Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- Epsilon Iron Oxide (ε-Fe2O3) as an Electromagnetic Functional Material: Properties, Synthesis, and Applications
- Ji Hyeong Jeong, Hwan Hee Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(6):465-479. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00290
- 3,461 View
- 90 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
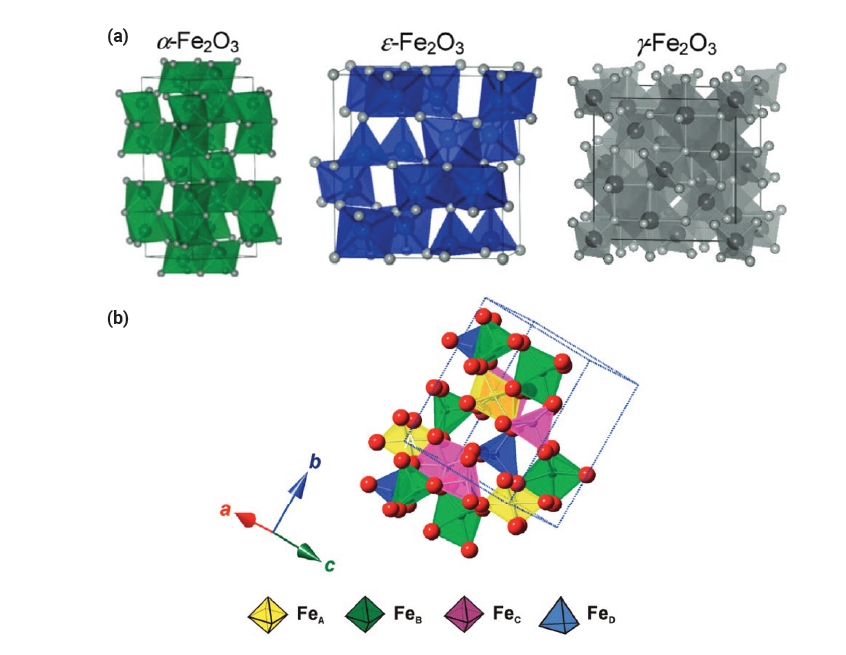
PDF - Iron oxide (ε-Fe₂O₃) is emerging as a promising electromagnetic material due to its unique magnetic and electronic properties. This review focuses on the intrinsic properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, particularly its high coercivity, comparable to that of rare-earth magnets, which is attributed to its significant magnetic anisotropy. These properties render it highly suitable for applications in millimeter wave absorption and high-density magnetic storage media. Furthermore, its semiconducting behavior offers potential applications in photocatalytic hydrogen production. The review also explores various synthesis methods for fabricating ε-Fe₂O₃ as nanoparticles or thin films, emphasizing the optimization of purity and stability. By exploring and harnessing the properties of ε-Fe₂O₃, this study aims to contribute to the advancement of next-generation electromagnetic materials with potential applications in 6G wireless telecommunications, spintronics, high-density data storage, and energy technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
Babak Enami Alamdari, Yu Tang, Danilo Erricolo, Lesley H. Sneed
Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Chemical Pressure Induced Strain Control of Magnetic Anisotropy in the Simple Perovskite ϵ-Fe2O3
Subir Roy, Gurleen K. Uppal, Alberto Acosta, Rachel Nickel, Charles A. Roberts, Johan van Lierop
Nano Letters.2026; 26(1): 34. CrossRef - Superparamagnetism of Baked Clays Containing Polymorphs of Iron Oxides: Experimental Study and Theoretical Modeling
Petr Kharitonskii, Andrei Krasilin, Nadezhda Belskaya, Svetlana Yanson, Nikita Bobrov, Andrey Ralin, Kamil Gareev, Nikita Zolotov, Dmitry Zaytsev, Elena Sergienko
Magnetochemistry.2025; 11(12): 103. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review of GPR Data Analysis for Bridge Deck Evaluation: From Conventional Methods to Emerging Artificial Intelligence Approaches
- [Korean]
- Research trend in Fabrication of Metastable-phase Iron Nitrides for Hard Magnetic Applications
- Kyung Min Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Youn-Kyoung Baek
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(2):146-155. Published online April 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.2.146

- 1,710 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Rare earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets and are integral to the high tech industry, particularly in clean energies, such as electric vehicle motors and wind turbine generators. However, the cost of rare earth materials and the imbalance in supply and demand still remain big problems to solve for permanent magnet related industries. Thus, a magnet with abundant elements and moderate magnetic performance is required to replace rare-earth magnets. Recently, a”-Fe16N2 has attracted considerable attention as a promising candidate for next-generation non-rare-earth permanent magnets due to its gigantic magnetization (3.23 T). Also, metastable a”-Fe16N2 exhibits high tetragonality (c/a = 1.1) by interstitial introduction of N atoms, leading to a high magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant (K1 = 1.0MJ/m3). In addition, Fe has a large amount of reserves on the Earth compared to other magnetic materials, leading to low cost of raw materials and manufacturing for industrial production. In this paper, we review the synthetic methods of metastable a”-Fe16N2 with film, powder and bulk form and discuss the approaches to enhance magnetocrystalline anisotropy of a”-Fe16N2. Future research prospects are also offered with patent trends observed thus far.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Failure Cases according to Photocuring-Based Alumina 3D Printing
