Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [English]
- The Effect of TiO2 Addition on Low-temperature Sintering Behaviors in a SnO2-CoO-CuO System
- Jae-Sang Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2024;31(2):146-151. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/jpm.2024.00024

- 1,131 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pure SnO2 has proven very difficult to densify. This poor densification can be useful for the fabrication of SnO2 with a porous microstructure, which is used in electronic devices such as gas sensors. Most electronic devices based on SnO2 have a porous microstructure, with a porosity of > 40%. In pure SnO2, a high sintering temperature of approximately 1300C is required to obtain > 40% porosity. In an attempt to reduce the required sintering temperature, the present study investigated the low-temperature sinterability of a current system. With the addition of TiO2, the compositions of the samples were Sn1-xTixO2-CoO(0.3wt%)-CuO(2wt%) in the range of x ≤ 0.04. Compared to the samples without added TiO2, densification was shown to be improved when the samples were sintered at 950C. The dominant mass transport mechanism appears to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 950C.
- [English]
- The Effect of SnO2 Addition on Sintering Behaviors in a Titanium Oxide-Copper Oxide System
- Ju-Won Lee, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung, Yeong-Kyeun Paek
- J Powder Mater. 2022;29(5):357-362. Published online October 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2022.29.5.357
- 783 View
- 4 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The low-temperature sinterability of TiO2-CuO systems was investigated using a solid solution of SnO2. Sample powders were prepared through conventional ball milling of mixed raw powders. With the SnO2 content, the compositions of the samples were Ti1-xSnxO2-CuO(2 wt.%) in the range of x ≤ 0.08. Compared with the samples without SnO2 addition, the densification was enhanced when the samples were sintered at 900°C. The dominant mass transport mechanism seemed to be grain-boundary diffusion during heat treatment at 900°C, where active grain-boundary diffusion was responsible for the improved densification. The rapid grain growth featured by activated sintering was also obstructed with the addition of SnO2. This suggested that both CuO as an activator and SnO2 dopant synergistically reduced the sintering temperature of TiO2.
- [Korean]
- Effect of Li2O-Bi2O3 Addition on the Piezoelectric Properties of Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 Ceramics
- Jae Hyuk Kim, Shi Yeon Kim, Jeoung Sik Choi, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(5):405-409. Published online October 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.5.405

- 713 View
- 1 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Piezoelectric ceramic specimens with the Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)0.65Ti0.35O3 (PMN-PT) composition are prepared by the solid state reaction method known as the “columbite precursor” method. Moreover, the effects of the Li2O-Bi2O3 additive on the microstructure, crystal structure, and piezoelectric properties of sintered PMN-PT ceramic samples are investigated. The addition of Li2O-Bi2O3 lowers the sintering temperature from 1,200°C to 950°C. Moreover, with the addition of >5 wt.% additive, the crystal structure changes from tetragonal to rhombohedral. Notably, the sample with 3 wt.% additive exhibits excellent piezoelectric properties (d33 = 596 pC/N and Kp = 57%) and a sintered density of 7.92 g/cm3 after sintering at 950°C. In addition, the sample exhibits a curie temperature of 138.6°C at 1 kHz. Finally, the compatibility of the sample with a Cu electrode is examined, because the energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy data indicate the absence of interdiffusion between Cu and the ceramic material.
- [Korean]
- Effects of the Mixing Method and Sintering Temperature on the Characteristics of PZNN-PZT Piezoelectric Ceramic Materials
- So Won Kim, Yong Jeong Jeong, Hee Chul Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(6):487-493. Published online December 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.6.487
- 906 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
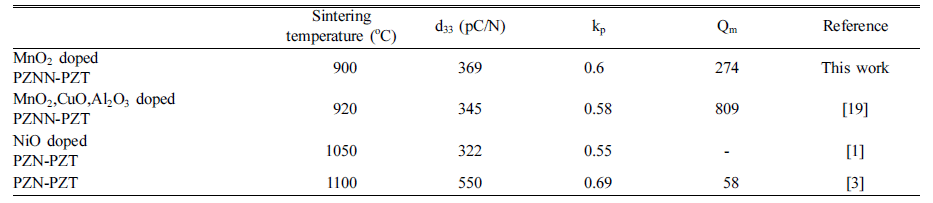
PDF The impact of different mixing methods and sintering temperatures on the microstructure and piezoelectric properties of PZNN-PZT ceramics is investigated. To improve the sinterability and piezoelectric properties of these ceramics, the composition of 0.13Pb((Zn0.8Ni0.2)1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.87Pb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 (PZNN-PZT) containing a Pb-based relaxor component is selected. Two methods are used to create the powder for the PZNN-PZT ceramics. The first involves blending all source powders at once, followed by calcination. The second involves the preferential creation of columbite as a precursor, by reacting NiO with Nb2O5 powder. Subsequently, PZNN-PZT powder can be prepared by mixing the columbite powder, PbO, and other components, followed by an additional calcination step. All the PZNNPZT powder samples in this study show a nearly-pure perovskite phase. High-density PZNN-PZT ceramics can be fabricated using powders prepared by a two-step calcination process, with the addition of 0.3 wt% MnO2 at even relatively low sintering temperatures from 800°C to 1000°C. The grain size of the ceramics at sintering temperatures above 900°C is increased to approximately 3 μm. The optimized PZNN-PZT piezoelectric ceramics show a piezoelectric constant (d33) of 360 pC/N, an electromechanical coupling factor (kp) of 0.61, and a quality factor (Qm) of 275.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
Haeseong Hwang, Seungho Han, Hyunseop Lee
Lubricants.2023; 11(7): 297. CrossRef - A generalized rule for phase transition generated by additives in piezoelectric ceramics
Jae-Min Cha, Young-Kook Moon, Jung-hwan Kim, Hyun-Ae Cha, Jong-Jin Choi, Byung-Dong Hahn, Seog-Young Yoon, Cheol-Woo Ahn
Materials Today Communications.2023; 37: 107290. CrossRef - Low-Temperature Sintering Properties of Bi2O3 Doped PZT-5H Piezoelectric Ceramics
Wanzi Mao, Qing Xu, Duanping Huang, Huajun Sun, Feng Zhang, Xiaobin Xie
Journal of Electronic Materials.2023; 52(5): 3334. CrossRef - Effect of LiBiO2 on low-temperature sintering of PZT-PZNN ceramics
Sung Cheul Hong, Shi Yeon Kim, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Zee Hoon Park, Sahn Nahm
Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society.2022; 59(5): 638. CrossRef - Two-Stage De-binding for Cu Electrode Application to PZT-PZNN Multilayer Actuator
Sung Cheul Hong, Zeehoon Park, Dong-Hun Yeo, Hyo-Soon Shin, Sahn Nahm
Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials.2022; 23(4): 348. CrossRef
- An Analysis of Edge Chipping in LiTaO3 Wafer Grinding Using a Scratch Test and FEA Simulation
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


