jin Oh, Junhyub Jeon, In-Jin Shon, Seok-Jae Lee
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(5): 389. CrossRef
- Effects of mechanical milling on microstructure and mechanical properties of CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy fabricated via spark plasma sintering
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Properties and Fabrication of TiAl Alloy by Pulsed Current Activated Sintering
- Song-Lee Du, Na-Ri Kim, Won-Baek Kim, Sung-Wook Cho, In-Jin Shon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2010;17(5):373-378.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2010.17.5.373

- 405 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nanostuctured TiAl powder was synthesized by high energy ball milling. A dense nanostuctured TiAl was consolidated using pulsed current activated sintering method within 2 minutes from mechanically synthesized powders of TiAl and horizontally milled powders of Ti+Al. The grain size and hardness of TiAl sintered from horizontally milled Ti+Al powders and high energy ball milled TiAl powder were 35 nm, 20 nm and 450 kg/mm2, 630 kg/mm2, respectively.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication of 4.25 Co0.53Fe0.47-Al2O3 Composite by High Frequency Induction Heated Combustion Synthesis
- Na-Ra Park, Hoon NamKung, In-Yong Ko, In-Jin Shon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(2):91-97.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.2.091

- 472 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nanopowders of Co_3O_4 and FeAl were fabricated by high energy ball milling. Dense 4.25 Co_0.53Fe_0.47-Al_2O_3 composite was simultaneously synthesized and consolidated by high frequency induction heated combustion method within 2 min from mechanically activated powders. Consolidation was accomplished under the combined effects of a induced current and mechanical pressure of 80 MPa.
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Properties and Fabrication of Nanostructured ReSi1.75 by High Frequency Induction Heated Combustion Synthesis
- Byung-Ryang Kim, Su-Chul Kim, In-Jin Shon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(1):16-21.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.1.016

- 601 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Nanostructured ReSi_1.75 was synthesized to have high density via rapid and cost effective process named as high-frequency induction heated combustion synthesis(HFIHCS) method. For the process, mechanically activated Re-Si powder was used, which had been prepared by mechanical ball milling of Re and Si powders with mixing ratio of 1:1.75. Both combustion synthesis and densification were accomplished simultaneously by applying electric current and mechanical pressure of 80 MPa during the process. The average grain size, hardness, and fracture toughness of the compound were 210 nm, 1085 kg/mm2 and 4 MPacdotm1/2, respectively. The experimental results show that HFIHCS is a promising process for synthesis of nanostructured ReSi_1.75 which has a potential for both high temperature and thermo-electric applications.
- [English]
- High-Frequency Induction-Heated Combustion Synthesis and Consolidation of Nanostructured NbSi2 from Mechanically Activated Powders
- Byung-Ryang Kim, Jin-Kook Yoon, Kee-Seok Nam, In-Jin Shon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2008;15(4):279-284.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2008.15.4.279

- 457 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dense nanostructured NbSi_2 was synthesized by high-frequency induction-heated combustion synthesis (HFIHCS) method within 1 minute in one step from mechanically activated Nb and Si powders. Highly dense NbSi_2 with relative density of up to 99% was simultaneously synthesized and consolidated under the combined effects of an induced current and mechanical pressure of 60 MPa. The average grain size and mechanical properties (hardness and fracture toughness) of the compound were investigated.
- [Korean]
- Mechanical Properties and Fabrication of Nanostructured 2MoSi2-SiC by Pulsed Current Activated Combustion Synthesis
- In-Jin Shon, Dong-Ki Kim, In-Kyoon Jeong, Jung-Mann Doh, Jin-Kook Yoon, In-Yong Ko
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2007;14(4):245-250.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2007.14.4.245

- 400 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dense nanostructured 2MoSi_2-SiC composites were synthesized by the pulsed current activated combustion synthesis (PCACS) method within 3 minutes in one step from mechanically activated powders of Mo_2C and 5Si. Simultaneous combustion synthesis and densification were accomplished under the combined effects of a pulsed current and mechanical pressure. Highly dense 2MoSi_2-SiC with relative density of up to 96% was produced under simultaneous application of a 60 MPa pressure and the pulsed current. The average grain size of MoSi_2 and SiC were about 120 nm and 90 nm, respectively. The hardness and fracture toughness values obtained were 1350 kg/mm2 and 4 MPacdotm1/2, respectively.
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Mechanical Properties of Dense WSi2-20vol.%SiC Composite by High-Frequency Induction-Heated Combustion Synthesis
- Dong-Young Oh, Hwan-Cheol Kim, Sang-Kwon Lee, In-Jin Shon
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2005;12(1):17-23.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2005.12.1.017

- 464 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Dense WSi_2-20vol.%SiC composite was synthesized by high-frequency induction-heated combustion synthesis(HFIHCS) method within 2 minutes in one step from elemental powder mixture of W, Si and C. Simultaneous combustion synthesis and densification were accomplished under the combined effects of an induced current and mechanical pressure. Highly dense WSi_2-20vol.%SiC with relative density of up to 97% was produced under simultaneous application of 60MPa pressure and the induced current. The average grain size of WSi_2 was about 5.2µm. The hardness and fracture toughness values obtained were 1700kg/mm2 and 4.4MPacdotm1/2, respectively.
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