So-Young Ko, Shin-Il Go, Kyoung-Jun Jang, Sang-Jin Lee
Korean Journal of Materials Research.2024; 34(10): 457. CrossRef
- Failure Cases according to Photocuring-Based Alumina 3D Printing
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of DyF3 paste and Magnetic Properties of GBDPed Nd-Fe-B Magnets
- Kwang-Won Jeon, Hee-Ryoung Cha, Jung-Goo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(6):437-441. Published online December 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.6.437
- 607 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Recently, the grain boundary diffusion process (GBDP), involving heavy rare-earth elements such as Dy and Tb, has been widely used to enhance the coercivity of Nd-Fe-B permanent magnets. For example, a Dy compound is coated onto the surface of Nd-Fe-B sintered magnets, and then the magnets are heat treated. Subsequently, Dy diffuses into the grain boundaries of Nd-Fe-B magnets, forming Dy-Fe-B or Nd-Dy-Fe-B. The dip-coating process is also used widely instead of the GBDP. However, it is quite hard to control the thickness uniformity using dip coating. In this study, first, a DyF3 paste is fabricated using DyF3 powder. Subsequently, the fabricated DyF3 paste is homogeneously coated onto the surface of a Nd-Fe-B sintered magnet. The magnet is then subjected to GBDP to enhance its coercivity. The weight ratio of binder and DyF3 powder is controlled, and we find that the coercivity enhances with decreasing binder content. In addition, the maximum coercivity is obtained with the paste containing 70 wt% of DyF3 powder.
- [Korean]
- Synthesis of KIT-1 Mesoporous Silicates Showing Two Different Macrosporous Strucrtues; Inverse-opal or Hollow Structures
- Youn-Kyoung Baek, Jung-Goo Lee, Young Kuk Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2016;23(3):189-194. Published online June 1, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2016.23.3.189
- 596 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
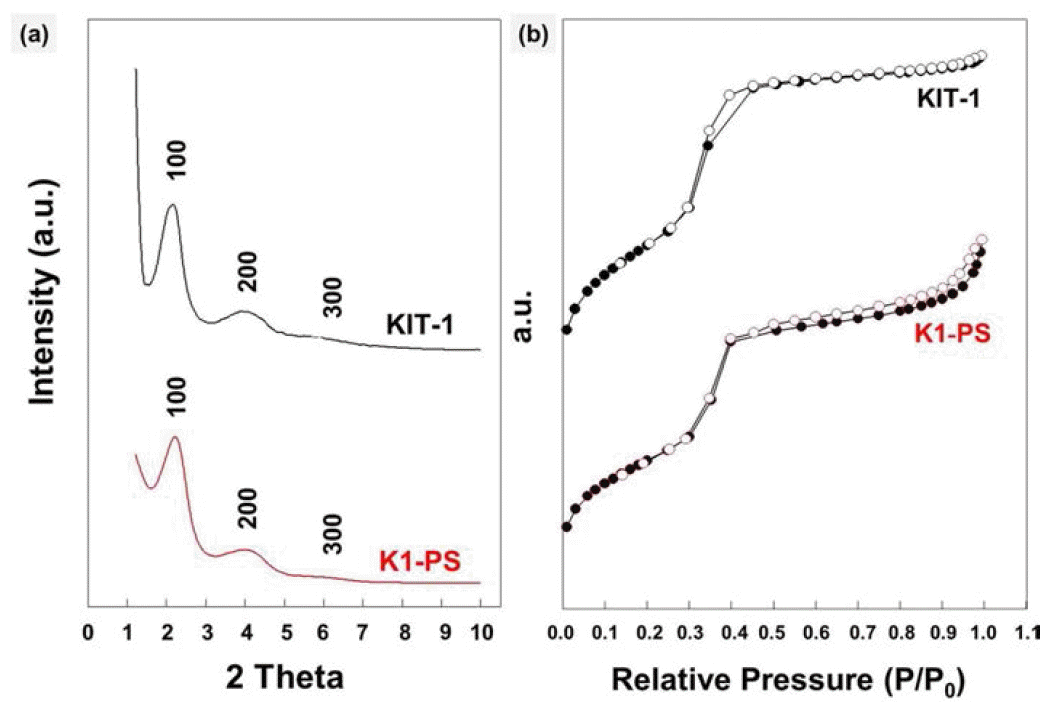
PDF We report a facile method for preparing KIT-1 mesoporous silicates with two different macroporous structures by dual templating. As a template for macropores, polystyrene (PS) beads are assembled into uniform three dimensional arrays by ice templating, i.e., by growing ice crystals during the freezing process of the particle suspension. Then, the polymeric templates are directly introduced into the precursor-gel solution with cationic surfactants for templating the mesopores, which is followed by hydrothermal crystallization and calcination. Later, by burning out the PS beads and the surfactants, KIT-1 mesoporous silicates with macropores are produced in a powder form. The macroporous structures of the silicates can be controlled by changing the amount of EDTANa4 salt under the same templating conditions using the PS beads and inverse-opal or hollow structures can be obtained. This strategy to prepare mesoporous powders with controllable macrostructures is potentially useful for various applications especially those dealing with bulky molecules such as, catalysis, separation, drug carriers and environmental adsorbents.
- [Korean]
- Research Trend of Ceramic Filter for Water Treatment
- In-Hyuck Song, Jang-Hoon Ha, Byungseo Bae, Young-Jo Park, Jae-Woong Ko, Youn-Kyoung Baek, Young-Kuk Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Yoo-Dong Hahn
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):62-71. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.62

