Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- A Study on the Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 Nanocrystalline Soft Magnetic Alloys with varying P Content - Hyun Ah Im, Kyoung-Hoon Bae, Yeong gyun Nam, Subong An, Sangsun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Jung Woo Lee, Jae Won Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2021;28(4):293-300. Published online August 1, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2021.28.4.293

- 883 View
- 11 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF We investigate the effect of phosphorous content on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33
x B10.67-0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys. The simultaneous addition of Cu and P to nanocrystalline alloys reportedly decreases the nanocrystalline size significantly, to 10–20 nm. In the P-containing nanocrystalline alloy, P atoms are distributed in an amorphous residual matrix, which suppresses grain growth, increases permeability, and decreases coercivity. In this study, nanocrystalline ribbons with a composition of Fe83.2Si5.33-0.33x B10.67- 0.67x Px Cu0.8 (x = 1–4 at.%) are fabricated by rapid quenching melt-spinning and thermal annealing. It is demonstrated that the addition of a small amount of P to the alloy improves the glass-forming ability and increases the resistance to undesirable Fex(B,P) crystallization. Among the alloys investigated in this work, an Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 nanocrystalline ribbon annealed at 460°C exhibits excellent soft-magnetic properties including low coercivity, low core loss, and high saturation magnetization. The uniform nanocrystallization of the Fe83.2Si5B10P1Cu0.8 alloy is confirmed by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy analysis.
- [English]
- Synthesis of Boron Nitride Nanotubes via inductively Coupled thermal Plasma process Catalyzed by Solid-state ammonium Chloride
- Mi Se Chang, Young Gyun Nam, Sangsun Yang, Kyung Tae Kim, Ji Hun Yu, Yong-Jin Kim, Jae Won Jeong
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(2):120-125. Published online April 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.25.2.120
- 683 View
- 7 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
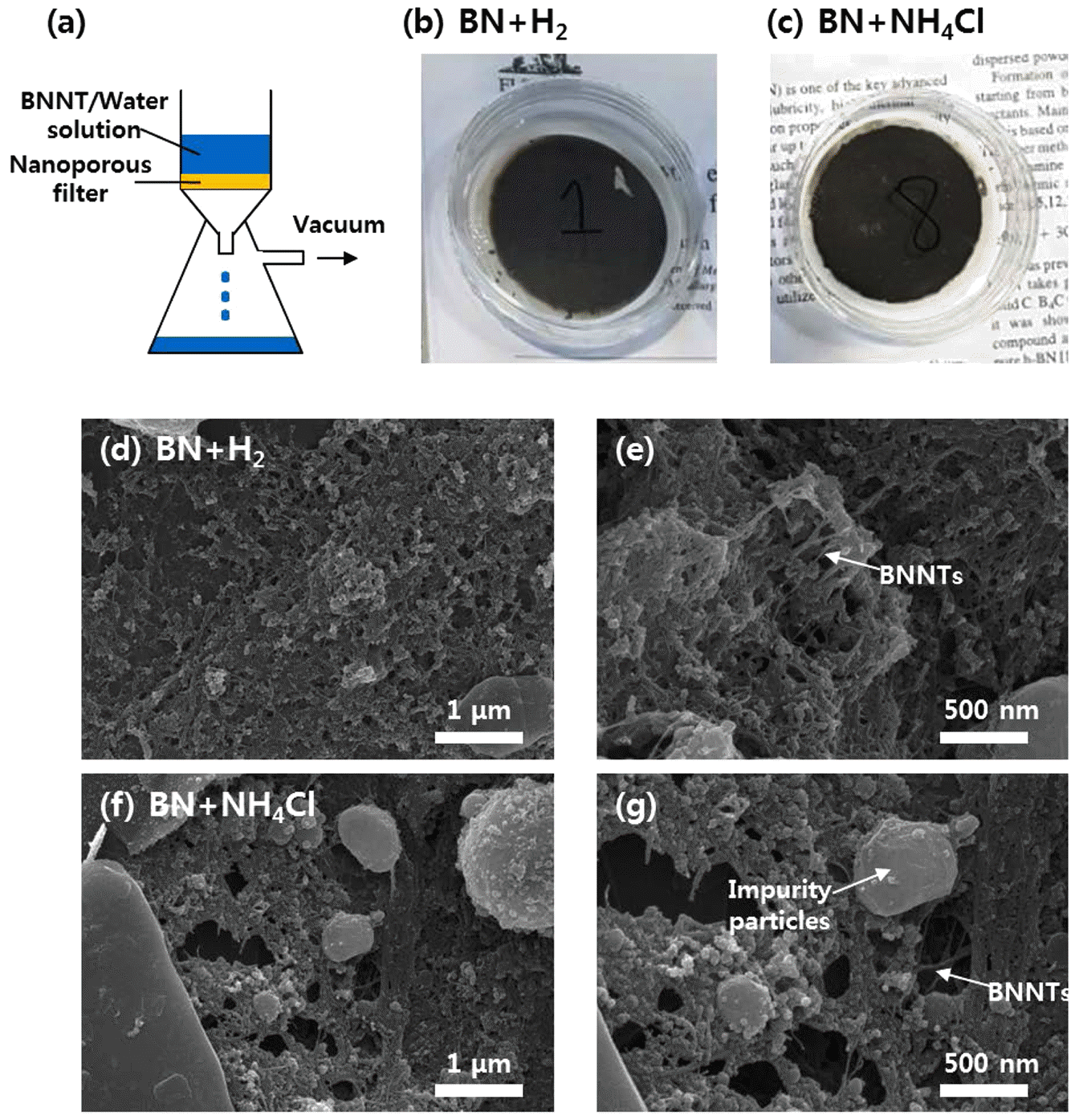
PDF Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) are receiving great attention because of their unusual material properties, such as high thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and electrical resistance. However, high-throughput and highefficiency synthesis of BNNTs has been hindered due to the high boiling point of boron (~ 4000°C) and weak interaction between boron and nitrogen. Although, hydrogen-catalyzed plasma synthesis has shown potential for scalable synthesis of BNNTs, the direct use of H2 gas as a precursor material is not strongly recommended, as it is extremely flammable. In the present study, BNNTs have been synthesized using radio-frequency