Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- [Korean]
- Fabrication and Characterization of Hexagonal Tungsten Oxide Nanopowders for High Performance Gas Sensing Application
- Jinsoo Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2019;26(1):28-33. Published online February 1, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2019.26.1.28
- 810 View
- 5 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF The gas sensor is essential to monitoring dangerous gases in our environment. Metal oxide (MO) gas sensors are primarily utilized for flammable, toxic and organic gases and O3 because of their high sensitivity, high response and high stability. Tungsten oxides (WO3) have versatile applications, particularly for gas sensor applications because of the wide bandgap and stability of WO3. Nanosize WO3 are synthesized using the hydrothermal method. Asprepared WO3 nanopowders are in the form of nanorods and nanorulers. The crystal structure is hexagonal tungsten bronze (MxWO3, x =< 0.33), characterized as a tunnel structure that accommodates alkali ions and the phase stabilizer. A gas detection test reveals that WO3 can detect acetone, butanol, ethanol, and gasoline. This is the first study to report this capability of WO3.
- [Korean]
- Thermoelectric Properties of PbTe Prepared by Spark Plasma Sintering of Nano Powders
- Eun-Young Jun, Ho-Young Kim, Cham Kim, Kyung-Sik Oh, Tai-Joo Chung
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2018;25(5):384-389. Published online October 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2018.25.5.384
- 1,074 View
- 8 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
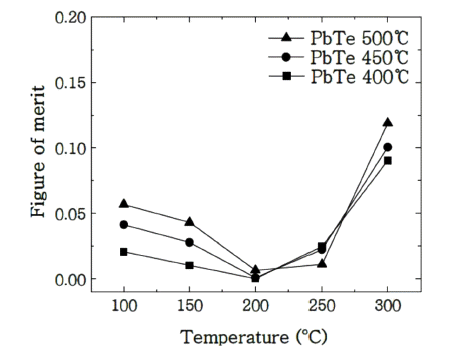
PDF Nanoparticles of PbTe are prepared via chemical reaction of the equimolar aqueous solutions of Pb(CH3COO)2 and Te at 120°C. The size of the obtained particles is 100 nm after calcination in a hydrogen atmosphere. Dense specimens for the thermoelectric characterization are produced by spark plasma sintering of prepared powders at 400°C to 500°C under 80 MPa for 5 min. The relative densities of the prepared specimens reach approximately 97% and are identified as cubic based on X-ray diffraction analyses. The thermoelectric properties are evaluated between 100°C and 300°C via electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal conductivity. Compared with PbTe ingot, the reduction of the thermal conductivities by more than 30% is verified via phonon scattering at the grain boundaries, which thus contributes to the increase in the figure of merit.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
Ho-Jeong Kim, Il-Ho Kim
Korean Journal of Metals and Materials.2023; 61(6): 422. CrossRef - Enhancing Electrical Properties of N-type Bismuth Telluride Alloys through Graphene Oxide Incorporation in Extrusion 3D Printing
Jinhee Bae, Seungki Jo, Kyung Tae Kim
journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2023; 30(4): 318. CrossRef
- Improved Thermoelectric Performance of Cu3Sb1−x−ySnxInySe4 Permingeatites Double-Doped with Sn and In
- [English]
- Optimization of Process Condition for Fe Nano Powder Injection Molding
- Joo Won Oh, Won Sik Lee, Seong Jin Park
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2017;24(3):223-228. Published online June 1, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2017.24.3.223

- 1,107 View
- 2 Download
- 3 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Nanopowders provide better details for micro features and surface finish in powder injection molding processes. However, the small size of such powders induces processing challenges, such as low solid loading, high feedstock viscosity, difficulty in debinding, and distinctive sintering behavior. Therefore, the optimization of process conditions for nanopowder injection molding is essential, and it should be carefully performed. In this study, the powder injection molding process for Fe nanopowder has been optimized. The feedstock has been formulated using commercially available Fe nanopowder and a wax-based binder system. The optimal solid loading has been determined from the critical solid loading, measured by a torque rheometer. The homogeneously mixed feedstock is injected as a cylindrical green body, and solvent and thermal debinding conditions are determined by observing the weight change of the sample. The influence of the sintering temperature and holding time on the density has also been investigated. Thereafter, the Vickers hardness and grain size of the sintered samples have been measured to optimize the sintering conditions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Investigation of stainless steel 316L/zirconia joint part fabricated by powder injection molding
Chang Woo Gal, Sang Soo Han, Jun Sae Han, Dongguo Lin, Seong Jin Park
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2019; 16(1): 315. CrossRef - Fabrication and properties of Si3N4 based ceramics using combustion synthesized powders
Chang Woo Gal, Gi Woung Song, Woon Hyung Baek, Hyung Kyu Kim, Dae Keun Lee, Ki Wook Lim, Seong Jin Park
International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials.2019; 81: 325. CrossRef - Powder Injection Molding Process in Industrial Fields
Joo Won OH, Chang Woo GAL, Daseul SHIN, Jae Man PARK, Woo Seok YANG, Seong Jin PARK
Journal of the Japan Society of Powder and Powder Metallurgy.2018; 65(9): 539. CrossRef
- Investigation of stainless steel 316L/zirconia joint part fabricated by powder injection molding
- [Korean]
- Electromagnetic Wave Shielding Effect of Nano-powder Dispersed Epoxy Resin Composite
- Jun-Young Han, Chul-Hee Lee, Min-Gyu Choi, Soon-Jik Hong, Joong-Hark Park, Dong-Jin Lee
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2015;22(4):234-239. Published online August 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2015.22.4.234