- 2,585 View
- 22 Download
- 4 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reactive ceramic pellets incorporated iron for removing As(III), As(V), and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions
Sunwon Rha, Yun Sik Gong, Ho Young Jo
Desalination and Water Treatment.2019; 158: 174. CrossRef - Application of Physical and Chemical Enhanced Backwashing to Reduce Membrane Fouling in the Water Treatment Process Using Ceramic Membranes
Seogyeong Park, Joon-Seok Kang, Jeong Jun Lee, Thi-Kim-Quyen Vo, Han-Seung Kim
Membranes.2018; 8(4): 110. CrossRef - Effects of particle size and forming pressure on pore properties of Fe-Cr-Al porous metal by pressureless sintering
Bon-Uk Koo, Yujeong Yi, Minjeong Lee, Byoung-Kee Kim
Metals and Materials International.2017; 23(2): 336. CrossRef - Characterization and Microstructure of an Extruded Flat-Tubular-Type Alumina Filter
Byung-Seo Bae, Jang-Hoon Ha, In-Hyuck Song
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2014; 51(5): 406. CrossRef
- Reactive ceramic pellets incorporated iron for removing As(III), As(V), and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions
- [English]
- Synthesis of Nickel and Copper Nanopowders by Plasma Arc Evaporation
- Young-Sang Cho, Jong Woo Moon, Kook Chae Chung, Jung-Goo Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(6):411-424.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.6.411

- 939 View
- 9 Download
- 8 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, the synthesis of nickel nanoparticles and copper nanospheres for the potential applications of MLCC electrode materials has been studied by plasma arc evaporation method. The change in the broad distribution of the size of nickel and copper nanopowders is successfully controlled by manifesting proper mixture of gas ambiance for plasma generation in the size range of 20 to 200 nm in diameter. The factors affecting the mean diameter of the nanopowder was studied by changing the composition of reactive gases, indicating that nitrogen enhances the formation of larger particles compared to hydrogen gas. The morphologies and particle sizes of the metal nanoparticles were observed by SEM, and ultrathin oxide layers on the powder surface generated during passivation step have been confirmed using TEM. The metallic FCC structure of the nanoparticles was confirmed using powder X-ray diffraction method.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research progress on the preparation methods and fundamental principles of ultrafine Mo powder
Lu Wang, Hong-Qi Li, Xiao Liu, Yu-Long Cao
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2025; 132: 107281. CrossRef - Arc Discharge Synthesis of Chitosan‐Mediated Copper Nanoparticles for Heterogeneous Catalysis in 4‐Nitrophenol Degradation
Noor Azfarena Ahmad, Mohammad Taghi Hajibeigy, Mohsen Nabi Poor, Aras Kartouzian, Hassan Moeini, Kamyar Shameli
Particle & Particle Systems Characterization.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Tribological properties and tribomechanism of nickel nanoparticles in-situ synthesized in rapeseed oil
Wenya Xu, Guangbin Yang, Shengmao Zhang, Jun Xu, Yujuan Zhang, Tianhua Sun, Ningning Song, Laigui Yu, Pingyu Zhang
Friction.2024; 12(3): 474. CrossRef - Oxidative Steam Reforming of Methanol over Cu-Based Catalysts
Matteo Tommasi, Davide Ceriotti, Alice Gramegna, Simge Naz Degerli, Gianguido Ramis, Ilenia Rossetti
Catalysts.2024; 14(11): 759. CrossRef - Functional metal powders: Design, properties, applications, and prospects
Xin Wang, Haitao Yang, Xiaohua Yu, Chaoquan Hu, Jiacheng Hu, Rongxing Li, Yingzhi Zhang
Materials Science and Engineering: B.2022; 280: 115708. CrossRef - Facile synthesis of Cu and CuO nanoparticles from copper scrap using plasma arc discharge method and evaluation of antibacterial activity