inductively coupled thermal plasma (RF-ITP) catalyzed by solid-state ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), a safe catalyst materials for BNNT synthesis. Similar to BNNTs synthesized from h-BN (hexagonal boron nitride) + H2, successful fabrication of BNNTs synthesized from h-BN+NH4Cl is confirmed by their sheet-like properties, FE-SEM images, and XRD analysis. In addition, improved dispersion properties in aqueous solution are found in BNNTs synthesized from h-BN +NH4Cl.
- [Korean]
- Investigation on Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C Soft Magnetic Powders Prepared by High-Pressure Gas Atomization
- Jae Won Jeong, Dong-Yeol Yang, Ki Bong Kim, Junhong Lee, Young Ja Kim, Tae-Soo Lim, Sangsun Yang, Min Ha Lee, Hwi Jun Kim, Yong-Jin Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(5):391-396. Published online October 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.5.391
- 830 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
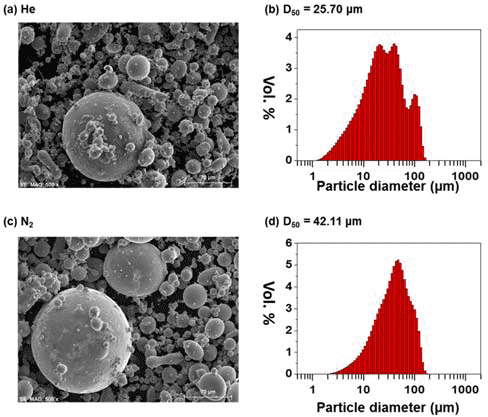
PDF In this study, ultra-fine soft-magnetic micro-powders are prepared by high-pressure gas atomization of an Fe-based alloy, Fe-Hf-B-Nb-P-C. Spherical powders are successfully obtained by disintegration of the alloy melts under high-pressure He or N2 gas. The mean particle diameter of the obtained powders is 25.7 μm and 42.1 μm for He and N2 gas, respectively. Their crystallographic structure is confirmed to be amorphous throughout the interior when the particle diameter is less than 45 μm. The prepared powders show excellent soft magnetic properties with a saturation magnetization of 164.5 emu/g and a coercivity of 9.0 Oe. Finally, a toroidal core is fabricated for measuring the magnetic permeability, and a μr of up to 78.5 is obtained. It is strongly believed that soft magnetic powders prepared by gas atomization will be beneficial in the fabrication of high-performance devices, including inductors and motors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
Jungjoon Kim, Dongchan Min, Suwon Park, Junhyub Jeon, Seok-Jae Lee, Youngkyun Kim, Hwi-Jun Kim, Youngjin Kim, Hyunjoo Choi
MATERIALS TRANSACTIONS.2022; 63(10): 1304. CrossRef - Optimizing the magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous powder by adjusting atomic structures from vitrification at different temperatures
Song-Yi Kim, Hye-Ryeong Oh, Hyeon-Ah Kim, A-Young Lee, Hwi-Jun Kim, Sang-Sun Yang, Yong-Jin Kim, Hyun-Joo Choi, Il-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Gil Kim, Jürgen Eckert, Jong-Ryoul Kim, Min-Ha Lee
Journal of Applied Physics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline hybrid materials
Yeonjoo Lee, Jonggyu Jeon, Seungjin Nam, Teasuk Jang, Hwijun Kim, Minwoo Lee, Yongjin Kim, Dongyeol Yang, Kyeongsik Min, Hyunjoo Choi
Powder Technology.2018; 339: 440. CrossRef
- Optimization of Densification Behavior of a Soft Magnetic Powder by Discrete Element Method and Machine Learning
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