- 556 View
- 2 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Electronic products are a major part of evolving industry and human life style; however most of them are known to emit electromagnetic waves that have severe health hazards. Therefore, different materials and fabrication techniques are understudy to control or limit transfer of such waves to human body. In this study, nanocomposite powder is dispersed into epoxy resin and shielding effects such as absorption, reflection, penetration and multiple reflections are investigated. In addition, nano size powder (Ni, Fe2O3, Fe-85Ni, C-Ni) is fabricated by pulsed wire evaporation method and dispersed manually into epoxy. Characterization techniques such as X-ray diffraction, Scanning electron microscopy and Transmission electron microscopy are used to investigate the phase analysis, size and shape as well as dispersion trend of a nano powder on epoxy matrix. Shielding effect is measured by standard test method to investigate the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of planar materials, ASTM D4935. At lower frequency, sample consisting nano-powder of Fe-85%Wt Ni shows better electromagnetic shielding effect compared to only epoxy, only Ni, Fe2O3 and C-Ni samples.
- [Korean]
- Analysis of the Change in Microstructures of Nano Copper Powders During the Hydrogen Reduction using X-ray Diffraction Patterns and Transmission Electron Microscope, and the Mechanical Property of Compacted Powders
- Dong-Hyun Ahn, Dong Jun Lee, Wooyeol Kim, Lee Ju Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(3):207-214. Published online June 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.3.207

- 611 View
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF In this study, nano-scale copper powders were reduction treated in a hydrogen atmosphere at the relatively high temperature of 350°C in order to eliminate surface oxide layers, which are the main obstacles for fabricating a nano/ultrafine grained bulk parts from the nano-scale powders. The changes in composition and microstructure before and after the hydrogen reduction treatment were evaluated by analyzing X-ray diffraction (XRD) line profile patterns using the convolutional multiple whole profile (CMWP) procedure. In order to confirm the result from the XRD line profile analysis, transmitted electron microscope observations were performed on the specimen of the hydrogen reduction treated powders fabricated using a focused ion beam process. A quasi-statically compacted specimen from the nanoscale powders was produced and Vickers micro-hardness was measured to verify the potential of the powders as the basis for a bulk nano/ultrafine grained material. Although the bonding between particles and the growth in size of the particles occurred, crystallites retained their nano-scale size evaluated using the XRD results. The hardness results demonstrate the usefulness of the powders for a nano/ultrafine grained material, once a good consolidation of powders is achieved.
- [Korean]
- Planar Shock Wave Compaction of Oxidized Copper Nano Powders using High Speed Collision and Its Mechanical Properties
- Dong-Hyun Ahn, Wooyeol Kim, Lee Ju Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
- J Korean Powder Metall Inst. 2014;21(1):39-43. Published online February 1, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4150/KPMI.2014.21.1.39

- 857 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Bulk nanostructured copper was fabricated by a shock compaction method using the planar shock wave generated by a single gas gun system. Nano sized powders, average diameter of 100 nm, were compacted into the capsule and target die, which were designed to eliminate the effect of undesired shock wave, and then impacted with an aluminum alloy target at 400 m/s. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the shock compact specimen were analyzed using an optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and micro indentation. Hardness results showed low values (approximately 45~80 Hv) similar or slightly higher than those of conventional coarse grained commercial purity copper. This result indicates the poor quality of bonding between particles. Images from OM and SEM also confirmed that no strong bonding was achieved between them due to the insufficient energy and surface oxygen layer of the powders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Compressibility of hierarchic-architectured agglomerates of hydrogen-reduced copper nanopowders
Dong-Hyun Ahn, Wooyeol Kim, Eun Yoo Yoon, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Materials Science.2016; 51(1): 82. CrossRef - Analysis of the Change in Microstructures of Nano Copper Powders During the Hydrogen Reduction using X-ray Diffraction Patterns and Transmission Electron Microscope, and the Mechanical Property of Compacted Powders
Dong-Hyun Ahn, Dong Jun Lee, Wooyeol Kim, Lee Ju Park, Hyoung Seop Kim
Journal of Korean Powder Metallurgy Institute.2014; 21(3): 207. CrossRef
- Compressibility of hierarchic-architectured agglomerates of hydrogen-reduced copper nanopowders
TOP
 KPMI
KPMI


 First
First Prev
Prev