S. B. Tharchanaa, K. Priyanka, K. Preethi, G. Shanmugavelayutham
Materials Technology.2021; 36(2): 97. CrossRef - Fabrication of Hollow or Macroporous Silica Particles by Spray Drying of Colloidal Dispersion
Young-Sang Cho
Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology.2016; 37(1): 23. CrossRef - Fabrication Of Colloidal Clusters Decorated With Dye Molecules For Potential Application As Photonic Molecules
Y.-S. Cho
Archives of Metallurgy and Materials.2015; 60(2): 1221. CrossRef
- Research progress on the preparation methods and fundamental principles of ultrafine Mo powder
- [Korean]
- Size Control of Nd-Fe-B Precursor Particles Prepared by Spray Drying and Its Effect on the Magnetic Properties of Nd-Fe-B Alloy Powders after Reduction-Diffusion
- Youn-Kyoung Baek, Young-Taek Seo, Jung-Goo Lee, Dong Su Kim, Dong Sik Bae, Chul-Jin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(5):359-365.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.5.359

- 683 View
- 6 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In this study, we fabricated Nd_2Fe_14B hard magnetic powders with various sizes via spray drying combined with reduction-diffusion process. Spray drying is widely used to produce nearly spherical particles that are relatively homogeneous. Thus, the precursor particles were prepared by spray drying using the aqueous solution containing Nd salts, Fe salts and boric acid with the target stoichiometric composition of Nd_2Fe_14B. The mean particle sizes of the spray-dried powders are in the range from one to seven micrometer, which are adjusted by controlling the concentrations of precursor solutions. After debinding the as-prepared precursor particles, ball milling was also conducted to control the particle sizes of Nd-Fe-B oxide powders. The resulting particles with different sizes were subjected to subsequent treatments including hydrogen reduction, Ca reduction and washing for CaO removal. The size effect of Nd-Fe-B oxide particles on the formation of Nd_2Fe_14B phase and magnetic properties was investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research trend in Fabrication of Metastable-phase Iron Nitrides for Hard Magnetic Applications
Kyung Min Kim, Jung-Goo Lee, Kyung Tae Kim, Youn-Kyoung Baek
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(2): 146. CrossRef - Synthesize of Nd2Fe14B Powders from 1-D Nd2Fe14B Wires using Electrospinning Process
Nu Si A Eom, Su Noh, Muhammad Aneeq Haq, Bum Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2019; 26(6): 477. CrossRef
- Research trend in Fabrication of Metastable-phase Iron Nitrides for Hard Magnetic Applications
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Mn Addition on Nitrogenation Behavior and Magnetic Properties of Sm-Fe Alloy Powder Produced by Reduction-diffusion Method
- Young-Taek Seo, Youn-Kyoung Baek, Jung-Goo Lee, Chul-Jin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2013;20(1):13-18.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.1.013

- 686 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - In the present study, we systematically investigated the effect of Mn addition on nitrogenation behavior and magnetic properties of Sm-Fe powders produced by reduction-diffusion process. Alloy powders with only Sm_2(Fe,Mn)_17 single phase were successfully produced by the reduction-diffusion process. The coercivity of Sm_2(Fe,Mn)_17 powder rapidly increased during nitrogenation and reached the maximum of 637 Oe after 16 hours. After further nitrogenation, it decreased. In contrast, the coercivity of Sm_2Fe_17 powder gradually increased during nitrogenation for 24 hours. The coercivity of Sm_2(Fe,Mn)_17 powder was higher than that of Sm_2Fe_17 powder at the same condition of nitrogenation. It was considered that the Mn addition facilitates the nitrogenation of Sm_2Fe_17 powder and enhances the coercivity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Nb content on Sm2Fe17−xNbx and its nitrides prepared by reduction-diffusion method
Guizhi Yao, Haiming Tian, Cong Zhang, Huan Shi, Shifan Zeng, Sheng Gao, Shuangjiu Feng, Kai Zhu, Xucai Kan, Xiansong Liu
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of Nb content on Sm2Fe17−xNbx and its nitrides prepared by reduction-diffusion method
- [Korean]
- Trend in Research and Development Related to Lean Heavy Rare-earth Permanent Magnets for Next-generation Motors
- Jung-Goo Lee, Youn-Kyoung Baek, Ji-Hun Yu, Chul-Jin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2012;19(2):151-159.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2012.19.2.151

- 711 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 PDF
PDF -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Study on the Demagnetization and Classification of NdFeB Magnets According to Different Heat Treatment Temperatures
Byeong Jun Kim, Ik Keun Park, Young Sung Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2021; 30(2): 119. CrossRef - Low Cost Design Study of Brushless DC Motor for Electric Water Pump Application
Tae-Uk Jung
Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology.2014; 9(3): 942. CrossRef - Optimized Design of Rotor Considering Cost-Reduction of Small BLDC Motor for the Water Pump
Hoe-Cheon Kim, Tae-Uk Jung
The Transactions of The Korean Institute of Electrical Engineers.2013; 62(4): 495. CrossRef
- Study on the Demagnetization and Classification of NdFeB Magnets According to Different Heat Treatment Temperatures
- [Korean]
- The Effect of Excess Samarium Oxide on the Preparation of Sm-Fe Alloy Powder by Reduction-diffusion Method
- Hun Kwak, Jung-Goo Lee, Chul-Jin Choi
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(5):336-341.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.5.336

- 906 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To produce alloy powders with only Sm_2Fe_17 single phase by reduction-diffusion (R-D) method, the effect of excess samarium oxide on the preparation of Sm-Fe alloy powder during R-D heat treatment was studied. The quantity of samarium oxide was varied from 5% to 50% whereas iron and calcium were taken 0% and 200% in excess of chemical equivalent, respectively. The pellet type mixture of samarium, iron powders and calcium granulars was subjected to heat treatment at 1100°C for 5 hours. The R-D treated pellet was moved into deionized water and agitated to separate Sm-Fe alloy powders. After washing them in deionized water several times, the powders were washed with acetic acid to remove the undesired reaction products such as CaO. By these washing and acid cleaning treatment, only 0.03 wt% calcium remained in Sm-Fe alloy powders. It was also confirmed that the content of unreacted alpha-Fe in Sm_2Fe_17 matrix gradually decreased as the percentage of samarium oxide is increased. However, there was no significant change above 40% excess samarium oxide.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Influence of Mechanical Milling on the Structure and Magnetic Properties of Sm-Fe-N Powder Produced by the Reduction-Diffusion Process
Jung-Goo Lee, Seok-Won Kang, Ping-Zhan Si, Chul-Jin Choi
Journal of Magnetics.2011; 16(2): 104. CrossRef
- The Influence of Mechanical Milling on the Structure and Magnetic Properties of Sm-Fe-N Powder Produced by the Reduction-Diffusion Process
- [Korean]
- Trend in Research and Development Related to Sm-Fe-N Bonded Magnets
- Jung-Goo Lee, Hun Kwak, Chul-Jin Choi, Joon-Chul Yun, Jai-Sung Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2009;16(1):1-8.
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2009.16.1.001

- 790 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Citations
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


